
by MH Team | May 23, 2024 | Platelet Disorders
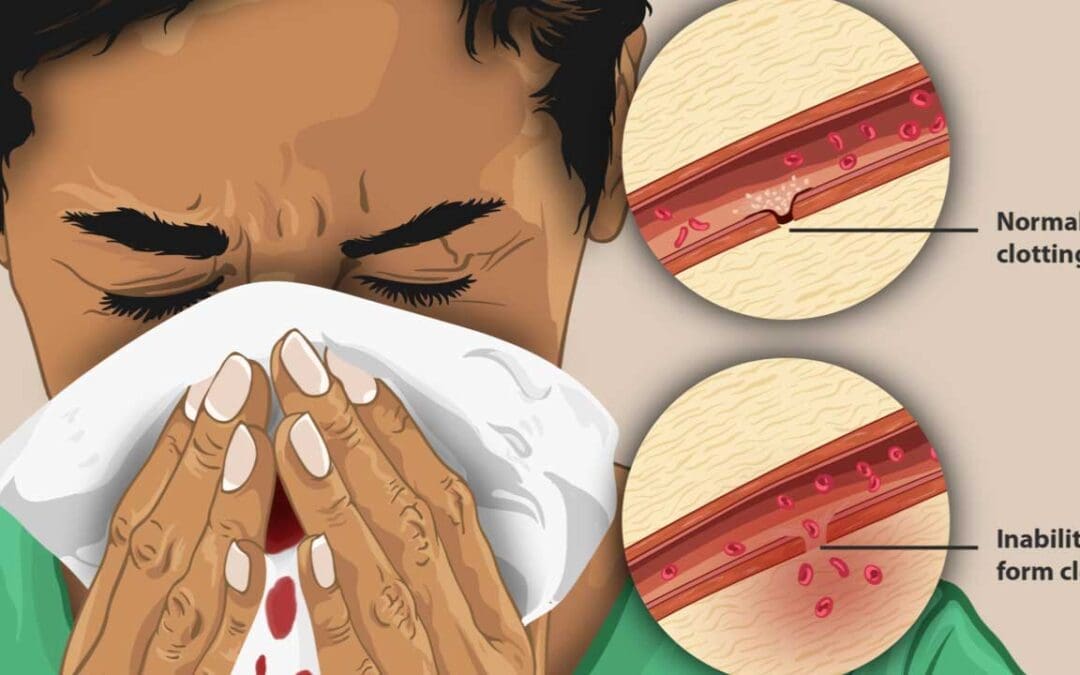
TL;DR Blood coagulation (clotting) disorders affect how blood clots, leading to either excessive bleeding or inappropriate clot formation within blood vessels. Types ▾ Inherited: Caused by genetic mutations affecting clotting factors (e.g., hemophilia A,...

by MH Team | May 19, 2024 | Platelet Disorders
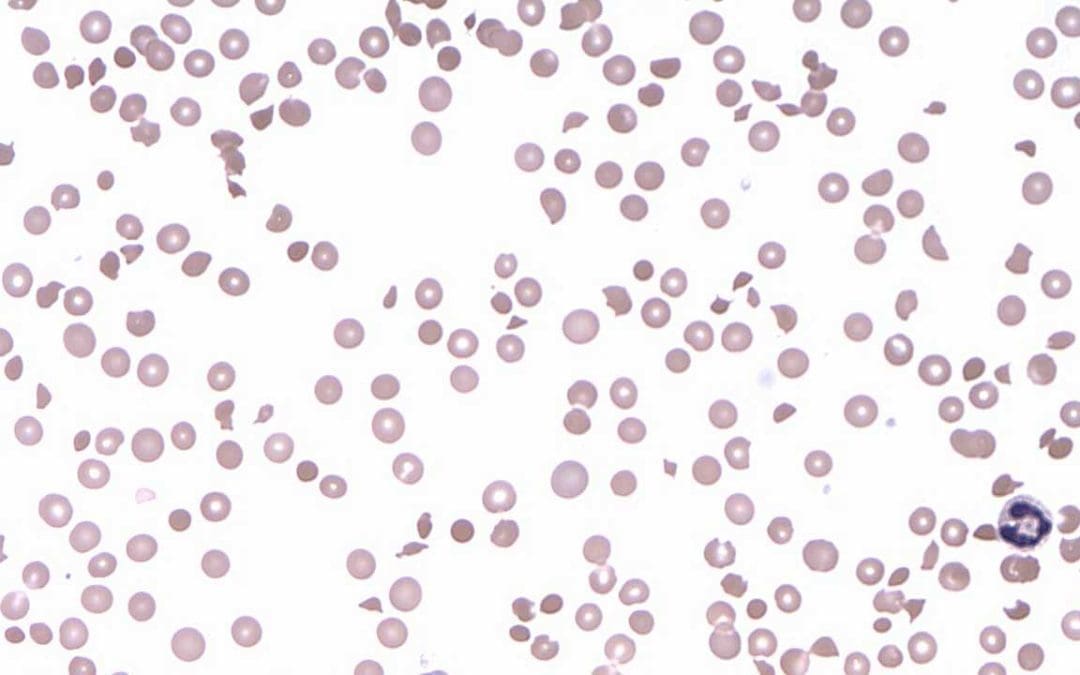
TL;DR Platelet function disorders disrupt the ability of platelets to clump together (aggregate) and form a proper clot. Platelets are blood cells essential for forming clots and stopping bleeding. Causes ▾ Inherited: Caused by genetic mutations affecting...

