
by MH Team | Mar 28, 2024 | Red Blood Cells
Introduction Red blood cell (RBC) morphology plays a crucial role in diagnosing hematological disorders. By examining the size, shape, and presence of RBC inclusion bodies, clinicians gain valuable insights into the underlying cause of abnormal blood function. RBC...

by MH Team | Mar 25, 2024 | Red Blood Cells
Introduction The unique red blood cell (RBC) morphology plays an important role in the optimal function of RBC as an oxygen transporter. This biconcave disc-shape offers a high surface area to volume ratio, allowing for efficient diffusion of oxygen molecules into and...

by MH Team | Mar 21, 2024 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Leukocytosis is an increase in white blood cell (WBC) count above the reference range. Significance ▾ Not a disease itself, but a marker of underlying infection, inflammation, or blood cancers. Causes ▾ Infections: Bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites battling...

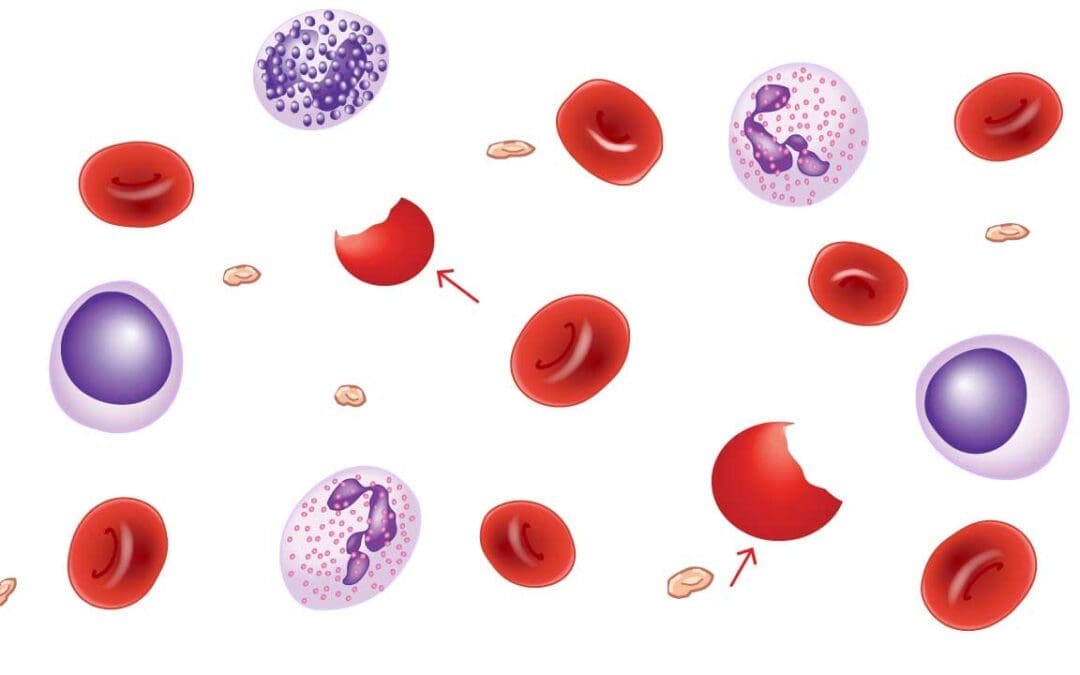
by MH Team | Mar 19, 2024 | Red Blood Cells
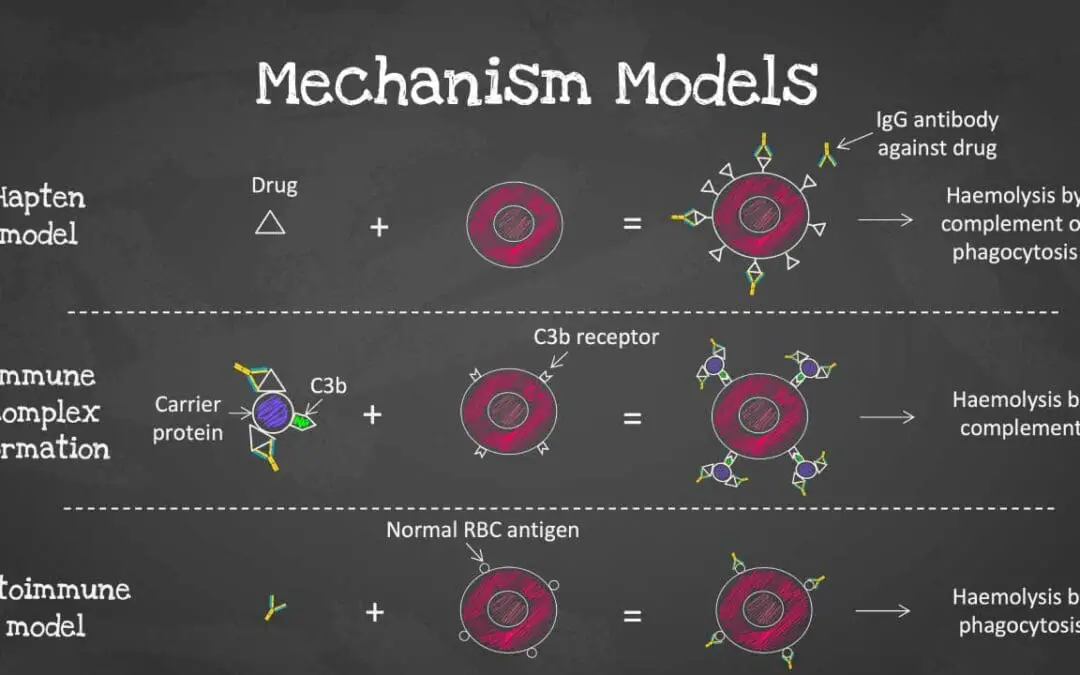
TL;DR Drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia are caused by drugs that trigger an immune response to attack red blood cells (RBCs), leading to hemolytic anemia. Mechanism ▾ Hapten Model (most common) (Drug-dependent Antibody Model) Immune Complex Formation (less common)...

