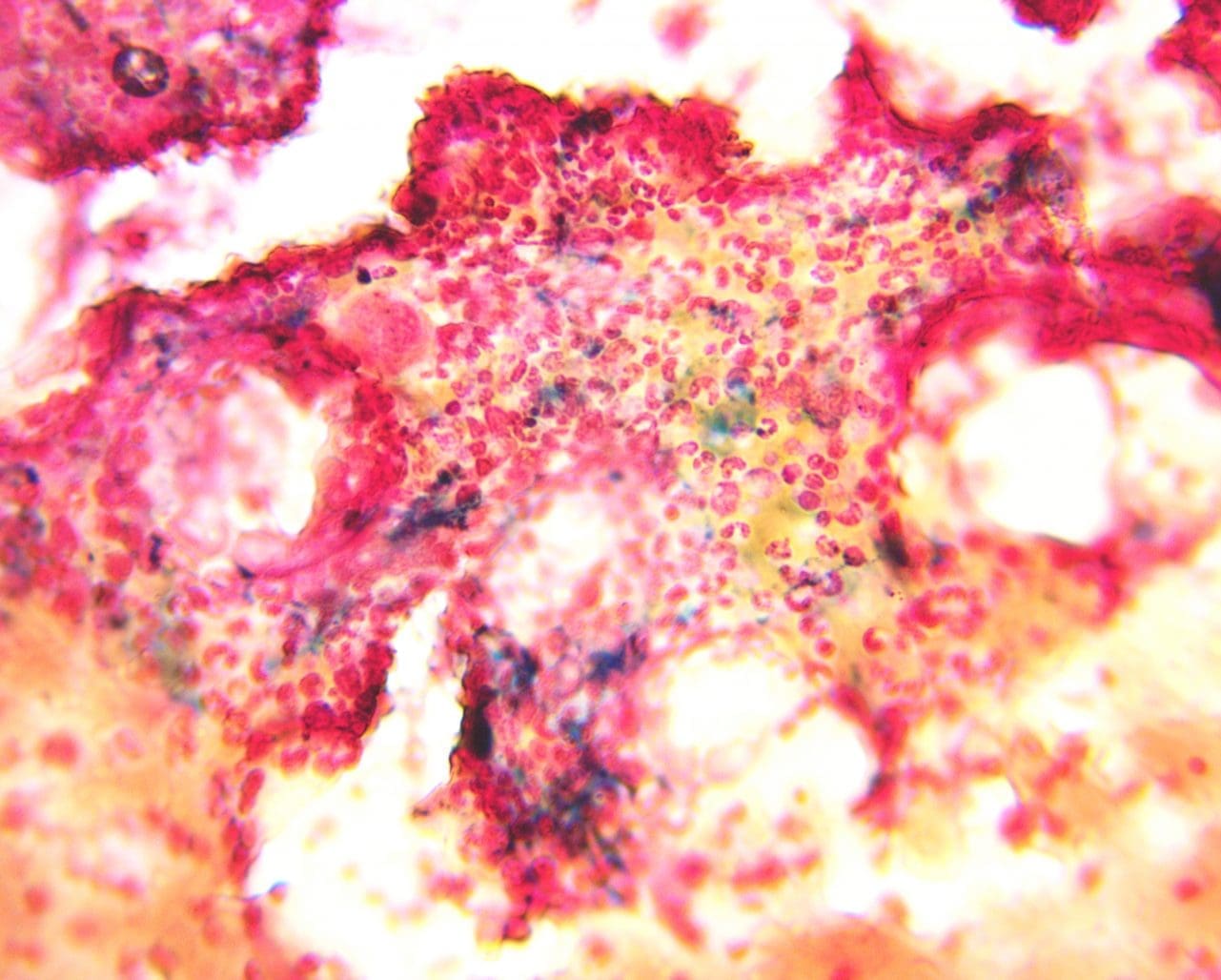
Procedure At A Glance
Perls’ Prussian blue stain is used to histochemically detect and visualize ferric iron (Fe3+) deposits in cells and tissues.
- Preparation: Select and label positive control and test sample slides. Fix slides in absolute methanol for 10 minutes and dry.
- Working Solution: Prepare a working solution by mixing 2% potassium ferrocyanide and 2% HCl in a Coplin jar.
- Incubation: Submerge fixed, dried slides in the working solution at room temperature or in a 50°C water bath for 10 minutes.
- Rinsing: Rinse slides with slow-running tap water for 3-5 minutes, then with distilled water.
- Counterstain: Counterstain with 1% aqueous safranin and rinse again.
- Drying & Mounting: Wipe excess liquid from the slide, dry carefully (e.g., with a hair dryer on low), mount with Depex, and cover with a coverslip.
