TL;DR
Megaloblastic anemia is caused by defective DNA synthesis due to B12 deficiency or folic acid deficiency resulting in delayed red cell nucleus maturation in the bone marrow leading to macrocytic red cells (MCV > 95 fL in adults).
Signs and symptoms ▾
| General | Specific | Specific B12 deficiency symptoms |
| General features related to anemia Mild jaundice | Glossitis Angular stomatitis Sterility Fetal neural tube defects | Symmetrical neuropathy Tingling in feet Difficulty in gait Visual or psychiatric disorders |
Causes ▾
| B12 deficiency causes | Folic acid deficiency causes |
| Lack of gastric intrinsic factor – Pernicious anemia (autoimmune gastritis) – Congenital or abnormality – Gastrectomy Intestinal malabsorption – Crohn’s disease – Ileal resection – Stagnant loop syndrome – Fish tapeworm Diet – Vegans | Diet Malabsorption – Celiac disease – Tropical sprue – Small bowel disease or resection Increased requirement – Pregnancy – Hemolytic anemia Myeloproliferative / malignancy / inflammatory Renal loss – Congestive cardiac failure – Dialysis Drugs – Anticonvulsants – Sulfasalazine |
Pernicious anemia causes
An autoimmune disease caused by anti-intrinsic factor antibodies or parietal cell antibodies. These antibodies damage the gastric mucosa with dense infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells leading to chronic atrophic gastritis and failure of intrinsic factor production.
Laboratory tests ▾
- Complete blood count: ↓ hemoglobin, ↑ mean cell volume and normal or ↑ mean cell hemoglobin, ↓ reticulocytes. Moderate reduction of white blood cell and platelet counts in severe anemia.
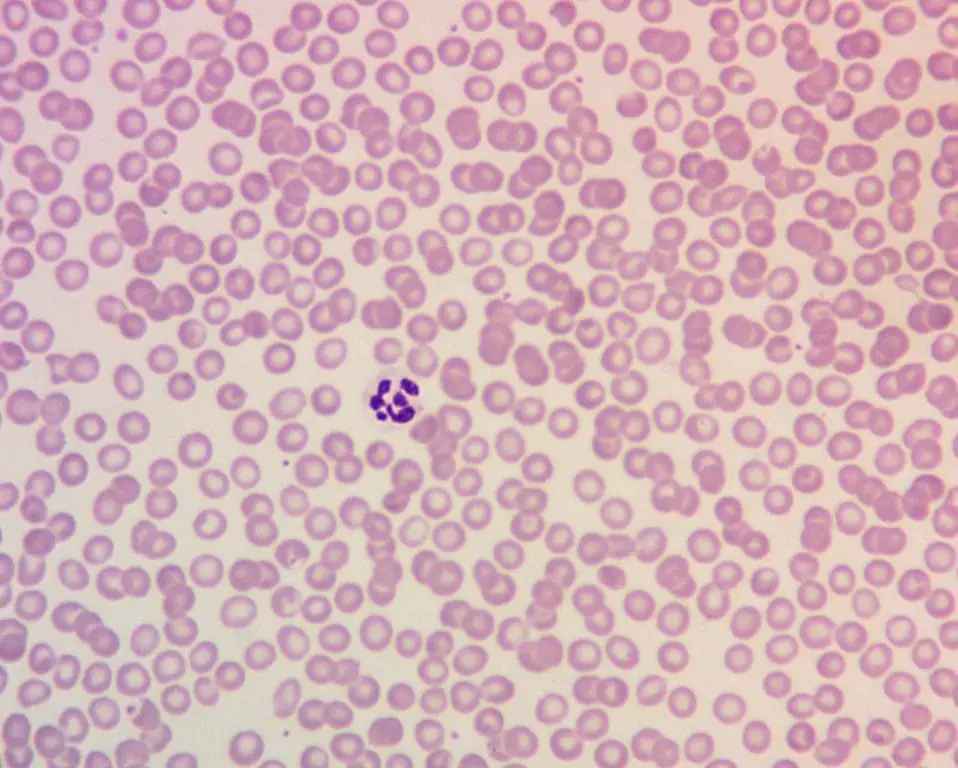
- Peripheral blood smear: Oval macrocytes, anisopoikilocytosis and hypersegmented neutrophils.
