Introduction
Acute leukemia, a devastating form of blood cancer, arises from the uncontrolled growth and proliferation of immature blood cells, known as blasts. These abnormal cells crowd out the healthy blood cells, disrupting the body’s ability to produce oxygen-rich red blood cells, clot-forming platelets, and infection-fighting white blood cells. This disruption leads to a cascade of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, bleeding, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Acute leukemia is classified into two main types: acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). AML, accounting for about 80% of acute leukemia cases, affects primarily adults, while ALL is more prevalent among children and adolescents. The distinction between AML and ALL lies in the type of immature blood cell involved. AML originates from myeloid cells, the precursors of red blood cells, platelets, and some white blood cells, while ALL stems from lymphoid cells, the precursors of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell.
The rapid progression of acute leukemia sets it apart from chronic leukemias, which typically progress slowly over years. In acute leukemia, the abnormal blasts accumulate rapidly in the bone marrow, the blood cell factory, and spill over into the bloodstream. This rapid growth and spread lead to the acute presentation of symptoms and the urgent need for treatment.
Sign and Symptoms
Acute leukemia manifests with a constellation of symptoms that reflect the disruption of normal blood cell production and the infiltration of abnormal blasts into various organs. The severity and presentation of these acute leukemia symptoms can vary depending on the type of acute leukemia, whether acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), and the stage of the disease.
General Acute Leukemia Symptoms
Fatigue, a hallmark acute leukemia symptom, stems from the depletion of oxygen-carrying red blood cells, leaving the body deprived of essential energy. This persistent tiredness, often accompanied by weakness, can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
Bleeding abnormalities, another common manifestation of acute leukemia, arise from the disruption of platelet production. These abnormalities can range from easy bruising to excessive bleeding from the gums, nose, or other sites. Such bleeding events can lead to anemia, further exacerbating fatigue and weakness.
Increased susceptibility to infections, a consequence of the impaired immune system, is a prevalent concern in acute leukemia. The rapidly proliferating leukemia cells suppress the production of healthy white blood cells, leaving the body vulnerable to infections. These infections can manifest as recurrent fevers, sore throat, or other signs of illness.
AML-Specific Symptoms
AML, characterized by the uncontrolled growth of myeloid blasts, often presents with acute leukemia symptoms specific to the myeloid lineage. Easy bruising and bleeding, a consequence of the reduced platelet count (thrombocytopenia), are common AML symptoms. Bone pain, a result of the infiltration of blasts into the bone marrow, can be a significant source of discomfort for AML patients.
ALL-Specific Symptoms
ALL, characterized by the proliferation of lymphocytic blasts, often displays acute leukemia symptoms related to the lymphatic system. Swollen lymph nodes, a result of the accumulation of blasts in lymph nodes, can be palpable in various regions of the body. Facial swelling, caused by the infiltration of blasts into lymph nodes around the face, may present in T-ALL patients. While, involvement of the central nervous system (CNS) and organomegaly may be present in B-ALL patients.
Stage-Dependent Symptom
The stage of acute leukemia significantly influences the severity and presentation of acute leukemia symptoms. In the early stages, acute leukemia symptoms may be subtle and often attributed to other conditions. As the disease progresses, symptoms become more pronounced and may include recurrent infections, weight loss, and shortness of breath.
Risk Factors for Acute Leukemia
Acute leukemia, a complex and multi-faceted disease, arises from a confluence of factors that increase an individual’s susceptibility. While the precise causes remain an ongoing area of research, several risk factors have been identified, shedding light on the interplay between genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices in influencing leukemia development.
Genetic Predisposition: A Blueprint for Leukemia Susceptibility
Genetics play a significant role in determining an individual’s predisposition to developing acute leukemia. Certain inherited genetic mutations, present from birth, can disrupt genes involved in regulating blood cell development and repair mechanisms, increasing the risk of uncontrolled cell growth and transformation into leukemic blasts. This risk is particularly notable for individuals with conditions like Down syndrome or Fanconi anemia, which carry inherent genetic aberrations that predispose them to leukemia.