by MH Team | Mar 15, 2024 | Red Blood Cells
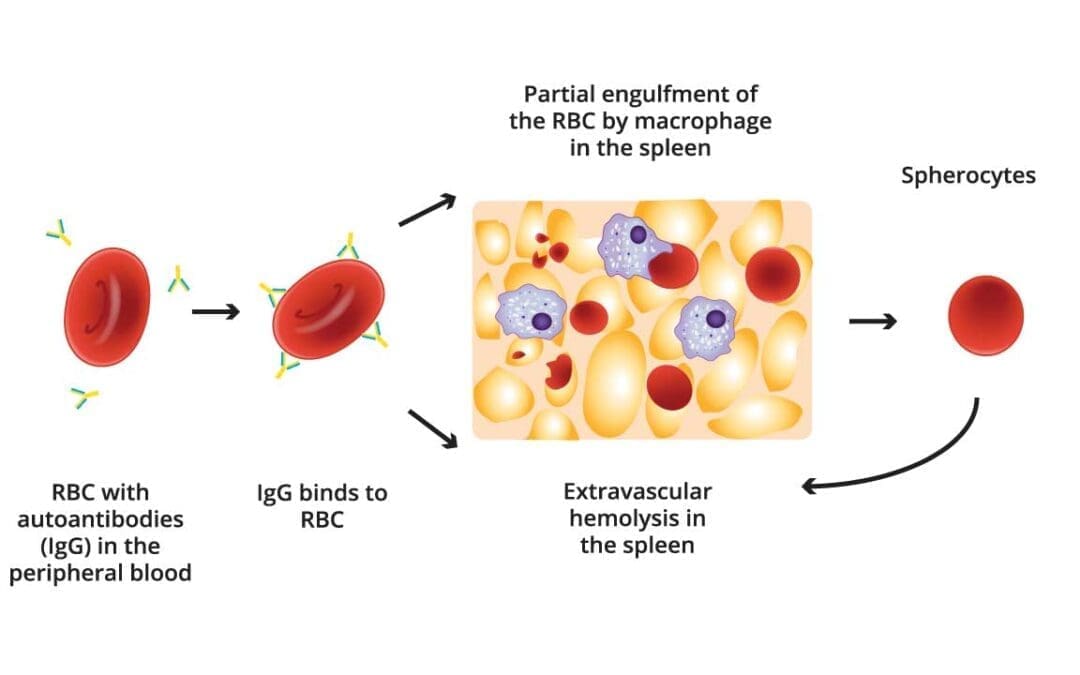
TL;DR Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) is a condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys its own red blood cells, leading to anemia. This destruction process is known as hemolysis. Types ▾: Warm AIHA Cold Agglutinin Disease (CAD)...


Recent Comments