Introduction
Perls’ stain, also known as Prussian blue stain, is a widely used histochemical method that specifically identifies ferric iron (Fe3+) deposits in tissue and cell samples. It works by causing the formation of an insoluble bright blue pigment, Prussian blue, when ferric iron reacts with potassium ferrocyanide in an acidic environment, making iron stores visible under a microscope.
Principle of Perls’ Prussian Blue Stain
The Perls’ Prussian Blue stain, a cornerstone in histopathology and hematology, offers a sensitive and specific method to visualize iron deposits in tissues.
The key player is hemosiderin, a protein complex storing iron, often found in macrophages and liver cells. This iron exists in the ferric (Fe³⁺) form, readily reacting with specific chemicals like potassium ferrocyanide (K₄Fe(CN)₆). Ferric ions (Fe³⁺) released from hemosiderin by the acid readily bind to ferrocyanide ions (Fe(CN)₆⁴⁻) from the potassium ferrocyanide, forming the insoluble, vibrantly blue ferric ferrocyanide (Fe₄[Fe(CN)₆]₃), more commonly known as Prussian Blue.
The Perls’ Prussian Blue stain offers valuable insights into iron distribution within tissues, making it useful across various clinical and research settings.
Diagnosing Iron Overload
- Hemochromatosis: Identifying excessive iron deposition in liver, spleen, and other organs.
- Secondary iron overload: Assessing iron accumulation due to blood transfusions, ineffective erythropoiesis, or certain medications.
Differentiating Anemias
- Refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts (RARS): Detecting ring sideroblasts, characteristic of this MDS subtype, where iron accumulates within erythrocyte precursors.
- Other anemias: Investigating potential iron deficiency or abnormal iron metabolism contributing to anemia.
Research Applications
- Iron metabolism studies: Understanding iron distribution and regulation in various tissues and diseases.
- Developmental biology: Studying iron involvement in fetal development and organogenesis.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Investigating potential roles of iron dysregulation in conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
Materials
- 2% Potassium Ferrocyanide ((K4Fe(CN)6.3H2O)
- 2% HCl
- 1% aqueous safranin (counterstain)
- Air dried peripheral blood or bone marrow smear
- Distilled water
- Methanol
- Coplin jars
Protocol
- Choose a suitable sample as a positive control and the stain together with a test sample. Label the slides as control and patient name / registration number (R/N) accordingly.
- Fix the slides in absolute methanol for 10 minutes. Leave it to dry.
- Prepare the working solution by adding 30 mL potassium ferrocyanide and 30 mL HCl in a Coplin jar (v/v potassium ferrocyanide:HCl = 1:1).
- Submerge the fixed and dried slides into the Coplin jar containing the working solution.
- Leave it at room temperature or incubate in a water bath at 50°C for 10 minutes.
- Rinse the slide with slow running running tap water for 3-5 minutes.
- Rinse thoroughly in distilled water, and then counterstain with safranin similar to steps 4 – 6.
- Wipe the back of the slide and edges with Kim wipes. Be careful not to touch the smear.
- Dry the slide using a hair dryer on the lowest speed (not more than 10 seconds at a time) or air dry in a tilted position.
- Mount the slide with Depex and cover the zone of morphology with a cover slip.
- This slide is now ready for viewing.
Interpretation
Positive Perls’ Prussian Blue stain Reaction: A positive Perls’ Prussian Blue stain reaction manifests as a distinct blue color in iron-containing structures.
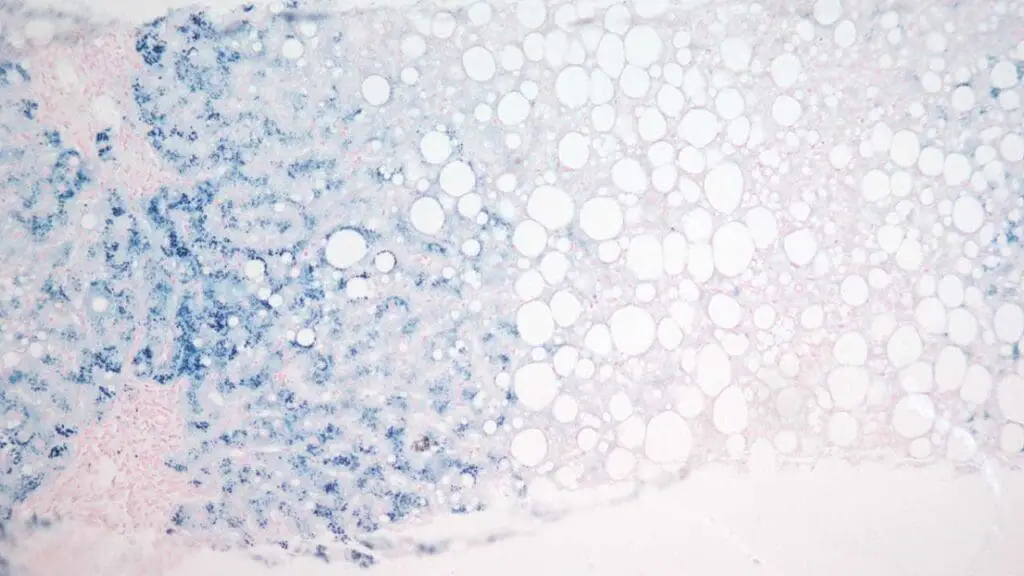
Negative Perls’ Prussian Blue stain Reaction: A complete absence of blue coloration signifies a negative Perls’ Prussian Blue stain reaction.