- Bone marrow characteristics: Hypercellular with large erythroblasts. Giant and abnormally shaped metamyelocytes are characteristic.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency specific tests
- ↓ serum vitamin B12
- ↑ serum methylmalonic acid
- ↑ serum homocysteine
- Folate deficiency specific tests
- ↓ serum folate
- ↓ red cell folate
- Pernicious anemia specific tests
- Abnormal Schilling test for vitamin B12 absorption
- Severe deficiency of intrinsic factor
- Serum antibodies to intrinsic factor
Treatment and management of megaloblastic anemia ▾
- Vitamin B12 deficiency treatment
- Hydroxocobalamin intramuscularly if not due to dietary intake
- Folic acid deficiency treatment
- Oral folic acid 5 mg once daily
*Click ▾ for more information
What is megaloblastic anemia?
Megaloblastic anemia is defined as a type of anemia caused by defective DNA synthesis due to Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) or folic acid (folate) deficiency. Anemia is defined as when a person’s hemoglobin level falls below the reference range or a reduction in the hemoglobin concentration of the blood according to gender and age. Megaloblastic anemia causes delayed red cell nucleus maturation in the bone marrow leading to macrocytic (abnormally large) red cells.
Importance of Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) and Folic Acid
Hematopoiesis or production of blood cells depends on orderly cell division and differentiation for expansion and maturation of progenitor (early) cells into members of circulating blood cells. For this to happen, vitamin B12 and folic acid is needed for nucleic acid or DNA formation. Vitamin B12 deficiency or folic acid deficiency in the body will lead to megaloblastic anemia in which DNA synthesis is impaired, resulting in slowing or arrest of cellular division during the DNA synthesis phase of the cell cycle which is the S phase. A high percentage of defective cells undergo apoptosis leading to ineffective erythropoiesis. However, RNA synthesis and cytoplasmic differentiation are relatively unaffected, thus surviving progenitors and progeny are enlarged or have the appearance of macrocytic cells which results in macrocytic or large red blood cells, hypersegmented neutrophils and thrombocytopenia (low production of platelets).
Sources of Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid
Vitamin B12 is found in foods of animal origin such as liver, meat, fish and dairy products but not in fruit, cereals nor vegetables.
Folic acid is present primarily in fruits, vegetables, liver and certain meat products and can be inactivated by prolonged cooking.
How are vitamin B12 and folic acid absorbed in the body?
