Introduction
Leishman stain is a versatile tool used in microscopy for a variety of applications, primarily in the fields of hematology and tropical medicine. It’s primary use is to visualize and identify different types of blood cells in the peripheral blood smear based on their nuclear morphology, cytoplasmic content and presence of granules. Malaria parasites like Plasmodium and other blood-borne pathogens like Babesia show characteristic features under Leishman stain using a thick peripheral blood smear, facilitating their identification and diagnosis.
However, the power of the Leishman stain for peripheral blood smear extends beyond routine investigations. Its ability to differentiate subtle variations in cellular morphology and staining patterns makes it invaluable in diagnosing various hematological disorders. The presence of immature cells, abnormal nuclear shapes, or unusual cytoplasmic inclusions can be indicative of conditions like leukemia, lymphoma, or anemia.
Principle of Leishman Stain
Romanowsky stains which include Leishman and Wright are commonly used to stain the peripheral blood smear. Chemical components of the Leishman dye are Azure B (blue in colour) and Eosin Y (orange) to stain different groups of molecules in the cells.
The DNA and acidic groupings of the proteins of cell nuclei and primitive cytoplasm determine the uptake of the basic dye Azure B. Conversely, the presence of the basic groupings on the hemoglobin molecules results in its affinity for acidic dye like Eosin Y.
Flood Slide Method
Materials for Flood Slide Method
- Leishman stain
- Phosphate buffer 0.66 M pH 6.8
- Solution A: KH2PO4 9.1 g/L
- Solution B: Na2HPO4 9.5 g/L
- Pasteur pipette
- Kim wipes
- Hair dryer
- Unstained peripheral blood smear slide
- Timer
- Cover slips (optional)
- Mounting medium (optional)
Protocol for Flood Slide Method
- Preparation of phosphate buffer for 100 mL volume: Add 50.8 mL of solution A to 49.2 mL of solution B to obtain pH 6.8.
- Cover the peripheral blood smear slide completely with the Leishman stain using a Pasteur pipette and wait for 2-3 minutes. Approximately 3 mL of stain is required to stain a single peripheral blood smear slide.
- Add an equal volume of phosphate buffer onto the slide (stain:buffer ratio = 1:1). Use a Pasteur pipette to blow gently over the peripheral blood smear slide to completely mix the stain and buffer. DO NOT touch the stain using the Pasteur pipette.
- Leave the peripheral blood smear slide to stain for 15-20 minutes.
- Remove the stain with slow running tap water. Wipe the back portion of the peripheral blood smear slide and the edges dry using Kim wipes without touching the peripheral blood smear.
- Dry the peripheral blood smear slide with a hair dryer on low speed.
- Mount the peripheral blood smear slide with Depex and cover the zone of morphology with a cover slip.
- This peripheral blood smear slide is now ready for viewing.
Dip Slide Method with Coplin Jars
Materials for Dip Slide Method
- Leishman stain
- Phosphate buffer 0.66 M pH 6.8
- Unstained peripheral blood smear slide
- 4 Coplin jars
- Deionized water
- Methanol (optional, for air-drying slides faster)
- Forceps
- Timer
- Cover slips (optional)
- Mounting medium (optional)
Protocol for Dip Slide Method
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for diluting the Leishman stain concentrate with the appropriate buffer solution. Mix well and let stand for 10 minutes before use.
- Pour enough methanol, Leishman stain solution, stain-buffer or phosphate buffer solution (according to manufacturer’s protocol) and deionized water into each Coplin jar, respectively to completely submerge the peripheral blood smear slides.
- Place peripheral blood smear slides in methanol (fixative) for 30 seconds.
- Using forceps, carefully dip each peripheral blood smear slide into the Coplin jar containing the stain solution for 3 minutes. Ensure the entire sample area is submerged.
- Remove the peripheral blood smear slides from the stain solution and dip them into the buffer solution Coplin jar for 6 minutes.
- Transfer the peripheral blood smear slides to a Coplin jar filled with deionized water. Rinse gently for 10-15 seconds.
