
by MH Team | Oct 9, 2023 | White Blood Cells
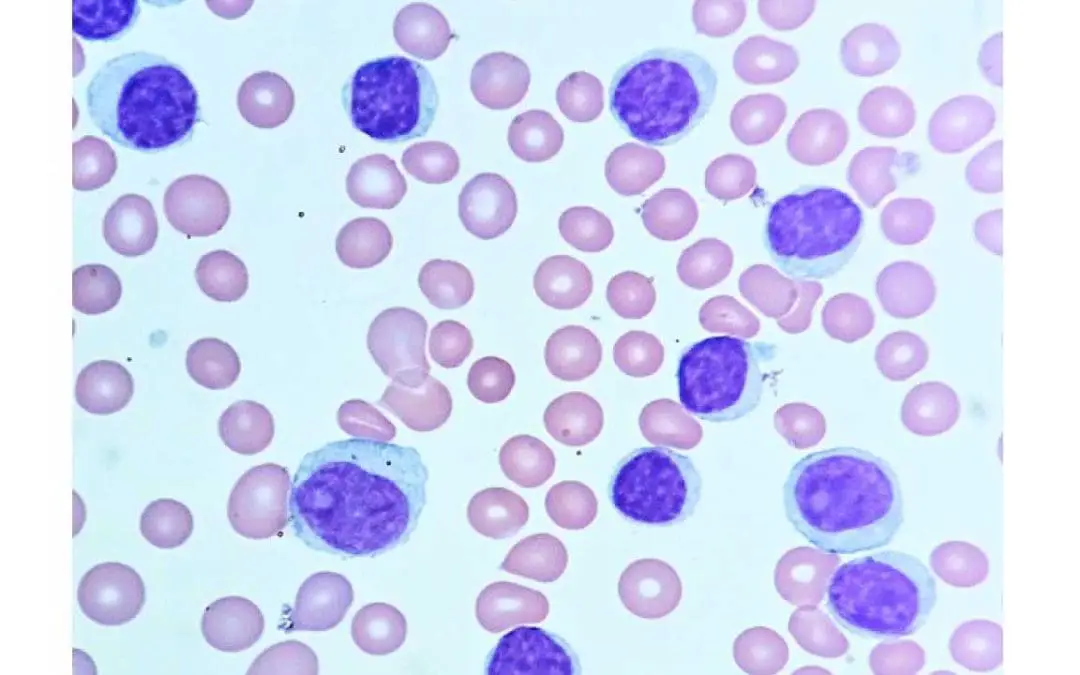
TL;DR Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a slow progressing cancer due to overgrowth and accumulation of small incompetent mature-looking B-lymphocytes in the blood, bone marrow and lymphoid tissues. Small lymphocytic leukemia is a different clinical manifestation...

by MH Team | Oct 9, 2023 | White Blood Cells
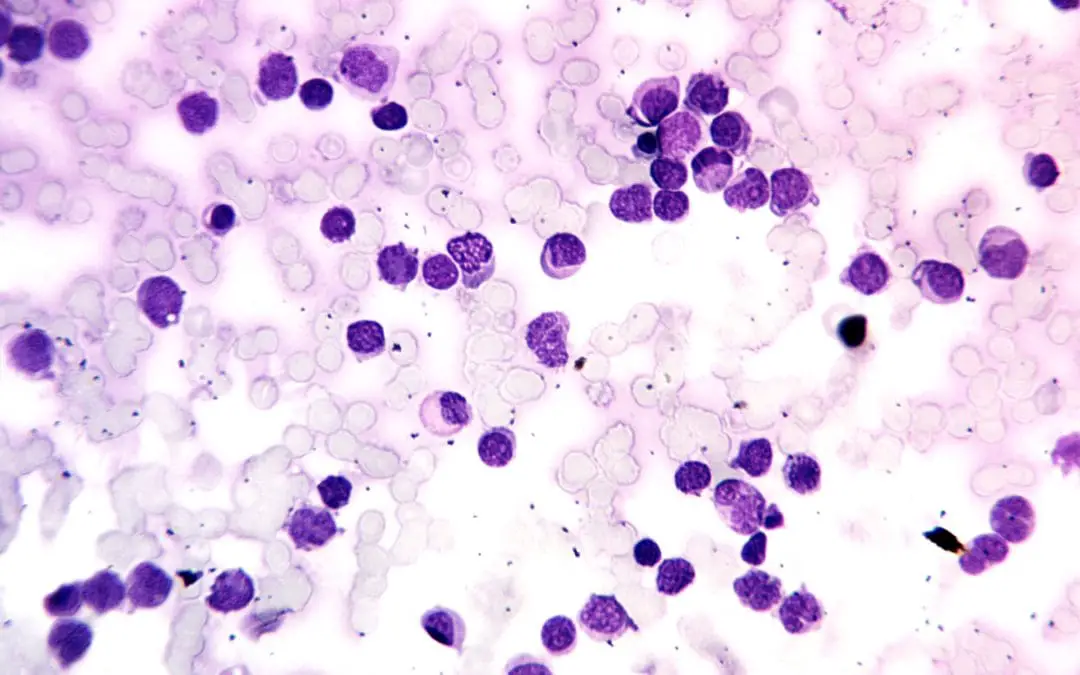
TL;DR Acute leukemia is an aggressive hematologic malignancy characterized by the rapid, uncontrolled proliferation and accumulation of immature hematopoietic progenitor cells (blasts) in the bone marrow and peripheral blood, leading to the suppression of normal...

