
by MH Team | Dec 31, 2023 | Lab Protocols, Transfusion Medicine
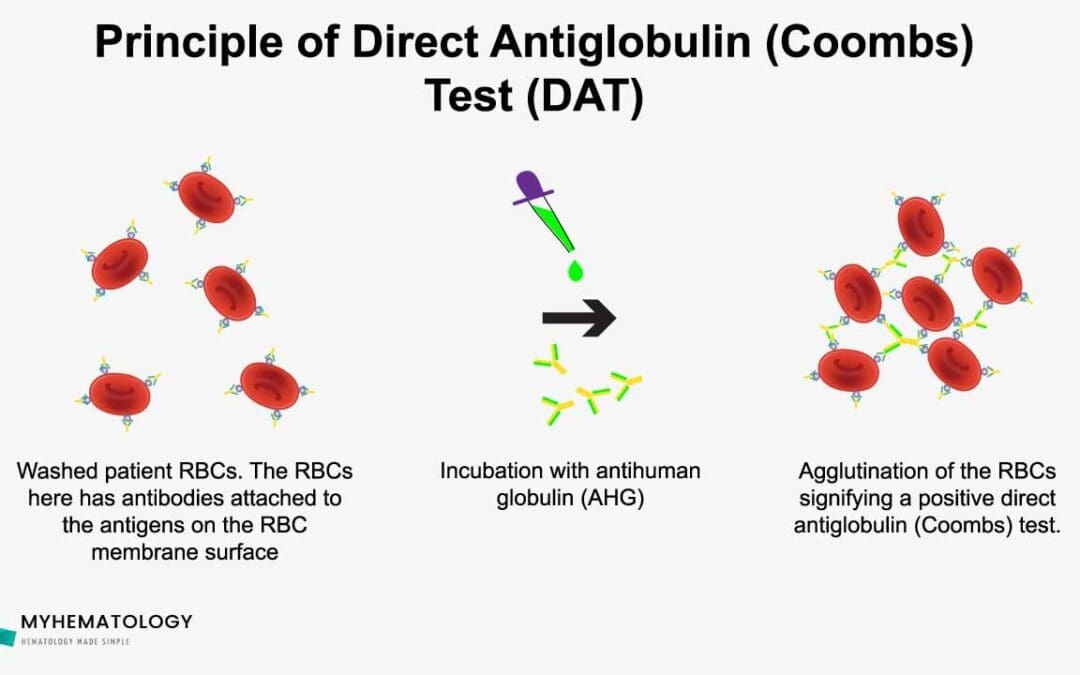
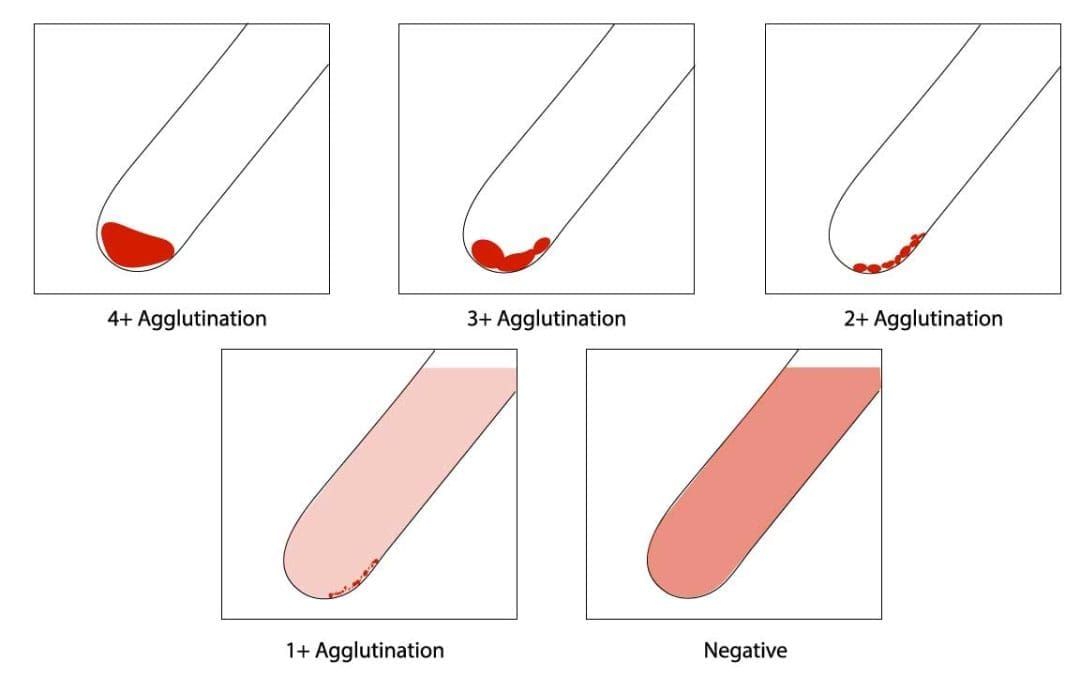
Procedure At a Glance The purpose of the Direct Antiglobulin (Coombs) Test (DAT) procedure is to detect in vivo sensitization of red blood cells with antibodies or complement components. Collect Patient Sample: Obtain an anticoagulated blood sample (e.g., in an EDTA...

by MH Team | Dec 30, 2023 | Platelet Disorders
TL;DR Primary hemostasis is the body’s rapid response to a broken blood vessel, plugging the leak before the “heavy artillery” of secondary hemostasis (coagulation cascade) kicks in. Key Players Platelets: They adhere to the injured vessel...