- Differentiate in methanol (optional): Briefly dip the peripheral blood smear slides in methanol for 1-2 seconds (avoid overexposure, as this can lead to excessive destaining). This step helps to enhance the color contrast.
- Allow the peripheral blood smear slides to air dry completely at room temperature.
- Place a drop of mounting medium like Depex on each peripheral blood smear slide and cover with a clean cover slip. Avoid trapping air bubbles. Allow the mounting medium to dry completely before microscopic examination.
Interpretation
Leishman Stain in Hematology
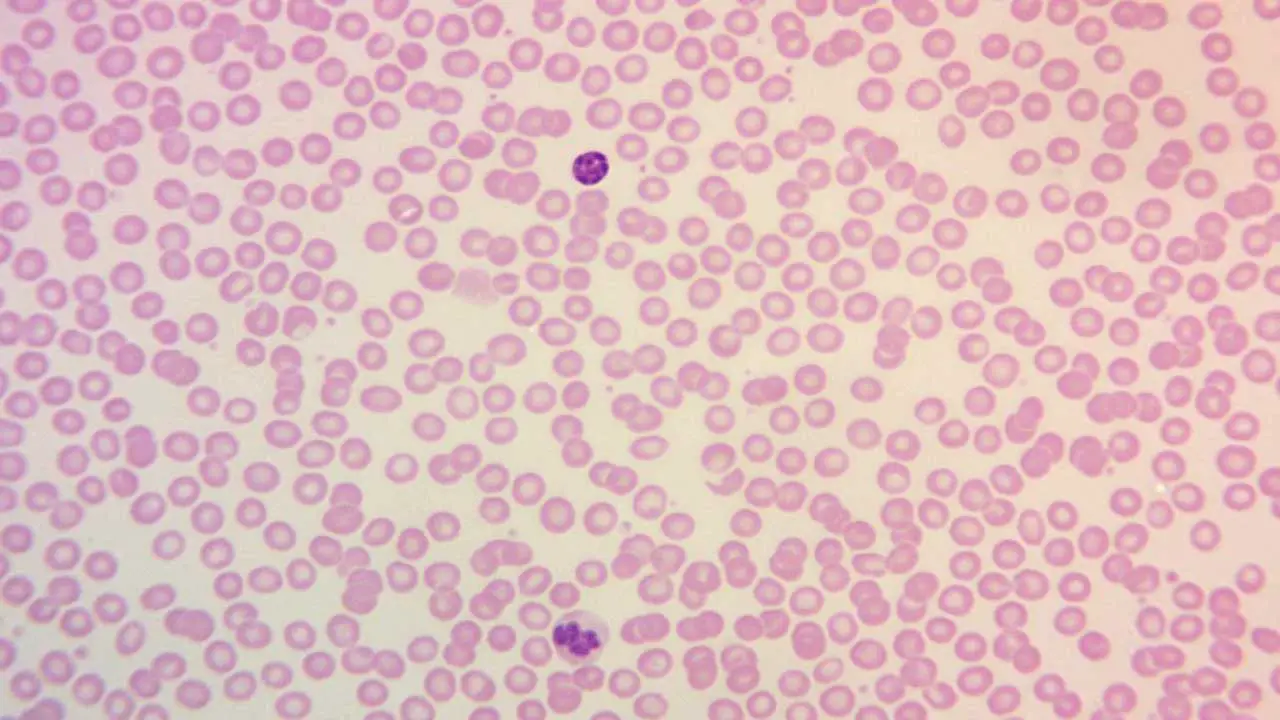
Table 1: Comprehensive Staining Characteristics of Blood Cells with Leishman Stain
| Cell Type | Nucleus Staining (Color, Characteristics) | Cytoplasm Staining (Color, Characteristics) | Granule Staining (Color, Presence / Specificity) | Key Morphological Features |
| Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) | N/A (Anucleated) | Yellowish red to pink | N/A | Biconcave disc, uniform size (anisocytosis / poikilocytosis indicate abnormality) |
| Neutrophils | Dark purple to deep blue-violet, lobed / segmented | Pale pink | Fine mauve/reddish violet | Band and segmented forms, often 2-5 lobes |
| Eosinophils | Blue, typically bilobed | Blue | Large, prominent red to orange | Coarse, uniform, bright red-orange granules |