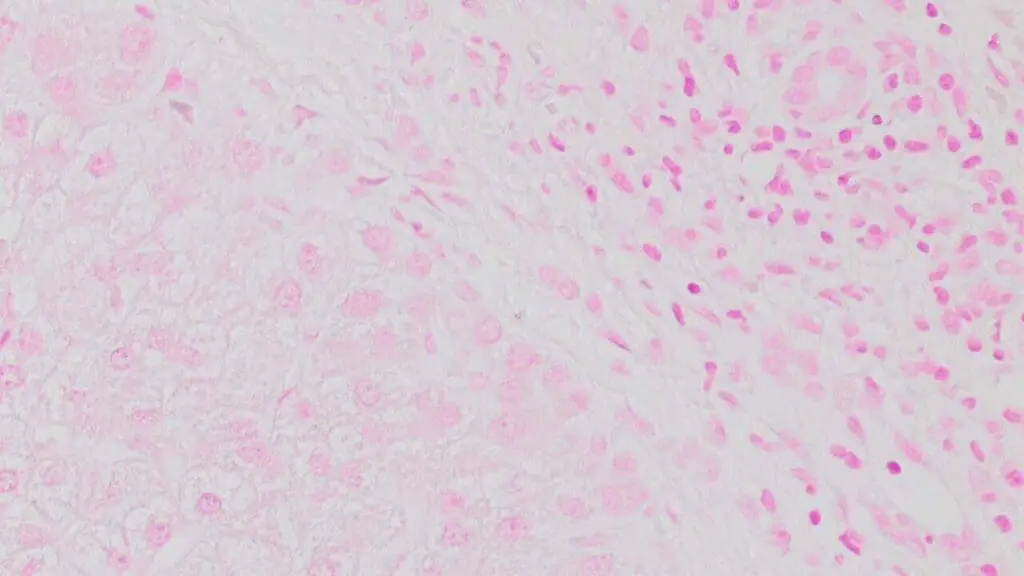
Pathological Variations: Deviations from the expected Perls’ Prussian Blue staining pattern can unveil hidden pathologies:
- Increased iron deposition: Abnormally high levels of hemosiderin, observed as intense blue staining, can be indicative of hemochromatosis, a condition characterized by iron overload.
- Abnormal distribution: Patchy or uneven Perls’ Prussian Blue staining may suggest iron dysregulation associated with various diseases.
- Ring sideroblasts: The presence of ring-shaped iron deposits within red blood cells, observed as blue rings, can indicate sideroblastic anemia, a rare blood disorder.
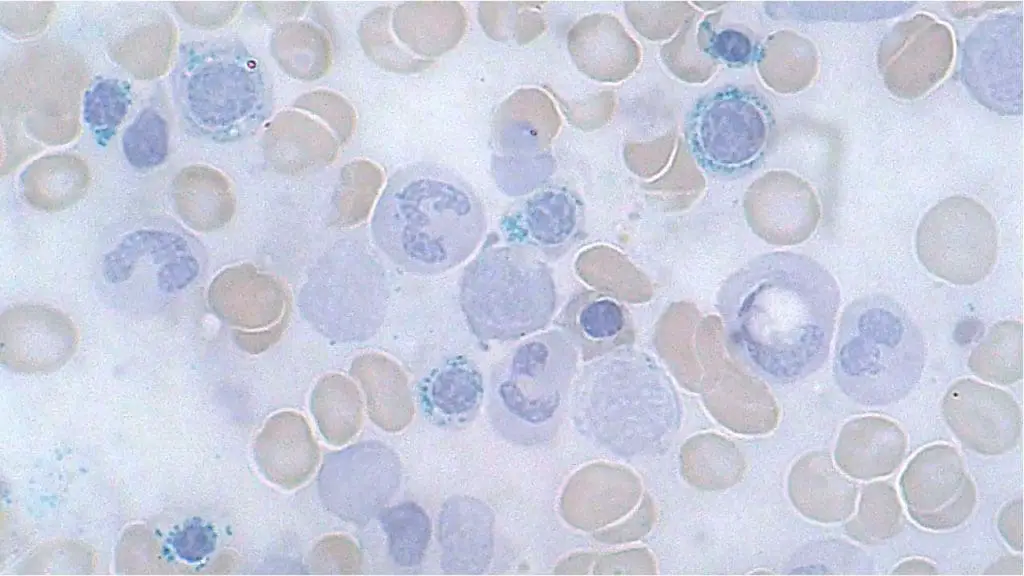
Iron Storage Grading in Bone Marrow Aspirate using Perls’ Prussian Blue Stain
| Grade | Description | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Absent | No blue staining, no iron granules seen |
| 1 | Minimal | Sparse, faint blue granules in few macrophages |
| 2 | Slight | Scattered, small blue granules in macrophages |
| 3 | Moderate | More numerous, medium-sized blue granules in macrophages |
| 4 | Increased | Abundant, large blue granules in most macrophages |
| 5 | Marked | Intensely blue staining of most macrophages, some cytoplasmic filling |
| 6 | Severe | Massive blue deposits obscuring cell outlines, often with hemosiderin crystals |
Summary of the positive and negative interpretations of Perls’ stain, along with common grading systems and examples of associated disorders
| Perls’ Stain Grading | Interpretation | Description of Staining | Examples of Disorders |
| Normal Iron Stores | |||
| Grade 1+ to 3+ | Normal iron stores (bone marrow) | Fine blue granules present in reticulum cells/macrophages within bone marrow fragments. Number and size of granules increase with higher grades within this range. | Healthy individuals. |
| Positive Interpretation (Increased Iron) | |||
| Grade 4+ to 6+ | Increased iron stores (bone marrow) | Numerous, larger blue granules, often forming clumps within macrophages and sometimes free in the bone marrow fragments. Grade 6+ indicates very heavy deposits that may obscure marrow detail. | Primary Hemochromatosis: Genetic disorder leading to excessive iron absorption and accumulation in organs (liver, heart, pancreas). Secondary Iron Overload: Due to repeated blood transfusions (e.g., in thalassemia). Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) with Ring Sideroblasts: Characterized by abnormal iron utilization, leading to iron accumulation around the nucleus of erythroid precursors (ring sideroblasts), even with systemic iron overload. |
| Negative Interpretation (Decreased/Absent Iron) | |||
| Grade 0 | Absent iron stores (bone marrow) | No visible blue granules in bone marrow fragments or cells. | Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA): The most common cause, due to insufficient iron intake, increased iron loss (e.g., chronic bleeding), or malabsorption. |