by MH Team | Oct 9, 2023 | Lab Protocols, Red Blood Cells
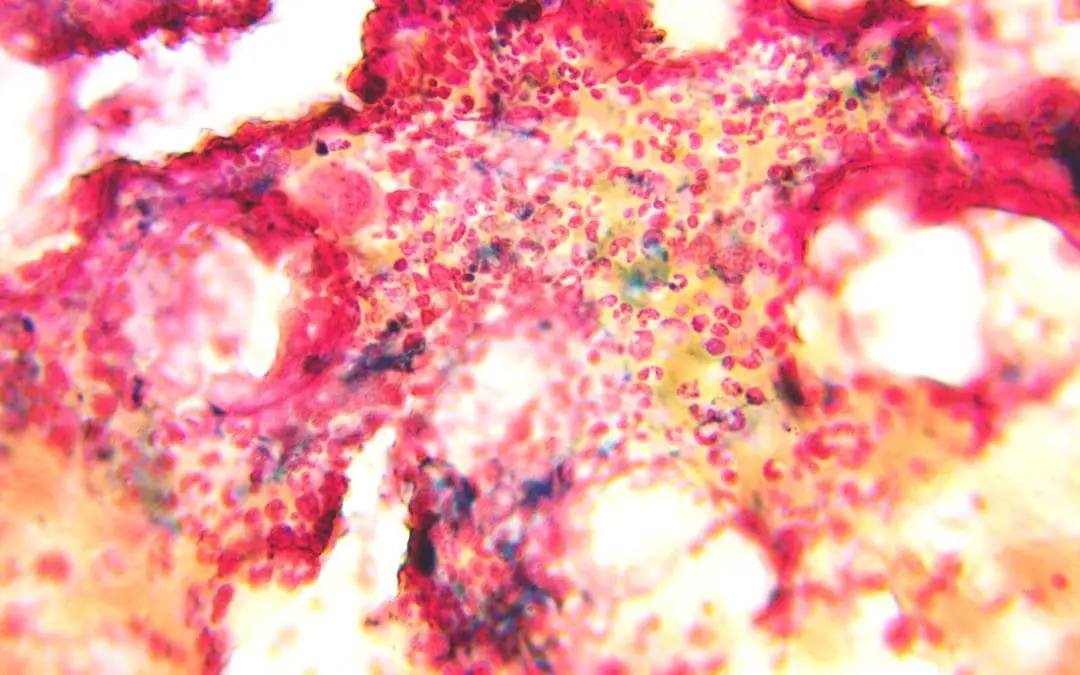
Procedure At A Glance Perls’ Prussian blue stain is used to histochemically detect and visualize ferric iron (Fe3+) deposits in cells and tissues. Preparation: Select and label positive control and test sample slides. Fix slides in absolute methanol for 10...

by MH Team | Oct 9, 2023 | Lab Protocols, Red Blood Cells
Procedure At-A-Glance Leishman stain is primarily used in microscopy to differentiate various types of blood cells and detect blood parasites in peripheral blood smears. Flood Slide Protocol Prepare phosphate buffer Completely cover the peripheral blood smear slide...

by MH Team | Oct 9, 2023 | Red Blood Cells
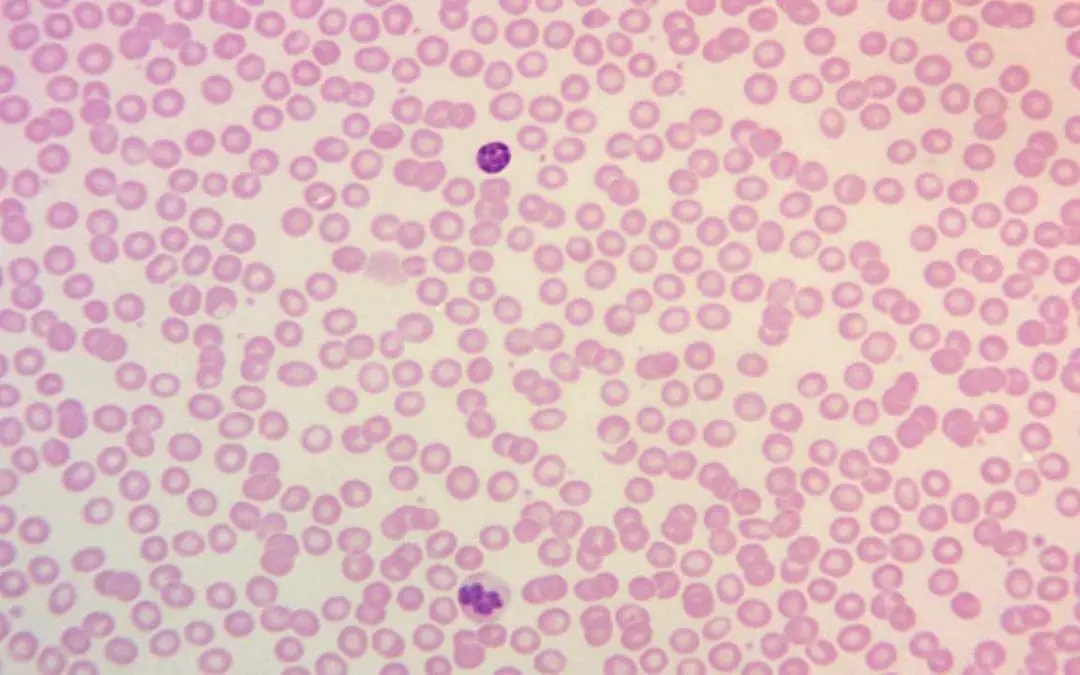
TL;DR Megaloblastic anemia is caused by defective DNA synthesis due to B12 deficiency or folate deficiency resulting in delayed red cell nucleus maturation in the bone marrow leading to macrocytic red cells (MCV > 95 fL in adults). Signs and symptoms...


Recent Comments