| Basophils | Purple to dark blue, often obscured by granules | N/A (obscured) | Large, prominent dark purple to black | Coarse, dark, often irregular granules |
| Monocytes | Deep blue-violet, kidney-shaped / indented / lobed | Grey-blue, often vacuolated | Fine azurophilic (rarely prominent) | Large cells, abundant cytoplasm, vacuoles |
| Lymphocytes | Deep, dark blue to blue-violet, round / oval | Light blue, scant to moderate | N/A (usually agranular) | Small to large size, clear cytoplasm |
| Platelets | N/A (Fragments) | N/A | Violet granules | Small, irregular, granular fragments |
| Malarial Parasites | Red (chromatin) | Blue (cytoplasm) | N/A | Ring forms, trophozoites, schizonts, gametocytes within RBCs |
| Trypanosomes | Red (chromatin) | N/A | N/A | Spindle-shaped, active wiggling movement, flagellum, kinetoplast |
| Myeloblasts (Leukemia) | Fine nuclear chromatin, 1+ prominent nucleoli | Varying amounts, azurophilic granules (may be present) | Azurophilic granules | Auer rods, Phi bodies, cup-like nucleus |
| Lymphoblasts (Leukemia) | Moderately condensed to dispersed chromatin, inconspicuous/prominent nucleoli | Scant to moderately abundant, variable basophilia & vacuolation | N/A | Hand-mirror morphology, nuclear cleavage |
| Monoblasts (Leukemia) | Less irregular contour than promonocytes | More basophilic, may contain fine azurophilic granules, rarely vacuoles | Fine azurophilic (may be present) | Prominent cytoplasmic vacuoles, pseudo-Chediak-Higashi granules |