| Sideroblasts | |||
| Normal Sideroblasts | Normal iron utilization | Normal number of erythroid precursors (sideroblasts) with few, fine blue granules in their cytoplasm, not encircling the nucleus. | Healthy individuals. |
| Ringed Sideroblasts (positive for Perls’ stain) | Abnormal iron utilization | Erythroid precursors (sideroblasts) with five or more blue iron granules arranged in a ring, encircling at least one-third of the nucleus. | Sideroblastic Anemia: A group of disorders characterized by defective heme synthesis, leading to iron accumulation in mitochondria around the nucleus of developing red blood cells. Can be hereditary or acquired (e.g., due to certain drugs, toxins, or as part of MDS). |
Troubleshooting
Pre-staining factors
- Tissue fixation: Improper fixation can damage hemosiderin, making it unavailable for staining. Overfixation can also lead to background staining.
- Decalcification: Decalcification methods using harsh chemicals can extract iron, leading to underestimation of iron stores.
- Tissue processing: Delays in processing or prolonged storage can degrade hemosiderin, impacting staining intensity.
Staining procedure
- Incorrect pH: The staining solution needs a slightly acidic pH for optimal iron release and Prussian Blue stain formation. Deviations can lead to weak or uneven staining.
- Inadequate incubation time: Under-incubation might not allow sufficient iron release, while over-incubation can cause excessive background staining.
- Inappropriate washing: Insufficient washing can leave behind unreacted reagents, causing background staining. Over-washing can remove Prussian Blue stain, leading to underestimation of iron stores.
- Reagent quality: Expired or contaminated reagents can affect staining intensity and specificity.
Post-staining factors
- Mounting media: Improper mounting media can fade the Perls’ Prussian Blue stain or cause artifacts.
- Microscope settings: Incorrect lighting or magnification can make it difficult to accurately assess iron deposits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is hemosiderin?
Hemosiderin is a yellowish-brown, granular pigment found within cells, especially macrophages. It’s essentially a storage form of iron, crucial for maintaining the body’s iron balance.
Hemosiderin is composed of partially digested ferritin, a protein that binds and stores iron safely. When red blood cells break down, releasing their iron-containing protein hemoglobin, macrophages engulf and process the hemoglobin.
Inside the macrophages, iron is either used for essential functions or stored as hemosiderin for later use. This storage mechanism prevents excessive free iron from causing damage to cells and tissues.
Location and Detection
Hemosiderin is primarily found in macrophages located in the liver, spleen, bone marrow, and other organs involved in iron metabolism.