Environmental Factors: Navigating External Influences
Exposure to certain environmental factors can contribute to leukemogenesis by triggering genetic alterations or damaging bone marrow cells, leading to uncontrolled proliferation. Exposure to ionizing radiation, especially high doses from radiation therapy or nuclear accidents, is a known risk factor. Similarly, exposure to certain chemicals like benzene, found in petroleum products and cigarette smoke, can increase leukemia risk.
Lifestyle Choices: A Modifiable Factor
While some risk factors are beyond individual control, certain lifestyle choices can influence the likelihood of developing leukemia. Smoking, a modifiable risk factor, has been linked to an increased risk of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Maintaining a healthy diet and managing body weight may play a role in leukemia prevention, as obesity has been associated with an increased risk of certain subtypes of leukemia.
Age: A Growing Concern
Age is a significant risk factor for both AML and ALL, with prevalence increasing with age. Adults over 65 are at greater risk for AML, while children under 5 and adults over 65 are more susceptible to ALL. The increased risk with age is likely associated with accumulated genetic mutations and a weakened immune system.
Laboratory Investigations for Acute Leukemia
In the realm of acute leukemia, where aberrant blood cells wreak havoc, laboratory investigations serve as invaluable tools for diagnosis, monitoring, and guiding treatment decisions. These investigations provide a comprehensive view into the intricacies of the disease, shedding light on the type, extent, and progression of acute leukemia.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