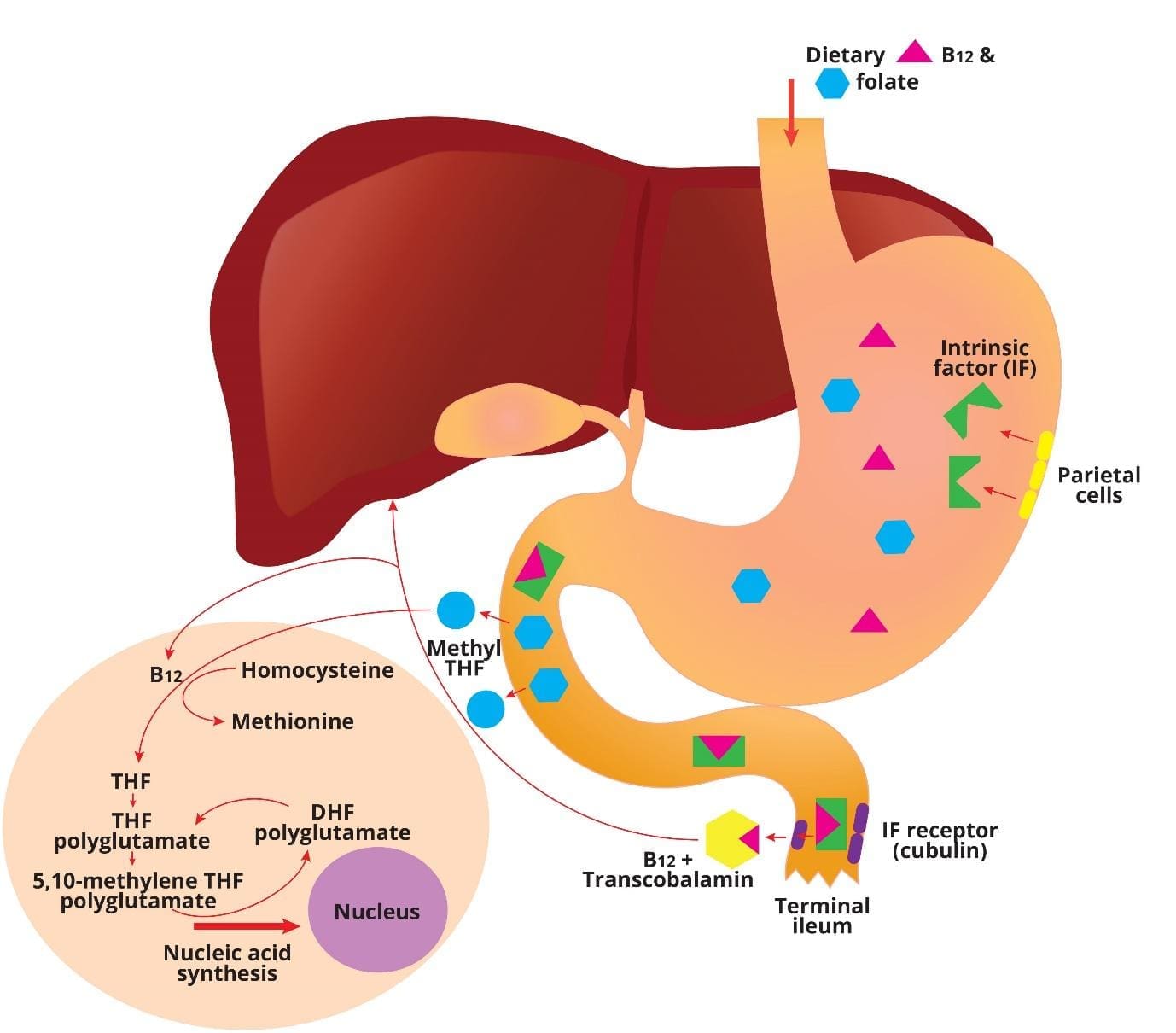
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) absorption
Following ingestion, some cobalamin or vitamin B12 in food is transferred to human haptocorrin in the saliva. The acidic environment of the stomach enables efficient release and transfer of the remaining food cobalamin to haptocorrin in gastric juice.
After transit to the duodenum, increase in pH enables the transfer of cobalamin from haptocorrin to intrinsic factor, a transport protein secreted by gastric parietal cells. The cobalamin-intrinsic factor complex resists digestion and travels down the gut until it encounters epithelial cells in the distal ileum that express cubilin, a specific receptor for this bimolecular complex.
The cobalamin that is absorbed in the ileum exits the basolateral side of the mucosal epithelial cell and enters the blood and binds to transcobalamin, in which it travels via the portal circulation to the liver. Circulating transcobalamin-cobalamin complexes then bind and are taken up into cells by transcobalamin receptors.
Folate absorption
Dietary folates are converted to methyl-tetrahydrofolate (THF) during absorption through the upper small intestine. Once inside the cell they are converted to folate polyglutamates. Folate binding proteins are present on cell surfaces including the enterocyte and facilitate entry of reduced folates into cells. All body cells, including those of the bone marrow, receive folate from plasma as methyl-THF.
How does cobalamin and folate work together?
Vitamin B12 is needed in the conversion of methyl-THF to THF, a reaction in which homocysteine is methylated to methionine. During another reaction involving the conversion of the amino acid serine to glycine, a methyl group is transferred to THF to form N5,10-methylene THF, which is required for both de novo purine biosynthesis and for the conversion of deoxyuridylate to deoxythymidylate. Thus, vitamin B12 and folate both play critical roles in the production of the building blocks of DNA.
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) and Folate cycle
Causes of megaloblastic anemia
Causes of B12 deficiency
In Western countries, severe vitamin B12 deficiency is usually caused by pernicious anemia. While less common causes are intestinal malabsorption like Crohn’s disease, veganism, gastrectomy or small intestinal lesions, fish tapeworm infestations and others.
Causes of folic acid deficiency
Folic acid deficiency on the other hand most often results from a poor dietary intake of folate alone like veganism or in combination with a condition of increased folate utilization or malabsorption like celiac disease.