Perls’ Prussian Blue stain is a commonly used method to detect hemosiderin in tissue samples. This stain reacts with iron in hemosiderin to create a characteristic blue color, allowing visualization and quantification of iron stores. Measuring hemosiderin levels through Perls’ Prussian Blue stain or other methods helps diagnose and manage iron-related disorders.
Clinical Significance
Increased hemosiderin levels can indicate iron overload, a condition where the body absorbs too much iron or struggles to eliminate excess iron. This can occur due to genetic disorders like hemochromatosis, blood transfusions, or certain medications.
Conversely, low hemosiderin levels can suggest iron deficiency anemia, where the body doesn’t have enough iron to produce healthy red blood cells.
What are the differences between hemosiderin and ferritin?
While both hemosiderin and ferritin play essential roles in iron storage within the body, they differ in several key aspects.
| Feature | Ferritin | Hemosiderin |
| Nature | A globular protein complex | An insoluble, granular aggregate of partially degraded ferritin, protein, and lipids |
| Structure | Spherical protein shell (apoferritin) with an iron core | Amorphous aggregates; not a distinct protein molecule |
| Solubility | Soluble (especially in its protein-bound form) | Insoluble |
| Iron Release | Readily releases iron when needed by the body | Releases iron slowly and with difficulty; less bioavailable |
| Formation | Primary storage form of iron; formed when iron is abundant | Forms when ferritin becomes saturated with iron and cannot store more; often seen with iron overload or hemorrhage |
| Location | Found in most cells, especially liver, spleen, bone marrow | Primarily found in macrophages (reticuloendothelial cells) in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow, often after red blood cell breakdown |
| Physiological Role | Primary iron storage, critical for iron homeostasis, acts as a buffer against iron deficiency and overload | Secondary iron storage, typically forms when iron levels are high; often a pathological accumulation |
| Clinical Significance | Serum ferritin levels directly reflect total body iron stores; used to diagnose iron deficiency or overload | Indicated by Perls’ stain in tissues; signifies significant iron accumulation or breakdown of red blood cells (e.g., hemorrhage) |
| Appearance (Histology) | May not be visible with routine stains; requires specific immunohistochemistry or electron microscopy for visualization (though high concentrations of iron within ferritin can contribute to Perls’ stain positivity) | Visible as golden-brown or yellowish-brown granules in unstained tissue sections; stains blue with Perls’ Prussian blue stain |
What are siderocyte granules?
Siderocyte granules are small, blue-staining aggregates of iron found within mature red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes. These granules are composed primarily of the iron storage protein hemosiderin, and their presence typically indicates an abnormal accumulation of iron within the erythrocytes.
What are sideroblasts?
Sideroblasts are nucleated red blood cell precursors (erythroblasts) that contain visible deposits of iron. These iron deposits can be scattered throughout the cytoplasm or arranged in a characteristic ring around the nucleus, forming ring sideroblasts. Their presence plays a crucial role in diagnosing various blood disorders related to iron metabolism.
Formation
During the development of red blood cells in the bone marrow, they take up iron to produce hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen. Normally, this iron gets efficiently utilized for hemoglobin synthesis, leaving minimal leftover. However, some conditions can lead to excess iron within erythroblasts, resulting in the formation of visible iron deposits known as sideroblasts.
Types
- Ring sideroblasts: As mentioned earlier, these have a characteristic ring-like arrangement of iron deposits surrounding the nucleus. Their presence is particularly significant in diagnosing certain conditions.
- Non-ring sideroblasts: These have scattered iron deposits without the distinctive ring-like pattern.
Significance
The presence and type of sideroblasts can indicate various underlying conditions:
- Iron overload disorders: Conditions like hemochromatosis can lead to excessive iron in the body, manifesting as sideroblasts in both mature red blood cells (siderocytes) and their precursors.
- Ineffective erythropoiesis: When red blood cell production is disrupted, iron from destroyed cells might not be used properly, accumulating in developing erythroblasts as sideroblasts.
- Congenital sideroblastic anemias: These rare genetic disorders impair iron utilization within erythroblasts, causing sideroblast formation even with normal iron levels.
- Acquired sideroblastic anemias: Certain medications, infections, and other conditions can trigger sideroblast formation.
Diagnosis
Sideroblasts are identified through a bone marrow aspirate stained with a special iron-specific stain, such as Perls’ Prussian Blue stain. The percentage of sideroblasts and their morphology (ring vs. non-ring, size, distribution) are crucial factors in diagnosis.
What are the pathological conditions related to increase iron storages and ringed sideroblasts?
Increased iron storage and ringed sideroblasts can be associated with several pathological conditions, categorized into two main groups.
Primary Iron Overload Disorders
- Hereditary hemochromatosis: This genetic disorder causes excessive iron absorption from the gut, leading to iron overload in various organs. Different gene mutations can cause various forms of hemochromatosis.