In acute leukemia, the CBC typically reveals an abnormal increase in immature white blood cells, known as blasts. The number and morphology of these blasts, along with the presence of other abnormalities like anemia or thrombocytopenia, provide clues about the type and severity of the disease.
Peripheral Blood Smear (PBS)
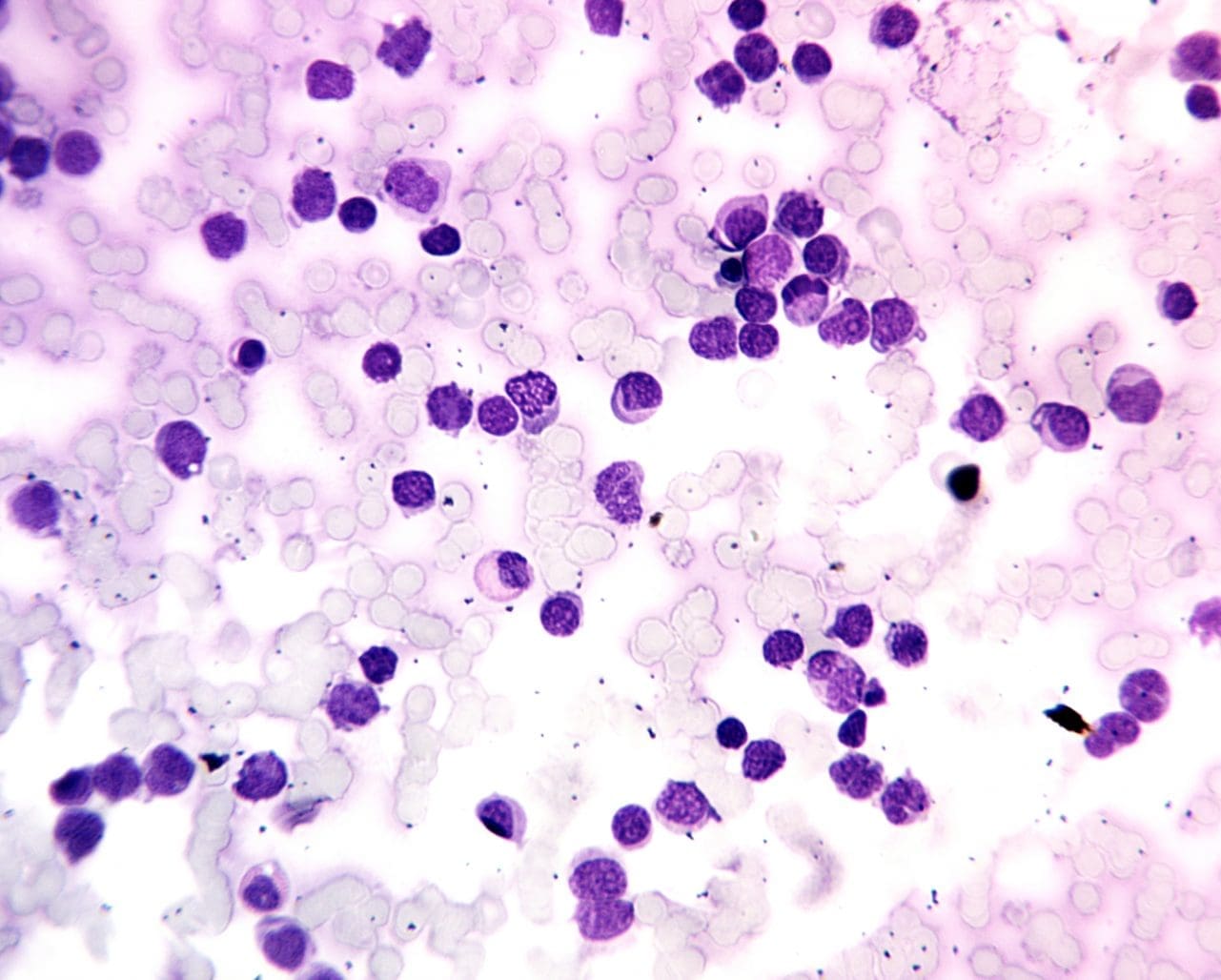
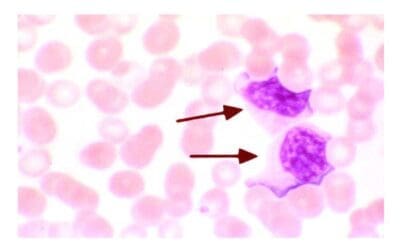
In the absence of acute leukemia, the PBS typically exhibits a balanced representation of mature red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. However, in acute leukemia, the landscape of the PBS is dramatically altered. Leukemic blasts, characterized by their large, irregular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and scant cytoplasm, infiltrate the bloodstream, disrupting the normal cellular equilibrium.
The morphology of leukemic blasts, as observed on the PBS, can provide clues to the subtype of acute leukemia. For instance, lymphoblasts, derived from lymphocytes, typically exhibit round or oval nuclei, while myeloblasts, derived from myeloid cells, often display horseshoe-shaped nuclei.
The percentage of leukemic blasts in the PBS, known as the blast count, is a crucial prognostic factor. A high blast count is associated with a more aggressive form of acute leukemia and may require more intensive treatment.
Beyond blast count and morphology, the PBS can reveal additional abnormalities that may be associated with acute leukemia, such as the presence of Auer rods, cytoplasmic inclusions specific to myeloid leukemia, or the absence of Auer rods in a setting of high blast count, suggesting lymphoblastic leukemia.
The PBS, in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as bone marrow aspiration and biopsy, plays a pivotal role in establishing the diagnosis of acute leukemia, guiding treatment decisions, and monitoring disease progression.