Excess cell turnover like in pregnancy is the main cause of an increased need for folate as the folate molecule degrades when DNA synthesis is increased. Other less common causes include certain drugs and renal loss through dialysis.
Pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is an autoimmune disorder due to the destruction of gastric parietal cells. Parietal cells are the source of intrinsic factors and are also responsible for pumping hydrochloric acid (HCl) into the gastric lumen.
It is believed that the autoimmune attack is initiated by gastric dendritic cells, which help to clear apoptotic parietal cells produced during the normal turnover of gastric mucosa. These dendritic cells migrate to paragastric lymph nodes, where they present peptides derived from the proton/potassium ATPase on the parietal cells to autoreactive CD4+ T lymphocytes. Over 90% of patients also have serum antibodies against parietal cells, and about 50% have antibodies against intrinsic factors.
Megaloblastic anemia symptoms & signs
Vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms
- Fatigue and weakness: This is one of the most common vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms. People with B12 deficiency may feel tired all the time, even after getting a good night’s sleep.
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet: This is caused by damage to the nerves.
- Problems with vision: One of the Vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms include vision problems, such as blurry vision or loss of vision in the peripheral (side) vision.
- Memory problems and difficulty concentrating: Vitamin B12 deficiency can also affect the brain and nervous system, leading to problems with memory, concentration, and thinking.
- Balance problems: Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause damage to the nerves in the spinal cord, which can lead to balance problems.
- Beefy tongue: This is a characteristic B12 deficiency symptom. The tongue can appear swollen, inflamed, and a deep red color, often with a smooth, almost bald appearance due to loss of papillae (tiny bumps on the tongue’s surface).
- Angular stomatitis: This shows up as red, cracked, and sometimes painful lesions at the corners of the mouth. While it can have other causes, it’s frequently seen in conjunction with B12 deficiency.
- Mouth ulcers: Mouth ulcers are a common vitamin B12 deficiency symptom.
- Pale skin: Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause anemia, which is a condition in which the body doesn’t have enough red blood cells. Anemia can make the skin look pale.
- Shortness of breath: Anemia can also cause shortness of breath.
- Hair loss: Hair loss can be a vitamin B12 deficiency symptom.
Folic acid symptoms
- Fatigue and weakness: This is a widespread folic acid deficiency symptom. People with the deficiency may feel tired all the time, even after getting a good night’s sleep.
- Headaches: Headaches are another common complaint of people with folate deficiency.
- Shortness of breath: Folate deficiency can lead to anemia, a condition in which the body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout the body. This can cause shortness of breath.
- Palpitations: Palpitations, or a feeling of a racing heart, can also occur with folate deficiency anemia.
- Loss of appetite: Some people with folate deficiency may experience a loss of appetite or weight loss.
- Mouth ulcers: Canker sores or mouth ulcers are a frequent folate deficiency symptom.
- Diarrhea: Diarrhea can occur in some individuals with folate deficiency.
- Irritability: Folate deficiency can sometimes cause irritability or mood swings.
- Neural tube defects in babies: Folate deficiency during pregnancy can increase the risk of neural tube defects in babies. The neural tube is the early formation of the brain and spinal cord in a developing fetus. Neural tube defects can cause serious health problems, such as spina bifida.
How do I test for megaloblastic anemia?
General laboratory tests
In laboratory investigations, there will be a general reduction in all blood cells production and the red blood cells are macrocytic. The peripheral blood smear reveals anisocytosis and macro-ovalocytes with hypersegmented neutrophil which is an important indicator of megaloblastic anemia.
Specific Vitamin B12 tests & Folic acid tests
Specific vitamin B12 deficiency tests
Specific tests for B12 deficiency will reveal decreased serum B12 level with increased serum methylmalonic acid and homocysteine levels.
Pernicious anemia test
Pernicious anemia can be tested using Schilling’s test. The patient is given radioactively-tagged oral doses of vitamin B12, and their 24-hour urine level of cobalamin is studied. The patient can also be tested for autoantibodies to intrinsic factors with an immunoassay or have their level of intrinsic factor evaluated.
Specific folate deficiency test
Specific folate deficiency tests include serum and red cell folate which should be reduced.
How is megaloblastic anemia treated?
Vitamin B12 deficiency treatment: hydroxocobalamin can be given orally or intramuscularly.
Folic acid deficiency treatment: Oral folic acid for those with folate deficiencies.