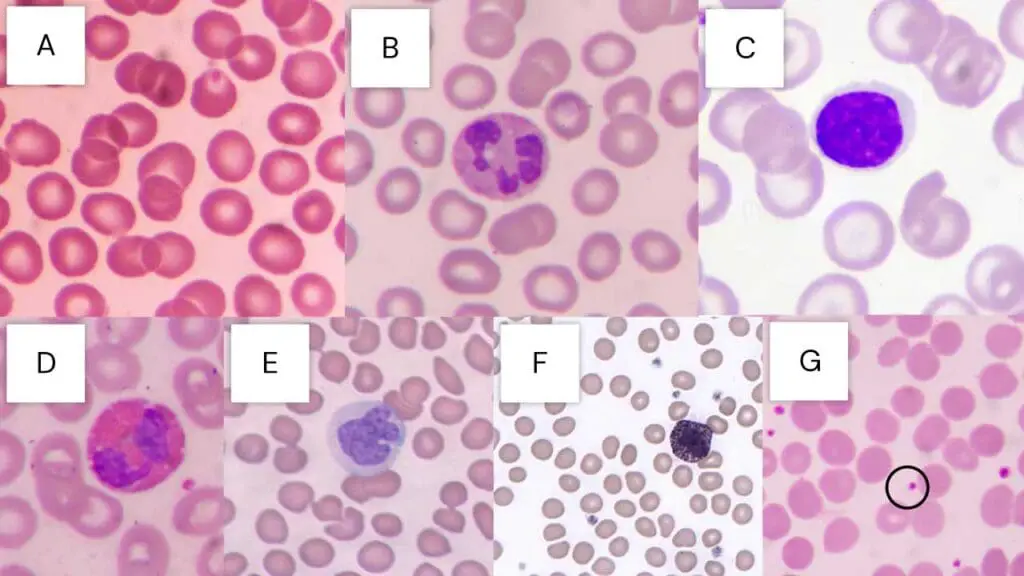
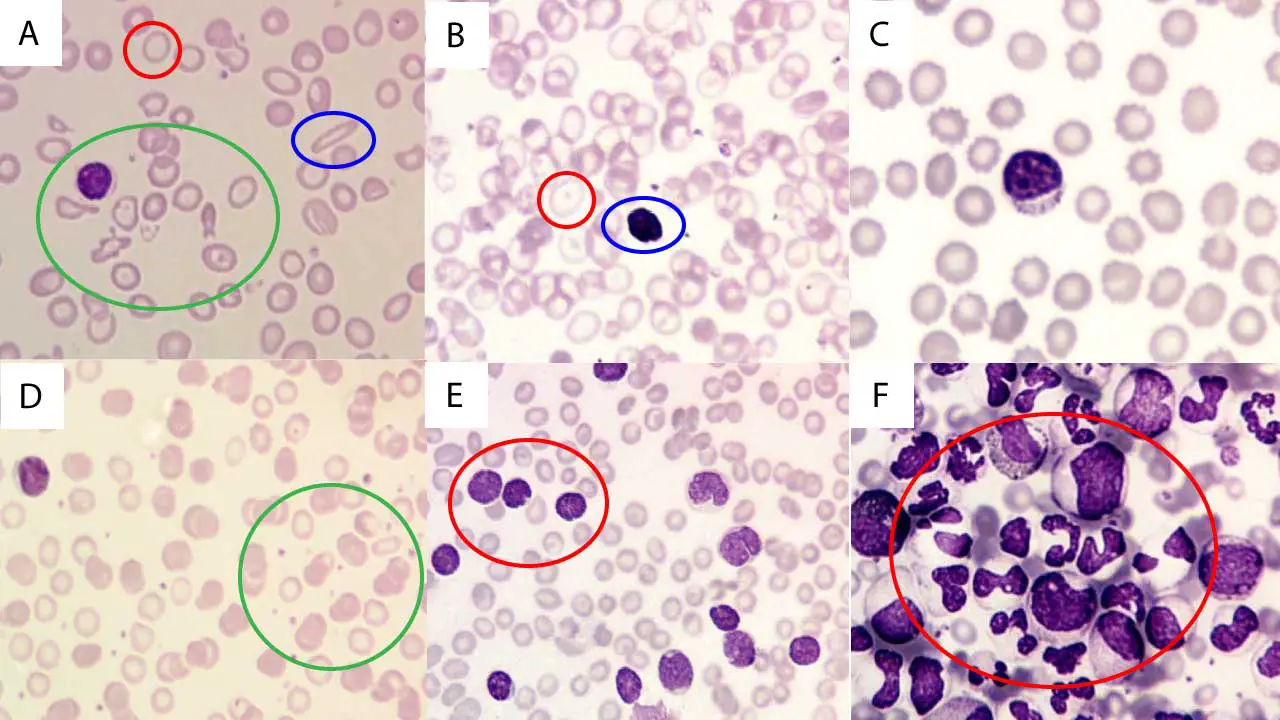
Leishman Stain in Parasitology
Leishman stain is a vital tool in the diagnosis of various parasitic infections, particularly those affecting blood.
- Malaria: Leishman stain is routinely used for diagnosing malaria by enabling the visualization of parasites within infected red blood cells. Research indicates its sensitivity for malaria parasite detection is comparable to fluorescent stains and superior to Field’s stain. While Giemsa staining is also commonly employed, Leishman stain offers distinct advantages in visualizing the nuclear chromatin pattern of host cells and provides better color contrast between the parasite cytoplasm and the red cell cytoplasm, especially in thin blood smears. Malarial parasites typically stain with red chromatin and blue cytoplasm using Leishman stain.
- Leishmaniasis: The diagnosis of leishmaniasis relies on the microscopic identification of nonmotile, intracellular amastigotes in stained tissue sections or smears. These amastigotes are typically spherical to ovoid, measuring 1-5 µm long by 1-2 µm wide, and possess a large nucleus and a prominent kinetoplast. While Giemsa and Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stains are often mentioned for their visualization , Leishman stain’s general utility for visualizing parasites within infected cells is also recognized.