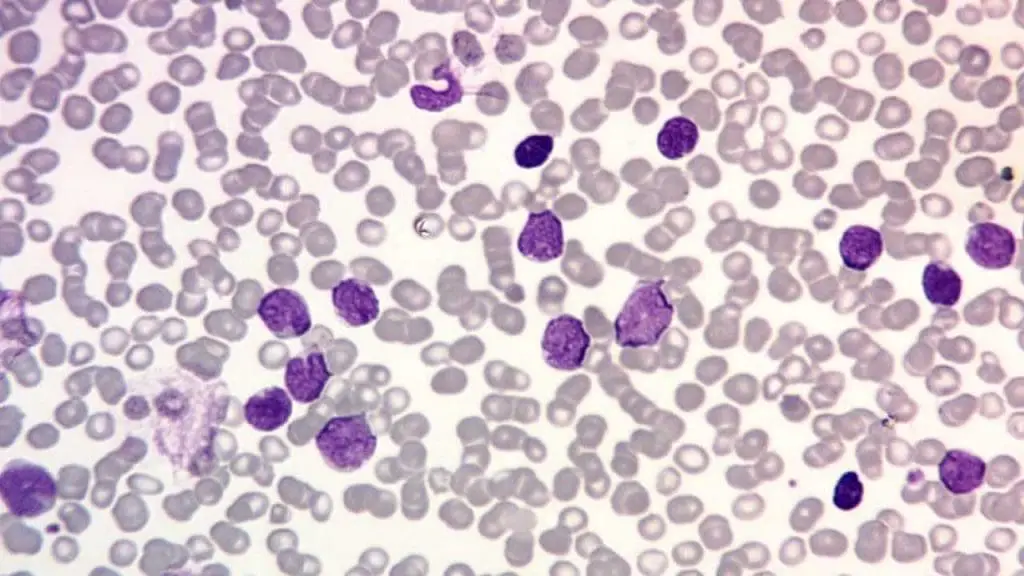
Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy
For a definitive diagnosis of acute leukemia, bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are essential procedures. Bone marrow, the factory of blood cells, harbors the earliest signs of leukemia. Aspiration involves withdrawing a small sample of liquid bone marrow, while biopsy involves removing a tiny piece of bone marrow tissue.
Microscopic examination of these samples allows pathologists to assess the cellular composition of the bone marrow, identifying the presence of blasts and their proportion relative to normal blood cells. The type and morphology of the blasts provide further insights into the leukemia subtype, guiding treatment decisions.
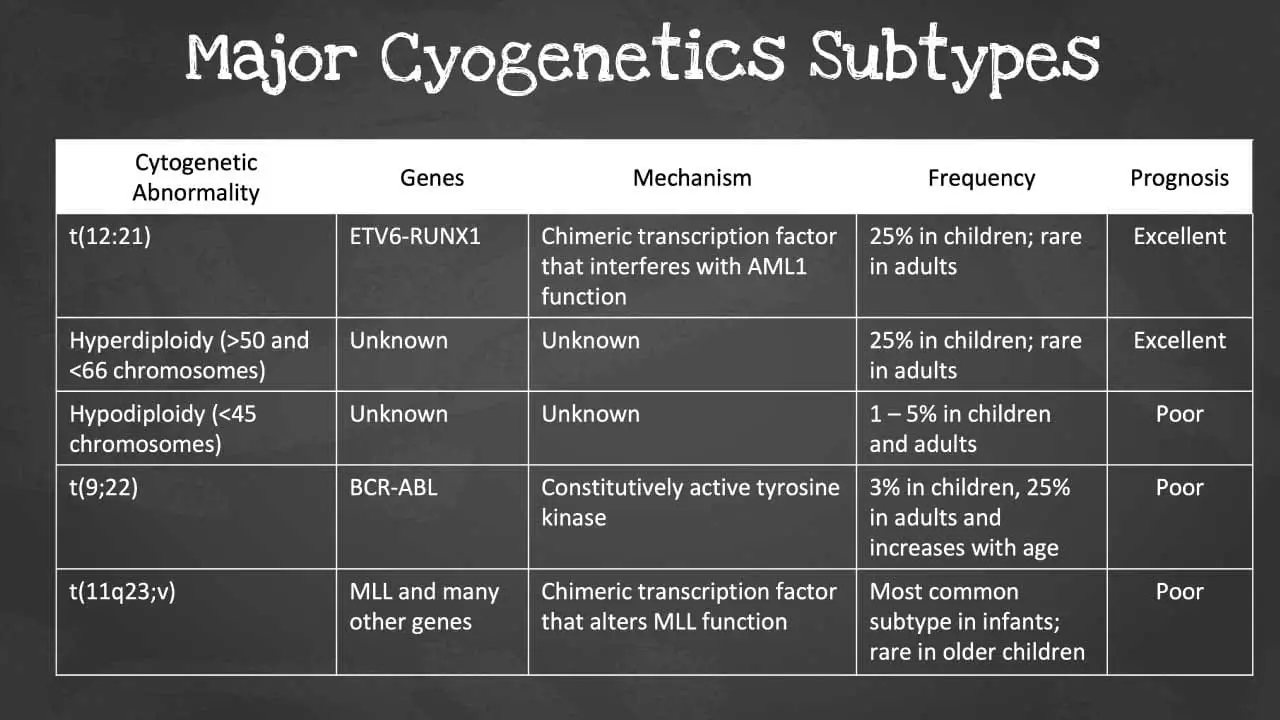
Cytogenetic Analysis
Acute leukemia often arises from genetic abnormalities that disrupt the normal processes of cell growth and differentiation. Cytogenetic analysis, utilizing specialized techniques like karyotyping and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), allows for the detection of these chromosomal aberrations.