Most cases only need therapy with the appropriate vitamin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does megaloblastic anemia affect my body?
Megaloblastic anemia affects your body in several ways, primarily due to the disruption of healthy red blood cell production.
Reduced Oxygen Delivery
- Fatigue and Weakness: The most common symptom is fatigue, as your body struggles to get enough oxygen to your tissues. This can lead to weakness, making even simple tasks feel difficult.
- Shortness of Breath: You may experience shortness of breath, especially during exertion, as your body tries to compensate for the lack of oxygen-carrying red blood cells.
- Pale Skin and Mucous Membranes: Due to fewer red blood cells circulating, your skin and mucous membranes (like the inside of your mouth) may appear paler than usual.
Disrupted Cell Growth
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Megaloblastic anemia can lead to diarrhea, nausea, and loss of appetite.
- Swollen and Smooth Tongue: The disrupted cell growth can also affect the cells on your tongue, causing it to become swollen and smooth, losing its bumpy texture.
- Numbness and Tingling: In severe cases, particularly with vitamin B12 deficiency, nerve damage can occur, leading to numbness and tingling in your hands and feet.
Other Potential Complications
- Heart Problems: Untreated megaloblastic anemia can strain your heart as it tries to pump oxygen-deficient blood throughout your body. This can lead to an enlarged heart and heart failure in severe cases.
- Neurological Problems: Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause more severe neurological problems like memory loss, depression, and even dementia if left untreated for a long time.
- Pregnancy Complications: During pregnancy, megaloblastic anemia can increase the risk of birth defects like neural tube defects and other complications.
Is megaloblastic anemia a serious illness?
While megaloblastic anemia itself isn’t inherently a life-threatening condition, its seriousness depends on the severity and the underlying cause.
Left untreated, it can lead to serious complications like heart problems, neurological damage (especially with B12 deficiency), and pregnancy complications. However, the good news is that early diagnosis and treatment are highly effective. With proper management, most people experiencing megaloblastic anemia recover fully and don’t experience long-term effects.
How common is megaloblastic anemia?
Overall, it’s not considered rare. Estimates suggest less than 1,000 people in the US have the disease, but this likely underestimates the true number due to undiagnosed cases.
- Macrocytosis (large red blood cells), a common sign, affects 2-4% of the population, with 60% having anemia, often due to folate or B12 deficiency.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency becomes more prevalent in older adults, with around 1 in 7,500 people developing pernicious anemia each year.
- Folic acid deficiency is also common, particularly among pregnant women, individuals with dietary limitations, and those with absorption issues.
How can I reduce my risk of developing megaloblastic anemia?
Here are some steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing megaloblastic anemia:
Diet
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamin B12 and folate: Include foods like:
- Vitamin B12: Animal products like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy. Fortified cereals and nutritional yeast can also be good sources.
- Folate: Leafy green vegetables, legumes, fruits (especially citrus fruits), fortified cereals and grains, and nuts and seeds.
- Consider supplementation: If you’re concerned about your intake or have risk factors like strict vegetarian/vegan diets, malabsorption issues, or pregnancy, talk to your doctor about vitamin B12 and/or folate supplements.
Lifestyle
- Moderate alcohol intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with vitamin B12 absorption.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking can increase your vitamin B12 requirements.
- Manage underlying conditions: If you have any conditions that affect nutrient absorption, like celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease, work with your doctor to manage them effectively.
What can I expect if I have megaloblastic anemia?
What you can expect if you have megaloblastic anemia depends on several factors, including:
Severity of the anemia: The degree to which your red blood cell count is affected will determine the intensity of symptoms and potential complications. Mild cases may not cause noticeable symptoms, while severe cases can lead to fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and other issues.
Underlying cause: The specific cause of your anemia will influence the treatment plan and potential complications. For example, vitamin B12 deficiency related to dietary restrictions is generally less concerning than pernicious anemia caused by an autoimmune attack.
Timeliness of diagnosis and treatment: Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing complications and ensuring a smooth recovery. With proper management, most individuals experience complete recovery and no long-term effects.
Here’s a general overview of what to expect:
Diagnosis
- Your doctor will likely perform a blood test to assess your red blood cell size and count. They may also recommend additional tests to identify the underlying cause, such as vitamin B12 or folate levels.