- Juvenile hemochromatosis: A rarer, autosomal recessive form characterized by early onset and rapid iron accumulation.
- Neonatal hemochromatosis: This rare and severe form presents in newborns with severe liver damage due to iron overload.
- African iron overload: A complex condition prevalent in parts of Africa, mainly due to dietary factors and genetic susceptibility.
Secondary Iron Overload Conditions
- Ineffective erythropoiesis: When red blood cell production is ineffective, iron from destroyed red blood cells cannot be recycled properly, leading to iron overload. Examples include thalassemias and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
- Multiple blood transfusions: Patients who receive frequent blood transfusions can accumulate excess iron as the body cannot effectively eliminate it.
- Iron overload associated with liver disease: Chronic liver diseases like hepatitis C and alcoholic liver disease can disrupt iron metabolism and lead to iron overload.
Specific conditions characterized by both increased iron storage and ringed sideroblasts
- Refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts (RARS): This subtype of MDS is defined by the presence of ring sideroblasts in the bone marrow and increased iron storage. Different subtypes of RARS exist based on genetic mutations and clinical features.
- Congenital sideroblastic anemia: This rare genetic disorder affects heme synthesis, leading to ring sideroblasts and iron overload.
- Acquired sideroblastic anemia: Certain medications, infections, and other conditions can trigger ring sideroblast formation and iron overload.
What are the different stains available for iron assessment?
Several stains are used to visualize iron deposits in tissue sections, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
| Stain | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Perls’ Prussian Blue Stain | Simple and widely available | Less sensitive than some other stains |
| Turnbull Blue (TB) | More sensitive than PPB | More complex and time-consuming procedure |
| Hemosiderin stain (e.g., Hale) | Stains both hemosiderin and ferritin | Less specific for iron |
| DAB-Iron (immunohistochemistry) | Highly specific for ferritin | Requires specialized equipment and reagents |
| Ferritin immunofluorescence | High sensitivity and specificity | Requires specialized equipment and expertise |
Other factors to consider:
Tissue type: Different stains may be more suitable for specific tissues based on their characteristics and fixation methods.
What are the counter stains that can be used in Perls’ Prussian Blue stain?
Different counterstains offer various advantages and disadvantages, depending on your specific needs.
| Counterstain | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Nuclear Fast Red | Excellent nuclear detail: Stains nuclei bright red, providing clear cellular morphology. Good contrast: Provides strong contrast against the blue iron deposits. Stable: Generally a stable stain. | Can sometimes obscure very fine iron granules if too intense. |
| Safranin O | Good nuclear staining: Stains nuclei and some cytoplasmic components red/orange. Good contrast: Offers good differentiation from blue iron. | May not provide as crisp nuclear detail as Nuclear Fast Red. Can fade over time. |
| Eosin (Aqueous) | Cytoplasmic contrast: Stains cytoplasm pink, providing a general overview of cellular outlines and background. Simplicity: Easy to use. | Poor nuclear detail: Does not stain nuclei well, making cellular identification challenging without a nuclear stain. Less specific: Can stain various tissue components, potentially leading to less clear visualization of cell types. |
| Hematoxylin (e.g., Mayer’s, Harris’) | Strong nuclear staining: Provides excellent detail of nuclei, which are stained blue/purple. Routine compatibility: Often used in routine H&E staining, so familiar to many histologists. | Potential for color clash: Can sometimes blend with the blue iron stain, making differentiation difficult, especially if the hematoxylin staining is too strong. Requires differentiation steps, adding complexity. |
| Neutral Red | Good nuclear staining: Stains nuclei red. Clear background: Generally provides a clear background allowing iron to stand out. | Can be more prone to fading than other nuclear counterstains over time. |
Additional factors to consider
- Tissue type: Choose a counterstain that works well with the specific tissue you are staining.
- Desired level of contrast: Consider the intensity of your iron staining and desired level of background staining when selecting a counterstain.
- Personal preference: Some histologists may prefer certain counterstains based on their experience and visual aesthetic preferences.
What tissue types are best suited for Perls’ Prussian Blue stain?
Here’s an overview of tissue types where Perls’ Prussian Blue stain proves particularly useful.
Excellent Suitability
- Liver: The primary site of iron storage in the body, making it ideal for detecting iron overload conditions like hemochromatosis. Perls’ Prussian Blue stain readily identifies both intracellular and hepatocellular iron.
- Spleen: Another crucial organ for iron storage, especially for recycling iron from senile red blood cells. Perls’ Prussian Blue stain effectively visualizes iron deposits within different spleen compartments.
- Bone marrow: As the site of red blood cell production, bone marrow aspirates stained with Perls’ Prussian Blue stain help assess cellular iron content and diagnose conditions like iron deficiency or ineffective erythropoiesis.
