Explore hydrops fetalis: a severe fetal condition marked by excessive fluid accumulation. Learn its diverse causes, from genetic to infectious.
Causes of Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia is excessive period bleeding. Explore the causes, symptoms and the approach to diagnose it.
Tachycardia in Hematological Patients
Tachycardia in hematology is critical. Often signals anemia, infection, or treatment issues. Early recognition improves patient outcomes.
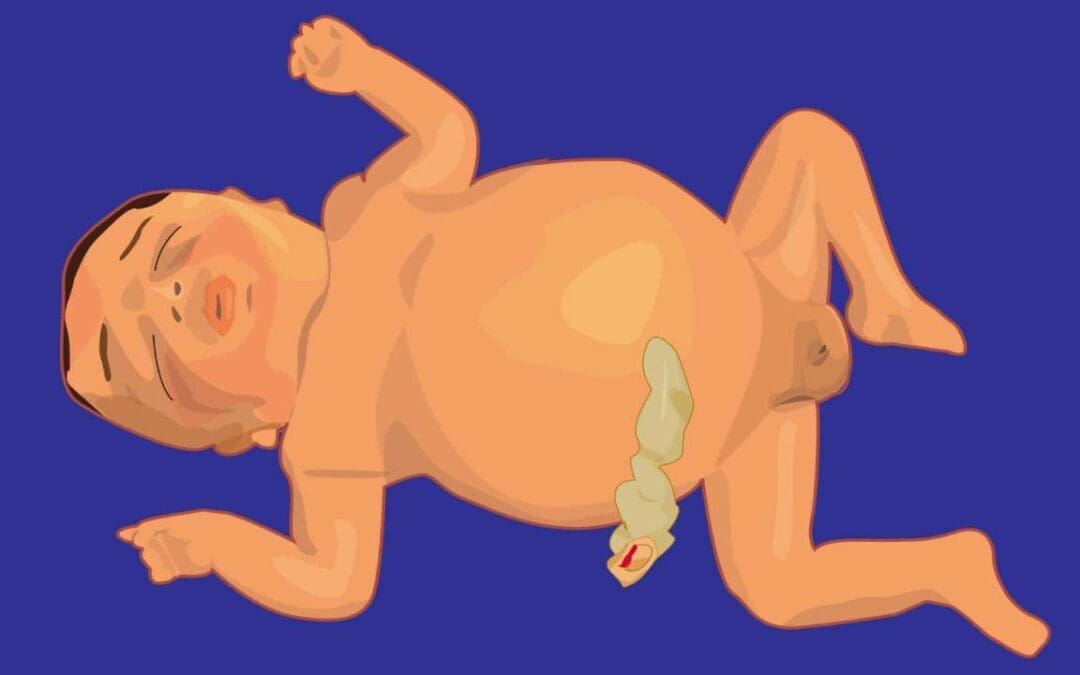
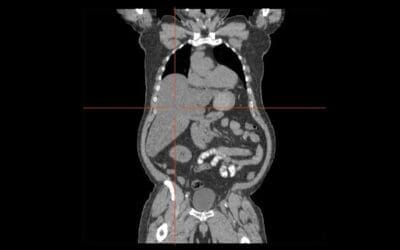
Hydrops Fetalis
Explore hydrops fetalis: a severe fetal condition marked by excessive fluid accumulation. Learn its diverse causes, from genetic to infectious.

Causes of Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia is excessive period bleeding. Explore the causes, symptoms and the approach to diagnose it.