Treatment
- The treatment plan will target the specific cause of your anemia. For vitamin B12 deficiency, this might involve oral or injected supplements. For folate deficiency, dietary changes or folic acid supplements may be recommended. In some cases, addressing underlying medical conditions is crucial.
Management
- Regular monitoring of your red blood cell count and other blood tests is important to track your progress and adjust treatment as needed.
- Depending on the cause, dietary changes or supplementation might be necessary to maintain healthy vitamin B12 and folate levels in the long term.
Potential Complications
- Untreated or severe megaloblastic anemia can lead to complications like heart problems, neurological damage (especially with B12 deficiency), and pregnancy complications.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to minimize these risks.
Recovery
- With proper treatment, most individuals with megaloblastic anemia experience a full recovery and don’t have long-term effects. The recovery time can vary depending on the severity of the anemia and the underlying cause.
What is the difference between B12 deficiency and megaloblastic anemia?
While B12 deficiency and megaloblastic anemia are closely related, they’re not the same thing. B12 deficiency is a nutritional deficiency where your body doesn’t have enough vitamin B12. This can happen due to various reasons, like dietary restrictions, malabsorption issues, age-related changes and certain medications. Megaloblastic anemia is a type of anemia characterized by the presence of large, immature red blood cells called megaloblasts. These abnormal cells are ineffective in carrying oxygen throughout the body, leading to anemia symptoms like fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
B12 deficiency is a major cause of megaloblastic anemia. However, not everyone with B12 deficiency develops megaloblastic anemia. Other causes besides B12 deficiency can also lead to megaloblastic anemia. Folate deficiency is another common cause, and rare genetic disorders can also play a role. Thus, B12 deficiency is a nutritional issue, while megaloblastic anemia is a type of blood disorder.
What is the difference between the terms megaloblastic and macrocytic?
The terms “megaloblastic” and “macrocytic” are related but distinct when describing red blood cells and anemia. Megaloblastic refers to the abnormal size and development of red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow called megaloblasts. These cells are larger than normal but functionally impaired, leading to ineffective red blood cell production. Not all macrocytic anemias are megaloblastic. Other causes can lead to large red blood cells without involving megaloblasts, such as liver disease or certain medications. Megaloblasts are associated with various causes, including vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies, genetic disorders, and certain medications.
Macrocytic simply describes red blood cells that are larger than normal. This is measured by the Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) in a blood test. It can be a sign of megaloblastic anemia, but not always. Other conditions can also cause macrocytosis without involving megaloblasts.
In summary, megaloblastic refers to the type of cell development, while macrocytic refers to the size of the red blood cells. Megaloblastic anemia is a specific type of macrocytic anemia caused by abnormal precursor cells. Not all macrocytic anemias are megaloblastic, and having macrocytic red blood cells requires further investigation for diagnosis.
How does vitamin B12 deficiency cause macrocytic anemia?
When your body lacks vitamin B12, it struggles to properly utilize B9 (folate) for DNA synthesis in developing red blood cells. This disrupts their maturation process, leading to the formation of abnormally large but dysfunctional cells called megaloblasts. These giants can’t properly divide or leave the bone marrow, resulting in fewer, oversized red blood cells in circulation – classic features of macrocytic anemia. This deficiency impacts oxygen delivery throughout your body, causing fatigue, weakness, and other symptoms.
What are the potential complications of untreated megaloblastic anemia?
Untreated megaloblastic anemia can lead to several potential complications, some of which can be very serious.
Neurological Issues
- Vitamin B12 deficiency, a major cause of megaloblastic anemia, can significantly impact the nervous system. Prolonged deficiency can lead to nerve damage, causing symptoms like:
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet.
- Muscle weakness and difficulty walking.
- Vision problems, including blurred vision and double vision.
- Cognitive decline, confusion, and memory problems.
- In severe cases, dementia may develop.
Heart Problems
- When your body lacks healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen efficiently, your heart has to work harder to pump blood and deliver oxygen to your tissues. This can lead to:
- Enlarged heart (cardiomegaly).
- Heart failure, where the heart struggles to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
- Increased risk of heart attack.
Other Complications
- Pregnancy complications: Untreated megaloblastic anemia during pregnancy can increase the risk of:
- Neural tube defects in the baby.