- Trypanosomiasis: Leishman stain is broadly used for the differentiation and identification of trypanosomes. Trypanosomes typically stain with red chromatin when using Leishman stain. Microscopic detection of trypanosomes, specifically the trypomastigote stage, in blood or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is key for diagnosis. These parasites are characterized by their spindle shape (12-42 by 1.5-3.5 µm), active wiggling movements, a flagellum, a central nucleus, and a subterminal kinetoplast, all of which are observable in stained preparations.
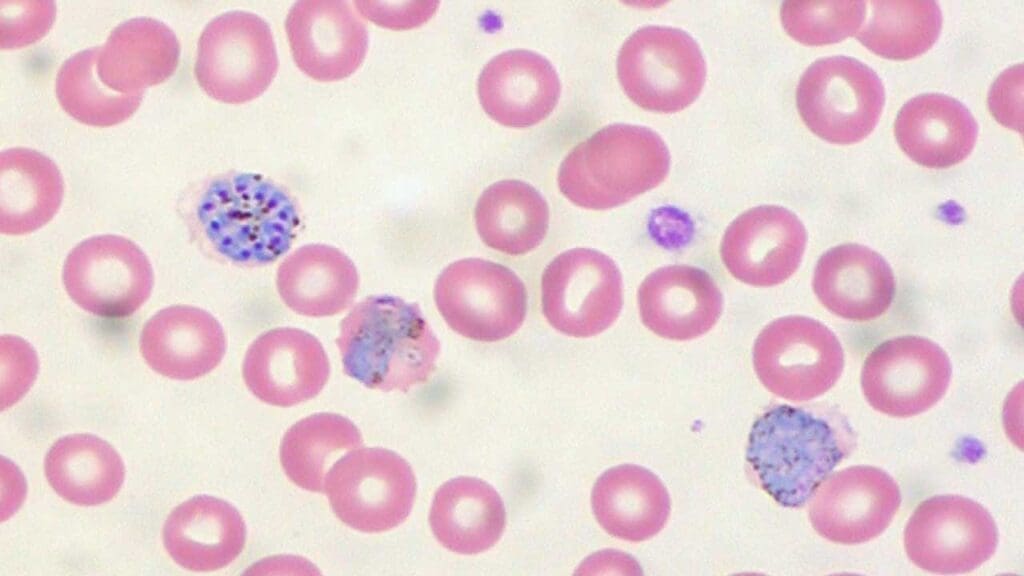
Troubleshooting
Table 2: Leishman Stain Troubleshooting Matrix: Issues, Causes, and Solutions
| Staining Problem | Common Causes | Solutions/Corrective Actions |
| Overall Faulty Stain | Incorrect stain prep, improper technique, dirty slides, poor water quality, expired/contaminated reagents, over-sliding/over-destaining, moisture interference, old reagents, insufficient washing | Use fresh solutions/reagents, maintain replacement schedule. Clean equipment regularly. Ensure clean, grease-free slides. Air-dry smears thoroughly. Avoid pipetting from stock solution. |
| Too Blue (Excessive Basophilia) | Low eosin concentration, bright daylight exposure, overused batch, impure dyes, short staining time, acidic stain solution, thick film, inadequate buffer time, alkaline buffer pH (>7.0), specimen degradation, reduced methanol concentration | Ensure correct Azure B:Eosin Y ratio. Adjust buffer pH to 6.8. Reduce time in stain/buffer mix. Fix fresh smear if degradation. Ensure proper methanol concentration. |
| Too Pink/Grey Cytoplasm (Excessive Eosinophilia/Pale Staining) | Incorrect Azure B:Eosin Y ratio, impure dyes, low buffer pH, excessive washing, acidic pH, reduced staining time, old/overused stain, incorrect stock prep, impure Azure A/C, high ambient temp | Adjust buffer pH (e.g., pH 6.4 for acidophilic results). Increase staining time. Ensure dye purity and concentration. |
| Unstained Neutrophil Granules | Insufficient Azure B | Adjust dye concentration and balance. |
| Pseudo-toxic Granules (Dark Blue/Black) | Excess Azure B | Adjust dye concentration and balance. |
| Precipitates/Stain Deposit | Uncovered stain jar, unfiltered stain, stain/buffer in equipment too long, stain sitting too long/not sealed, shaking bottle before use | Filter stain solution. Dilute stain with 5% methanol then filter. Keep stain covered. Do NOT shake bottle before use. Increase stain concentration in stain/buffer mix (1:10 to 1:5). |
| Blue Background | Inadequate fixation, prolonged storage before fixation, heparin anticoagulant | Ensure immediate and proper fixation. Use EDTA as anticoagulant. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to prepare Leishman stain from powder?