Identifying these genetic abnormalities has significant implications for diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment selection. For instance, certain genetic alterations, such as the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph+) in acute myeloid leukemia, are associated with specific treatment approaches and prognostic factors.
Monitoring Disease Progression
Laboratory investigations play a crucial role in monitoring the progression of acute leukemia and the response to treatment. Serial CBCs and bone marrow examinations are regularly performed to assess changes in blast count, peripheral blood cell counts, and the eradication of abnormal blasts.
These serial investigations provide valuable information for evaluating the effectiveness of treatment, identifying potential complications, and guiding treatment adjustments. Monitoring the presence of minimal residual disease (MRD), low levels of undetectable blasts, is crucial for assessing the risk of relapse and guiding long-term follow-up strategies.
Treatment and Management Approach for Acute Leukemia
The overarching goal of acute leukemia treatment is to eradicate the abnormal leukemic cells, restoring normal blood cell production and halting the disease’s progression. This complex endeavor involves a combination of treatment modalities, each with its own unique challenges and potential side effects.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy utilizes cytotoxic drugs to target and destroy rapidly dividing leukemia cells. These drugs, administered intravenously or orally, circulate throughout the body, seeking out and eliminating abnormal cells.
While chemotherapy is effective in eradicating a significant proportion of leukemic cells, it also poses challenges due to its non-discriminatory nature, affecting both healthy and cancerous cells. This can lead to a range of side effects, including fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy beams to directly target and destroy leukemic cells. This therapy is particularly useful for localized leukemia, where blasts have accumulated in specific areas, such as the central nervous system.
Radiation therapy, however, is not without its challenges. Exposure to radiation can damage healthy tissues and cells, leading to side effects like skin irritation, fatigue, and organ dysfunction. Careful planning and administration are crucial to minimize these adverse effects.
Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation, a potentially curative treatment option, involves replacing the patient’s diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a donor. These stem cells have the ability to differentiate into all types of blood cells, restoring normal blood cell production and potentially eradicating the remaining leukemic cells.
Stem cell transplantation is a complex procedure with inherent risks, including the potential for graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), where the donor’s immune system attacks the recipient’s body. Careful patient selection, donor matching, and supportive care are essential to minimize these risks and optimize transplant outcomes.
| AML | ALL |
| Induction (e.g. vincristine, asparginase, dexamethasone ± daunorubicin) ↓ Consolidation (daunorubicin, cytosine arabinoside, vincristine, etoposide, thioguanine or mercaptopurine, cyclophosphoamide) ↓ Cranial prophylaxis ↓ Maintenance therapy (e.g. mercaptopurine, methotrexate, vincristine, dexamethasone) ↓ Late intensification ↓ Maintenance therapy | Induction (daunorubicin, cytosine arabinoside, etoposide) ↓ Consolidation (daunorubicin, cytosine arabinoside, etoposide) ↓ Consolidation (m-AMSA, etoposide, cytosine arabinoside) ↓ Possible stem cell transplantation / further consolidation (mitoxantrone, idarubicin, high dose cytosine arabinoside) |
Supportive Care
Supportive care, a crucial component of acute leukemia management, focuses on alleviating symptoms, managing side effects, and addressing complications arising from the disease and its treatment. This encompasses a range of interventions, including blood transfusions to combat anemia, platelet transfusions to prevent bleeding, and administration of medications to manage infections and pain.