- Premature birth.
- Low birth weight.
- Bone problems: Folate deficiency, another cause of megaloblastic anemia, can weaken bones and increase the risk of fractures.
- Psychological problems: Fatigue and other symptoms of anemia can lead to depression and anxiety.
What dietary changes can help prevent or manage megaloblastic anemia?
Here are some dietary changes that can help prevent or manage megaloblastic anemia by increasing your intake of vitamin B12 and folate.
For Vitamin B12
- Animal products: These are the most reliable sources of vitamin B12. Include them in your diet regularly.
- Meat: Beef, lamb, pork, chicken, and turkey.
- Poultry: Chicken, duck, and goose.
- Fish and shellfish: Salmon, tuna, mackerel, sardines, clams, and oysters.
- Eggs: A good source of both B12 and folate.
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt.
For Folate
- Leafy green vegetables: These are packed with folate. Aim for at least one serving per day, such as spinach, kale, collard greens, romaine lettuce, and Swiss chard.
- Other vegetables: Broccoli, asparagus, Brussels sprouts, beets, and okra are also good sources.
- Fruits: Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruit, and tangerines are good sources of folate. Other fruits like papaya, mango, and kiwi also contain some folate.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of folate and other nutrients.
- Fortified foods: Many breakfast cereals, grains, and nutritional yeast are fortified with folic acid, the synthetic form of folate.
Additional tips
- Cook food gently: Overcooking can destroy folate, so steam, stir-fry, or microwave vegetables instead of boiling them.
- Eat fortified foods in moderation: While helpful, don’t rely solely on fortified foods as they may not offer the same range of nutrients as naturally folate-rich options.
- Consider supplements: If you have difficulty meeting your needs through diet alone, talk to your doctor about vitamin B12 or folate supplements.
What other health conditions can be mistaken for megaloblastic anemia?
Several health conditions can sometimes be mistaken for megaloblastic anemia due to overlapping symptoms or similar blood test findings. Here are some key examples:
Iron deficiency anemia: This is the most common type of anemia and also presents with fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. However, unlike megaloblastic anemia, red blood cells in iron deficiency are smaller and paler (microcytic). Additional tests like iron levels and reticulocyte count can help differentiate between the two.
Other macrocytic anemias: Not all macrocytic anemias (large red blood cells) are megaloblastic. Conditions like:
- Liver disease: Can affect red blood cell production and lead to macrocytosis without involving abnormal precursors.
- Alcoholism: May interfere with vitamin B12 absorption and cause macrocytosis.
- Certain medications: Can have a similar effect on red blood cell size.
Other conditions with similar symptoms: Fatigue, a common symptom of megaloblastic anemia, can also occur in various conditions like:
- Thyroid disorders: Hypothyroidism can cause fatigue and other symptoms that might be mistaken for anemia.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome: Features persistent fatigue without a clear medical cause.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Deficiencies in other vitamins and minerals besides B12 and folate can also cause fatigue and weakness.
Differentiating diagnosis
- A thorough medical history, physical examination, and blood tests are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
- Red blood cell size, shape, and number, along with vitamin B12 and folate levels should be assessed.
- In some cases, bone marrow examination might be necessary to determine the exact cause of the anemia.
How does megaloblastic anemia affect different age groups?
Megaloblastic anemia can affect individuals across all age groups, but the specific impacts and risk factors can vary depending on age.
Children
- Causes: Most common causes in children include:
- Dietary deficiencies: Especially in strict vegetarians/vegans or children with limited dietary variety, leading to B12 or folate deficiency.
- Congenital conditions: Rare genetic disorders affecting vitamin B12 metabolism or folate absorption can cause megaloblastic anemia.
- Impacts: Growth delays, developmental problems, fatigue, paleness, and poor appetite. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to minimize impact on growth and development.
- Additional concerns: Children with underlying medical conditions like celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease are at increased risk due to potential nutrient absorption issues.
Adults
- Causes: Most common causes include:
- Vitamin B12 deficiency: Often due to dietary limitations (vegans, older adults), malabsorption issues, or medications interfering with B12 absorption.
- Folate deficiency: Less common but can occur due to dietary limitations, malabsorption, or pregnancy/breastfeeding.
- Impacts: Fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale skin, and tingling/numbness in extremities. Neurological problems can develop with prolonged B12 deficiency.