While preparing Leishman stain from powder is possible, it’s generally not recommended due to several reasons:
- Safety Concerns: Handling methanol requires appropriate safety precautions and proper disposal procedures.
- Accuracy and Consistency: Ready-made solutions offer standardized quality and minimize errors in dilution and handling.
- Convenience and Time Saving: Utilizing prepared solutions is quicker and avoids the potential inconsistencies of homemade stains.
However, if you must prepare Leishman stain from powder, follow these steps with caution.
Materials
- Leishman stain powder (e.g., Sigma-Aldrich 67690)
- Methanol
- Deionized water
- Measuring flask
- Magnetic stirrer (optional)
- pH meter (optional)
- Phosphate buffer pH 6.8 (optional)
- Safety glasses, gloves, and fume hood
Procedure
- Consult the safety data sheet (SDS) for methanol and follow all safety precautions.
- Work in a well-ventilated fume hood.
- Weigh 0.12 g of Leishman stain powder using an accurate balance.
- Dissolve the powder in 100 mL of methanol in a measuring flask. Stir or use a magnetic stirrer until completely dissolved.
- Leave the solution to stand for 5 days at room temperature, allowing for complete dye extraction.
- Filter the solution through a Whatman No. 1 filter paper.
- Optionally, dilute the filtered solution further based on the manufacturer’s instructions or established protocols. This usually involves diluting with a mixture of deionized water and phosphate buffer (pH 6.8).
- Measure the pH of the final solution and adjust if necessary using small amounts of the buffer.
- Store the prepared stain in a light-protected, airtight container. Label it clearly with the date and concentration.
How does Leishman stain work?
Leishman stain works by utilizing two contrasting dyes to highlight different components of cells in a peripheral blood smear.
1. Eosin (acidic dye): Binds to basic structures like cytoplasm and ribosomes, staining them pink to red but has low affinity for nuclei and acidic structures.
2. Methylene blue (basic dye): Forms a complex with various Azure dyes depending on pH, staining nuclei and nucleoli a deep blue to purple and also stains some cytoplasmic granules like those in neutrophils purple to violet.
The overall staining mechanism involves:
Electrostatic interactions
- Oppositely charged dyes interact with charged groups on cellular components.
- Positively charged methylene blue binds to negatively charged DNA in nuclei and ribosomes in cytoplasm.
- Negatively charged Eosin binds to positively charged proteins and RNA in cytoplasm.
pH-dependent Azure formation
- Methylene blue undergoes partial demethylation in methanol to form various Azure dyes with different staining properties.
- The specific Azure formed depends on the pH of the stain solution, influencing the final staining profile.
Specific dye affinities
- Certain dyes within the stain mixture have specific affinities for specific cell structures based on their chemical composition.
- For example, Azure B preferentially stains nucleic acids, while Eosin Y stains basic proteins.
By combining these mechanisms, Leishman stain differentiates various cell types based on their:
- Nuclear morphology: Size, shape, chromatin pattern
- Cytoplasmic content: Ribosomes, granules, vacuoles
- Presence of parasites: Plasmodium (malaria), Babesia, etc.
Additional factors affecting staining:
- Fixation: Stabilizes cellular structures and affects dye accessibility.
- Staining time and temperature: Influence dye uptake and intensity.
- Differentiation: Controlled removal of excess stain using methanol.
What is the difference between Giemsa and Leishman staining?
Both Giemsa and Leishman stains are commonly used in microscopy for hematological and parasitological examinations, but they have some key differences:
Similarities
- Both are Romanowsky stains, meaning they utilize a combination of eosin and methylene blue dyes to differentiate various cellular components based on their pH affinity.