- Kidney: Kidneys can accumulate iron in certain disorders, and Perls’ Prussian Blue stain helps locate and characterize these deposits.
Good Suitability with Optimization
- Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: Certain segments of the GI tract, particularly the duodenum and jejunum, can be suitable for Perls’ Prussian Blue stain to assess iron absorption or potential mucosal iron deposition. However, careful fixation and decalcification may be necessary.
- Heart: Myocardial iron accumulation can occur in some conditions, and Perls’ Prussian Blue stain, combined with other techniques like immunohistochemical analysis, can provide valuable insights.
- Skin: Although not a primary target organ for iron overload, Perls’ Prussian Blue stain can identify dermal iron deposits in specific situations like hemosiderin tattoos.
Limited Suitability
- Central nervous system (CNS): Iron-related pathologies in the brain often involve ferritin, which doesn’t stain well with Perls’ Prussian Blue stain. Immunohistochemical techniques are preferred for visualizing iron in the nervous system.
- Bone: Due to the high mineral content of bone, Perls’ Prussian Blue stain is generally not effective for detecting iron deposits within the bone matrix.
Additional factors to consider
- Tissue fixation: Proper fixation is crucial for optimal Perls’ Prussian Blue stain results. Different fixatives might be needed depending on the specific tissue and desired outcome.
- Cellular context: While helpful for identifying iron deposits, Perls’ Prussian Blue stain doesn’t necessarily distinguish between specific cell types containing iron. Additional markers or techniques might be needed for specific investigations.
- Iron distribution: Perls’ Prussian Blue stain is most effective for visualizing aggregated forms of iron (hemosiderin). Diffusible iron pools may not be readily detected.
How can I differentiate hemosiderin from other blue-staining pigments?
Differentiating hemosiderin from other blue-staining pigments in tissue samples can be challenging, but several methods can be helpful.
Visual clues
- Location: Hemosiderin is typically found within specific cell types and locations depending on the tissue. For example, in liver, it’s mainly in hepatocytes and macrophages, while in spleen, it’s in macrophages and red pulp. Knowing the expected distribution of hemosiderin in your target tissue can be a first clue.
- Color and morphology: While both hemosiderin and other pigments might stain blue with certain techniques, subtle differences in hue, intensity, and distribution can be observed. Hemosiderin often appears as coarse, granular deposits, while other pigments might be more diffuse or have a different shade of blue.
Specific staining techniques
- Turnbull Blue stain: This is a more sensitive iron stain compared Perls’ Prussian Blue stain. While both stain hemosiderin blue, Turnbull Blue doesn’t react with some other pigments that can interfere with Perls’ Prussian Blue stain, potentially offering better specificity.
- Immunohistochemistry: Techniques like ferritin immunohistochemistry specifically target the protein ferritin, a major component of hemosiderin. This provides high specificity for iron, even if the morphology might not be as readily distinguishable as with Perls’ Prussian Blue stain.
- Combined staining: Utilizing both Perls’ Prussian Blue stain and ferritin immunohistochemistry can be powerful, as the combination offers both morphological information and specific protein identification.
Additional techniques
- Spectrophotometry: Analyzing the specific light absorption characteristics of the blue pigment under a microscope can sometimes help differentiate between different compounds.
- Electron microscopy: This advanced technique allows visualizing the ultrastructure of the pigment deposits, revealing characteristic features of hemosiderin like its crystalline nature.
Can Perls’ Prussian Blue stain be used to detect iron in other biological samples besides tissues?
Perls’ Prussian Blue stain primarily serves for detecting iron deposits within tissue sections. While its application to other biological samples like cells and fluids is possible, it has limitations and requires adaptations compared to its standard tissue staining protocol.
- Cell suspensions: Perls’ Prussian Blue stain can be used to detect iron content in isolated cell populations, often following specific preparation steps like cytocentrifugation to concentrate the cells onto a slide. However, interpreting individual cell iron levels can be challenging due to potential variability within the population.
- Cultured cells: Perls’ Prussian Blue stain can be applied directly to cultured cells fixed on coverslips or culture plates. However, specific fixation protocols and optimization might be needed depending on the cell type and culture conditions.
- Blood smears: Perls’ Prussian Blue stain can be used on peripheral blood smears to identify siderocytes, red blood cells containing visible iron deposits, indicating potential iron overload. However, it’s not suitable for quantifying total iron content in blood.
- Other body fluids: While technically possible, applying Perls’ Prussian Blue stain directly to fluids like cerebrospinal fluid or synovial fluid is generally not recommended due to low iron content and potential interference from other components.
Limitations and Consideration
- Sensitivity: Perls’ Prussian Blue stain might not be sensitive enough to detect low iron levels in certain cell types or fluids.