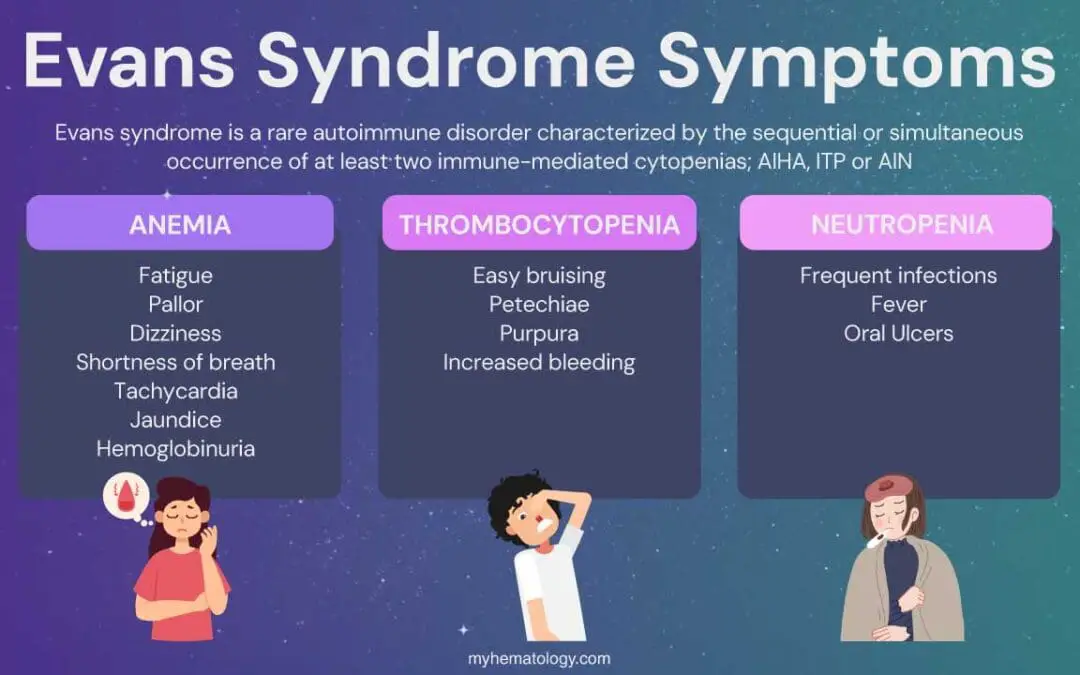
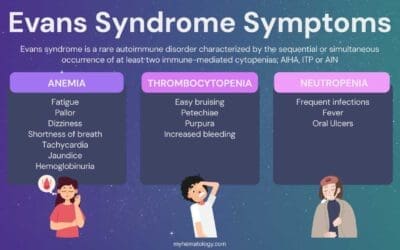
Evans Syndrome
Evans syndrome: Rare autoimmune disorder causing low red blood cells & platelets (AIHA & ITP). Can lead to fatigue, bruising, and bleeding.
Liver and Causes of Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly means an enlarged liver, often a sign of underlying conditions like hepatitis, fatty liver, or heart failure. Diagnosis involves physical exams and imaging.
Evans Syndrome
Evans syndrome: Rare autoimmune disorder causing low red blood cells & platelets (AIHA & ITP). Can lead to fatigue, bruising, and bleeding.
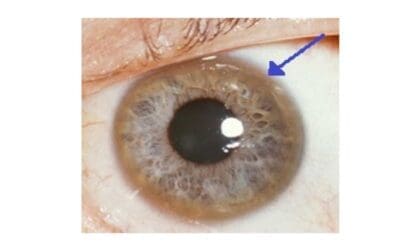
Wilson’s Disease
Wilson’s disease: A rare genetic disorder causing toxic copper buildup in the liver and brain. Early diagnosis and lifelong treatment are crucial.
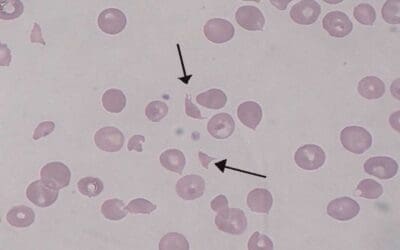
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS): A rare but serious condition causing red blood cell damage, low platelets, and kidney failure. Early diagnosis is key.
Hemoglobinuria: Overview and Causes
Hemoglobinuria: Red urine from free hemoglobin, not whole RBCs. Signals serious issues like hemolysis. Prompt diagnosis is vital.
Hematuria (Blood in Urine): Overview & Causes
Hematuria: Blood in urine, gross (visible) or microscopic. Could signal infection, stones, or more serious issues.