- Both work effectively on blood smears and tissue sections.
- Both provide good visualization of nuclei, cytoplasm, and cell morphology.
Differences
1. Staining composition
- Leishman stain: Contains eosin and a mixture of Azure dyes formed from methylene blue in methanol.
- Giemsa stain: Contains eosin and pre-formed Azure dyes (Azure A, B, and C) derived from methylene blue.
2. Staining intensity and color
- Leishman stain: Generally produces slightly less intense staining compared to Giemsa. Colors tend to be more blue-toned, with less emphasis on red hues.
- Giemsa stain: Delivers more intense and vibrant colors, with a richer red component in the cytoplasm.
3. Preferred applications
- Leishman stain: Often preferred for:
- Rapid screening: Easier and faster to prepare due to the absence of pre-formed Azure dyes.
- Malaria parasite detection: Provides good visualization of malaria parasites like Plasmodium.
- Giemsa stain: Often preferred for:
- Detailed morphology assessment: Offers richer colors and sharper contrast for better morphological evaluation of cells.
- Bone marrow examination: More effective in highlighting specific cell types in bone marrow smears.
Table 3: Comparative Utility of Romanowsky Stains (Leishman, Giemsa, Wright, Field’s)
| Stain Name | Key Characteristics | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Leishman Stain | Methanolic mixture of polychromed methylene blue & eosin; fixes smear directly; 10-15 min staining | Simplicity, affordability, rapid results, good cell differentiation, good contrast (nucleus, neutrophil granules), good sensitivity for malaria (thin films), better host cell morphology (nuclear chromatin, cytoplasmic contrast) | Less detailed morphology, susceptible to errors, not universal, methanol safety concerns, inconsistent staining (dye oxidation/impurities), potency deterioration (powder) |
| Giemsa Stain | Alcohol-based, pure dyes (Azure B, Eosin Y) with glycerin; 30 min staining | Most commonly used, good for parasite identification (thick films), good for general blood film morphology | Longer staining time, can give bluish tinge to RBCs (less parasite contrast in thin films) |
| Wright Stain | Romanowsky-type dye; often combined with Giemsa | Simpler method than Giemsa; good for blood cell morphology | May not reliably show Plasmodium parasites alone |
| Field’s Stain | Rapid stain | Very rapid results (1 min) for malaria | Primarily for malarial parasites (thin films); less sensitive than Leishman for malaria |
| Leishman-Giemsa (LG) Cocktail | Combination of Leishman & Giemsa; rapid (4 min for modified version) | Good nuclear morphology, fine nuclear & cytoplasmic contrast, good cytoplasmic granule staining, good metachromatic background, cheaper & faster than MGG, comparable to Pap for oral cancer diagnosis | Requires careful preparation/optimization |
Why alcohol is used in Leishman stain?
Alcohol plays a crucial role in Leishman stain for several reasons.
1. Dissolving the stain components
- The main dye component of Leishman stain, methylene blue, is insoluble in water but readily dissolves in alcohol. This allows for preparation of a concentrated stock solution.
- Eosin, the other major dye, while slightly soluble in water, also benefits from alcohol’s dissolving power to ensure complete dissolution and prevent precipitation.
2. Promoting dye penetration
- Alcohol acts as a fixative, helping to stabilize cellular structures and improve dye penetration. This ensures the stain can reach and interact with cellular components effectively.
- It also slightly dehydrates the cells, making them more receptive to dye uptake.
3. Controlling staining intensity and differentiation
- A brief dip in alcohol (methanol) is used as a controlled destaining step during the Leishman staining procedure. This removes excess stain, particularly from the cytoplasm, while preserving staining in nuclei and granules. This helps achieve optimal balance between color intensity and clarity for accurate interpretation.
4. Other benefits
- Alcohol helps to prevent bacterial growth in the stain solution, contributing to its shelf life.
- It aids in evaporating water after rinsing steps, facilitating faster slide drying.
It’s important to note that:
- The specific type of alcohol used in Leishman stain is typically methanol. However, in certain protocols, ethanol might be used as an alternative.