- Additional concerns: Older adults are more prone to B12 deficiency due to decreased stomach acid production and potential changes in dietary habits.
Elderly:
- Causes: Similar to adults, with additional factors like:
- Increased prevalence of age-related conditions: Malabsorption issues like celiac disease or medications affecting B12 absorption become more common.
- Cognitive decline: May make individuals less aware of dietary needs or hinder medication adherence.
- Impacts: Similar to adults, with potentially more severe consequences due to underlying health conditions.
- Increased risk of falls: Due to fatigue and weakness.
- Cognitive decline: May be exacerbated by B12 deficiency.
- Additional concerns: Regular monitoring and personalized management are crucial to prevent complications and ensure overall well-being.
What are the specific risks and considerations for pregnant women with megaloblastic anemia?
Pregnant women with megaloblastic anemia face unique risks and considerations compared to the general population.
Risks to the mother
- Increased risk of complications: Untreated megaloblastic anemia can lead to
- Preeclampsia: A serious pregnancy complication with high blood pressure and potential organ damage.
- Preterm birth: Delivering the baby before 37 weeks.
- Low birth weight: The baby being smaller than expected for gestational age.
- Postpartum hemorrhage: Excessive bleeding after childbirth.
- Neurological damage: Vitamin B12 deficiency, a major cause, can cause nerve damage if left untreated. This can lead to weakness, numbness, and cognitive problems.
Risks to the baby
- Neural tube defects: Folate deficiency, another cause, significantly increases the risk of these birth defects affecting the brain and spinal cord.
- Growth problems: The baby may not grow and develop as expected due to nutrient deficiencies.
- Increased risk of miscarriage: Studies suggest a potential link between untreated anemia and miscarriage, although more research is needed.
Considerations for management
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial: Prompt intervention minimizes risks to both mother and baby.
- Identifying the underlying cause: Addressing the root cause of the anemia, like B12 deficiency or dietary limitations, is essential.
- Prenatal vitamins: Folic acid supplementation is standard for all pregnant women, but those with anemia may need additional vitamin B12 supplements.
- Regular monitoring: Close monitoring of blood counts, vitamin levels, and fetal development is critical.
- Multidisciplinary care: Collaboration between obstetricians, hematologists, and nutritionists is often recommended for optimal management.
Are there any genetic factors that contribute to the development of megaloblastic anemia?
Inborn errors of metabolism: These are genetic mutations affecting enzymes involved in vitamin B12 or folate metabolism. This can lead to impaired absorption, utilization, or transport of these vitamins, ultimately causing megaloblastic anemia. Examples include:
- Megaloblastic anemia type I (cblC/cblD deficiency): Affects the conversion of vitamin B12 to its active form.
- Megaloblastic anemia type II (cblB deficiency): Affects the transport of vitamin B12 inside cells.
- Congenital folate malabsorption: Impairs the absorption of folate from the gut.
Fanconi anemia: This genetic disorder affects DNA repair mechanisms and can lead to bone marrow problems, including megaloblastic anemia initially before presenting with aplastic anemia.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and is specifically targeted towards medical students. It is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. While the information presented here is derived from credible medical sources and is believed to be accurate and up-to-date, it is not guaranteed to be complete or error-free. See additional information.
References
- Anemia: Diagnosis and Treatment (Willis, 2016).
- Management of Anemia: A Comprehensive Guide for Clinicians (Provenzano et al., 2018)
- Goldberg S, Hoffman J. Clinical Hematology Made Ridiculously Simple, 1st Edition: An Incredibly Easy Way to Learn for Medical, Nursing, PA Students, and General Practitioners (MedMaster Medical Books). 2021.
- Brosh RM Jr, Bellani M, Liu Y, Seidman MM. Fanconi Anemia: A DNA repair disorder characterized by accelerated decline of the hematopoietic stem cell compartment and other features of aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2017 Jan;33:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 17. PMID: 27223997; PMCID: PMC5114166.
- Nugraheni, A. I., Wijayanti, K. R. D., & Manuaba, I. A. I. M. (2023). Severe Megaloblastic Anemia & Thrombocytopenia in Pregnancy: A Case Report. European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences, 5(2), 14–19. https://doi.org/10.24018/ejmed.2023.5.2.1667