by MH Team | Dec 27, 2023 | Platelet Disorders
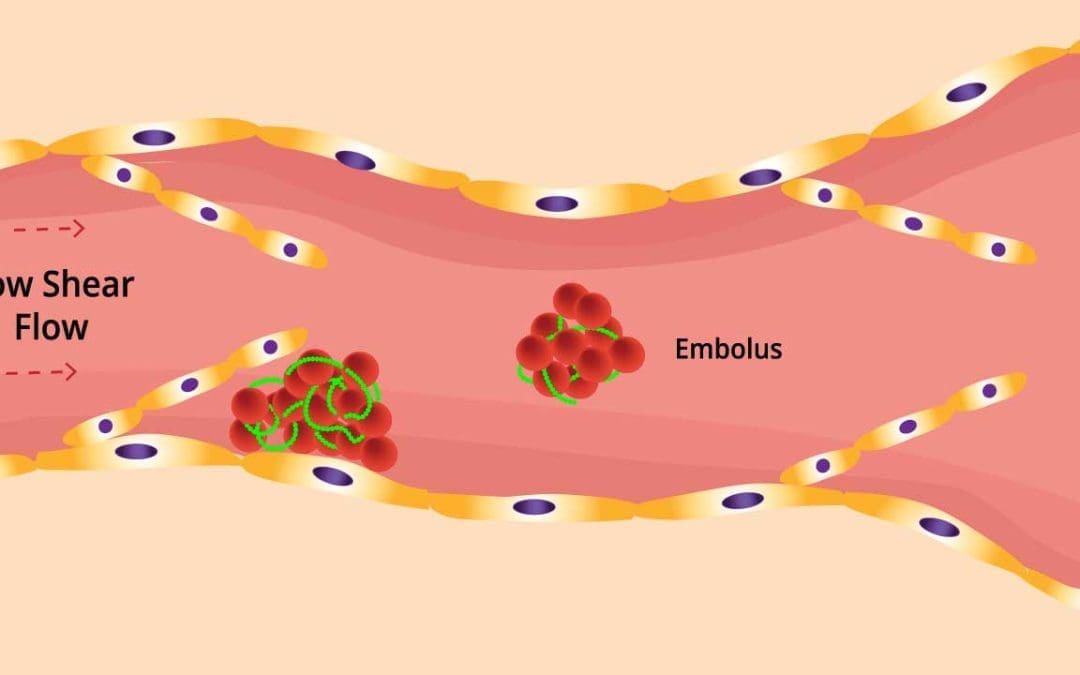
TL;DR Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a condition where a blood clot (thrombosis) forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg (deep vein thrombosis) or pelvis, and can travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. This is a serious condition that can be...

by MH Team | Dec 22, 2023 | Platelet Disorders
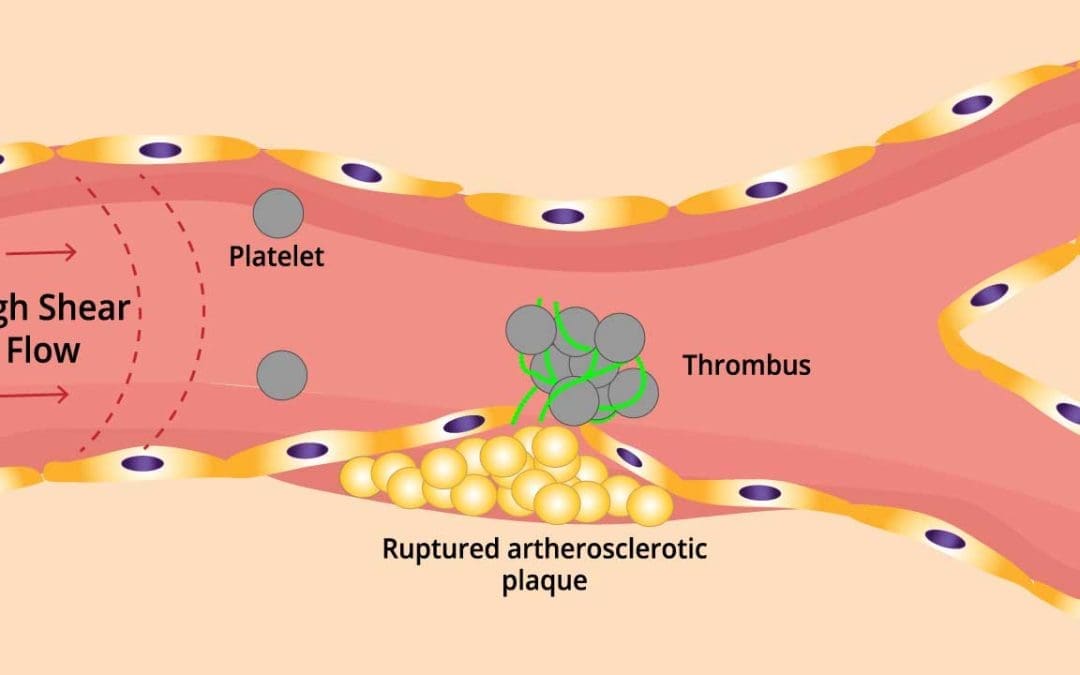
TL;DR Arterial thrombosis forms when a clot blocks an artery, cutting off blood supply to vital organs. Risk factors ▾: Age, smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, and others. Symptoms ▾: Sudden pain, weakness, numbness, and discoloration can signal a clot. Related...

by MH Team | Dec 21, 2023 | Lab Protocols, Transfusion Medicine
Procedure At A Glance The purpose of Rh typing is to determine the presence or absence of the RhD antigen on an individual’s red blood cells to prevent transfusion reactions and hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN). Label tubes. Add a drop of a 2-5% patient...


Recent Comments