- Excessive exposure to alcohol during the staining process can lead to over-destaining, negatively impacting staining quality and information content.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Leishman stain?
Advantages of Leishman Stain
- Simple and affordable: Easy to prepare and readily available compared to other staining techniques.
- Rapid and efficient: Offers quick results within minutes, ideal for rapid screening and diagnosis.
- Good differentiation: Effectively distinguishes between various white blood cell types based on nuclear morphology, cytoplasmic content, and presence of granules.
- Easy to interpret: Clear color differentiation facilitates easier analysis and identification of blood cells and parasites.
- Highlights parasites: Useful for detecting malaria parasites (Plasmodium) and other blood-borne pathogens.
- Relatively stable: Can be stored for long periods with proper care.
Disadvantages of Leishman Stain
- Less detailed morphology: Compared to Giemsa stain, Leishman stain provides less intense and vibrant colors, limiting detailed morphological evaluation.
- Susceptible to technical errors: Sensitive to factors like staining time, temperature, and methanol exposure, which can affect results.
- Not universal: Primarily used for blood and bone marrow smears, not as versatile as some other stains.
- Requires training and experience: Accurate interpretation relies on proper training and experience to differentiate cell types correctly.
- Safety concerns: Methanol is flammable and requires proper handling and disposal procedures.
Can Leishman stain be used for other cell types besides blood cells?
While Leishman stain is primarily used for blood and bone marrow smears, it can be applied to other cell types in certain situations.
- Tissue sections: Leishman stain can be used for basic visualization of nuclei and cytoplasm in tissue sections for initial screening or rough assessment. However, specific stains are often preferred for detailed analysis of different tissue types due to their tailored color profiles and highlighting capabilities.
- Cultured cells: Leishman stain might be used for quick assessment of cultured cells, but dedicated stains are usually chosen for detailed morphological evaluation or specific markers.
- Parasites: While effective for blood-borne parasites like Plasmodium, Leishman stain might not be ideal for all parasite types due to potential differences in staining affinity.
How do you dispose of Leishman stain waste?
Disposing of Leishman stain waste requires careful handling due to the presence of hazardous materials.
Main components to consider:
- Methanol: Flammable, toxic if ingested or inhaled.
- Heavy metals: Depending on the specific stain formulation, trace amounts of heavy metals like copper sulfate might be present.
Safe disposal practices:
- Neutralize liquid waste: Before disposal, neutralize the methanol content by adding a buffer solution with a pH of 8-10. This reduces the flammability and toxicity of the waste.
- Use appropriate containers: Collect neutralized waste in leak-proof, labeled containers specifically designed for hazardous waste disposal. Double-bagging is recommended for added security.
- Follow institutional guidelines: Most institutions have established protocols and designated waste disposal procedures for hazardous materials. Familiarize yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and follow them strictly.
Additional precautions:
- Wear gloves and eye protection when handling waste materials.
- Work in a well-ventilated area and avoid open flames or sparks.
- Never dispose of Leishman stain waste down the drain or in regular trash.
- Never evaporate the stain solution, as this concentrates the hazardous components.
- Maintain proper documentation of waste disposal procedures for compliance and safety records.
Disclaimer: This protocol is intended for informational purposes only and may need to be modified depending on the specific laboratory procedures and patient circumstances. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for guidance. See additional information.
References
- Bain BJ. A Practical Guide. 6th Edition (Wiley). 2022.
- Bain BJ, Bates I, Laffan MA. Dacie and Lewis Practical Haematology: Expert Consult: Online and Print 12th Edition (Elsevier). 2016.
- Carr JH. Clinical Hematology Atlas 6th Edition (Elsevier). 2021.
- Sathpathi, S., Mohanty, A.K., Satpathi, P. et al. Comparing Leishman and Giemsa staining for the assessment of peripheral blood smear preparations in a malaria-endemic region in India. Malar J 13, 512 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-13-512.
- Sareen, R., Kapil, M., & Gupta, G. N. (2018). Incubation and its effect on Leishman stain. Journal of laboratory physicians, 10(3), 357–361. https://doi.org/10.4103/JLP.JLP_154_17