- Specificity: Non-specific blue staining from other pigments or background elements can occur, requiring careful interpretation and potentially additional confirmation techniques.
- Preparation: Modifying the standard Perls’ Prussian Blue stain protocol for cells and fluids often requires specific expertise and optimization for reliable results.
Alternatives for non-tissue samples
- Iron quantification assays: Various biochemical assays measure iron levels in cell lysates or fluids, offering quantitative data but not spatial information.
- Ferritin immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence: These techniques specifically target the ferritin protein, a major iron storage component, offering higher specificity than Perls’ stain in some cases.
What are the limitations of using Perls’ Prussian Blue stain for iron quantification?
Perls’ Prussian Blue stain is a valuable tool for visualizing iron deposits in tissues, but it has limitations as a quantitative method.
- Limited Sensitivity: Perls’ Prussian Blue stain primarily detects aggregated iron (hemosiderin) and might not be sensitive enough to identify smaller, more diffuse iron pools within cells. This can lead to underestimation of total iron content, especially in samples with low hemosiderin levels.
- Non-specificity: While staining iron blue, Perls’ Prussian Blue stain can also react with other blue-staining pigments or background elements within tissues, potentially leading to misinterpretation. Additional techniques like Turnbull Blue stain or immunohistochemistry for ferritin might be needed for confirmation.
- Variability in color intensity: The intensity of the blue stain can vary depending on the amount of iron present, but also other factors like tissue fixation, staining duration, and observer subjectivity.
- Lack of standardized calibration: Unlike assays with specific calibration standards, Perls’ Prussian Blue stain doesn’t have a readily available and universally accepted standard for quantifying iron based on stain intensity.
- Qualitative rather than quantitative: Perls’ Prussian Blue stain primarily provides qualitative information about the presence and location of iron deposits, but not accurate numerical values for iron concentration.
- Alternatives for iron quantification:
- Biochemical assays: Techniques like atomic absorption spectroscopy or colorimetric assays offer quantitative measurements of iron concentration in tissue homogenates or lysates.
- Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS): This highly sensitive technique provides accurate iron quantification in various biological samples.
- Ferritin immunohistochemistry: While not directly measuring iron, this technique quantifies ferritin, a major iron storage protein, offering an indirect but more specific indicator of iron content than Perls’ stain.
How can I properly dispose of waste generated from the staining procedure?
The proper disposal of waste generated from Perls’ Prussian Blue (PPB) staining procedures depends on various factors, including your location, specific reagents used, and local regulations. Here’s a general guide, but always consult your institution’s safety protocols and waste disposal guidelines for the most accurate and compliant approach:
1. Identify the hazardous components
- Potassium ferrocyanide: This is the main hazardous component in the Perls’ Prussian Blue stain, classified as harmful and an environmental irritant. It’s crucial to handle and dispose of it with appropriate caution.
- Hydrochloric acid: Depending on the concentration used, it can be corrosive and require specific handling procedures.
- Other reagents: Review the safety data sheets (SDS) of any additional reagents used in your staining protocol to identify potential hazards and disposal requirements.
2. Segregate and label waste
Separate solid waste (slides, filters, contaminated paper) from liquid waste (used staining solutions). Clearly label both solid and liquid waste containers with the contents, date, and potential hazards (e.g., “Perls’ Prussian Blue waste, contains potassium ferrocyanide”).
3. Follow local regulations
Most institutions have established protocols for hazardous waste disposal. Contact your environmental health and safety department (EH&S) to understand the specific procedures and authorized waste disposal companies in your area.
Never dispose of hazardous waste down the drain or with regular trash.
4. Consider neutralization options (if applicable)
Depending on your local regulations and the specific composition of your waste, certain neutralization procedures might be possible before disposal. However, always consult with EH&S before attempting any neutralization to ensure it’s safe and compliant.
Disclaimer: This protocol is intended for informational purposes only and may need to be modified depending on the specific laboratory procedures and patient circumstances. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for guidance. See additional information.
References
- Bain BJ. A Practical Guide. 6th Edition (Wiley). 2022.
- Bain BJ, Bates I, Laffan MA. Dacie and Lewis Practical Haematology: Expert Consult: Online and Print 12th Edition (Elsevier). 2016.
- Carr JH. Clinical Hematology Atlas 6th Edition (Elsevier). 2021.
- Lours C, Cottin L, Wiber M, Andrieu V, Baccini V, Baseggio L, Brouzes C, Chatelain B, Daliphard S, Fenneteau O, Geneviève F, Girard S, Leymarie V, Maloum K, Rieu JB, Sebahoun G, Sudaka I, Troussard X, Wagner-Ballon O, Wuilleme S, Bardet V, Lesesve JF. Perls’ Stain Guidelines from the French-Speaking Cellular Hematology Group (GFHC). Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jul 12;12(7):1698. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12071698. PMID: 35885602; PMCID: PMC9318570.