Supportive care also plays a significant role in addressing the psychological and emotional impact of acute leukemia. Providing emotional support, counseling, and psychosocial services can help patients and their families cope with the challenges and uncertainties associated with the disease.
Navigating the Treatment Landscape
The treatment of acute leukemia is a complex and individualized process, tailored to the patient’s age, overall health, leukemia subtype, and genetic abnormalities. The choice of treatment modality or combination of modalities depends on these factors and may involve induction therapy to achieve remission, consolidation therapy to eradicate residual leukemia cells, and maintenance therapy to prevent relapse.
Striving for a Cure: Continuous Advancements
While significant strides have been made in the treatment of acute leukemia, challenges remain in achieving a cure for all patients. Ongoing research continues to explore novel treatment approaches, including targeted therapies that specifically target genetic abnormalities in leukemic cells, immunotherapy that harnesses the body’s immune system to combat cancer, and gene therapy that aims to correct underlying genetic defects.
In conclusion, the treatment and management of acute leukemia require a multifaceted approach, combining chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplantation, and supportive care. While each treatment modality presents its own unique challenges, the goal of eradicating leukemic cells, restoring normal blood cell production, and improving patient outcomes remains at the forefront of research and clinical practice.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and is specifically targeted towards medical students. It is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. While the information presented here is derived from credible medical sources and is believed to be accurate and up-to-date, it is not guaranteed to be complete or error-free. See additional information.
References
- National Cancer Institute (2023). Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treatment (PDQ®) – Health Professional Version. National Institutes of Health.
- Pollyea DA, Altman JK, Assi R, Bixby D, Fathi AT, Foran JM, Gojo I, Hall AC, Jonas BA, Kishtagari A, Lancet J, Maness L, Mangan J, Mannis G, Marcucci G, Mims A, Moriarty K, Mustafa Ali M, Neff J, Nejati R, Olin R, Percival ME, Perl A, Przespolewski A, Rao D, Ravandi F, Shallis R, Shami PJ, Stein E, Stone RM, Sweet K, Thota S, Uy G, Vachhani P, Cassara CJ, Freedman-Cass DA, Stehman K. Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Version 3.2023, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023 May;21(5):503-513. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2023.0025. PMID: 37156478.
- Alaggio R, Amador C, Anagnostopoulos I, Attygalle AD, Araujo IBO, Berti E, Bhagat G, Borges AM, Boyer D, Calaminici M, Chadburn A, Chan JKC, Cheuk W, Chng WJ, Choi JK, Chuang SS, Coupland SE, Czader M, Dave SS, de Jong D, Du MQ, Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Ferry J, Geyer J, Gratzinger D, Guitart J, Gujral S, Harris M, Harrison CJ, Hartmann S, Hochhaus A, Jansen PM, Karube K, Kempf W, Khoury J, Kimura H, Klapper W, Kovach AE, Kumar S, Lazar AJ, Lazzi S, Leoncini L, Leung N, Leventaki V, Li XQ, Lim MS, Liu WP, Louissaint A Jr, Marcogliese A, Medeiros LJ, Michal M, Miranda RN, Mitteldorf C, Montes-Moreno S, Morice W, Nardi V, Naresh KN, Natkunam Y, Ng SB, Oschlies I, Ott G, Parrens M, Pulitzer M, Rajkumar SV, Rawstron AC, Rech K, Rosenwald A, Said J, Sarkozy C, Sayed S, Saygin C, Schuh A, Sewell W, Siebert R, Sohani AR, Tooze R, Traverse-Glehen A, Vega F, Vergier B, Wechalekar AD, Wood B, Xerri L, Xiao W. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022 Jul;36(7):1720-1748. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01620-2. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Erratum in: Leukemia. 2023 Sep;37(9):1944-1951. PMID: 35732829; PMCID: PMC9214472.
- Schlenk RF. Acute myeloid leukemia: introduction to a series highlighting progress and ongoing challenges. Haematologica. 2023 Feb 1;108(2):306-307. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.280803. PMID: 36722401; PMCID: PMC9890027.