by MH Team | May 17, 2024 | Platelet Disorders
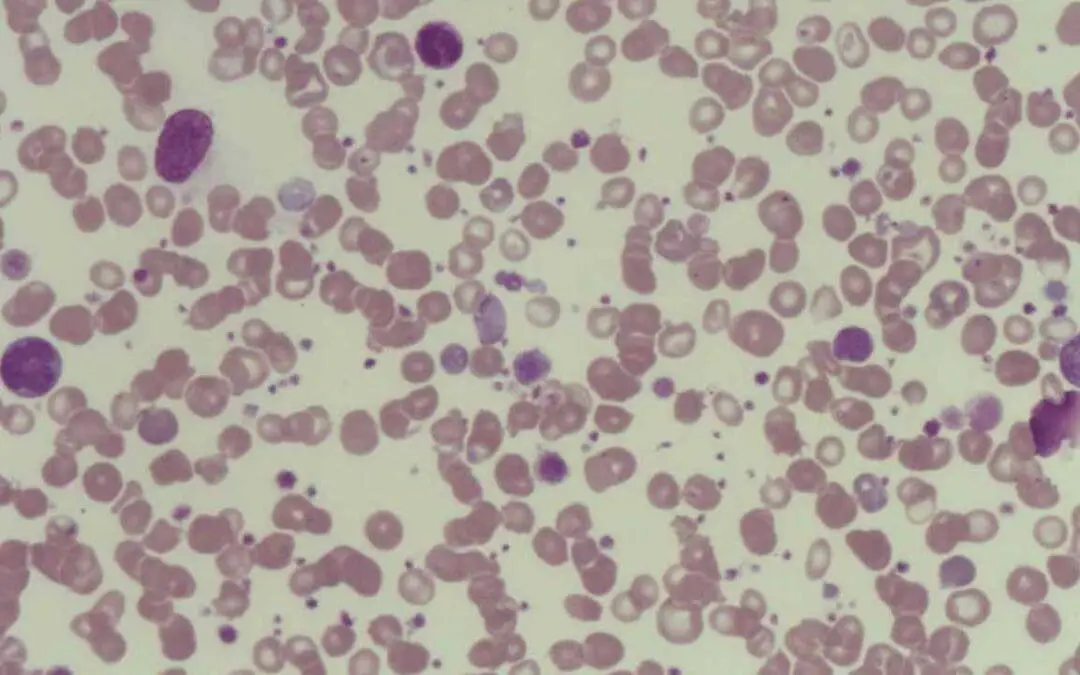
TL;DR Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by an abnormally low platelets in the blood (generally below 150,000 platelets per microliter). Causes ▾ Decreased Platelet Production: Bone marrow disorders, vitamin deficiencies, medications,...

by MH Team | May 15, 2024 | Platelet Disorders
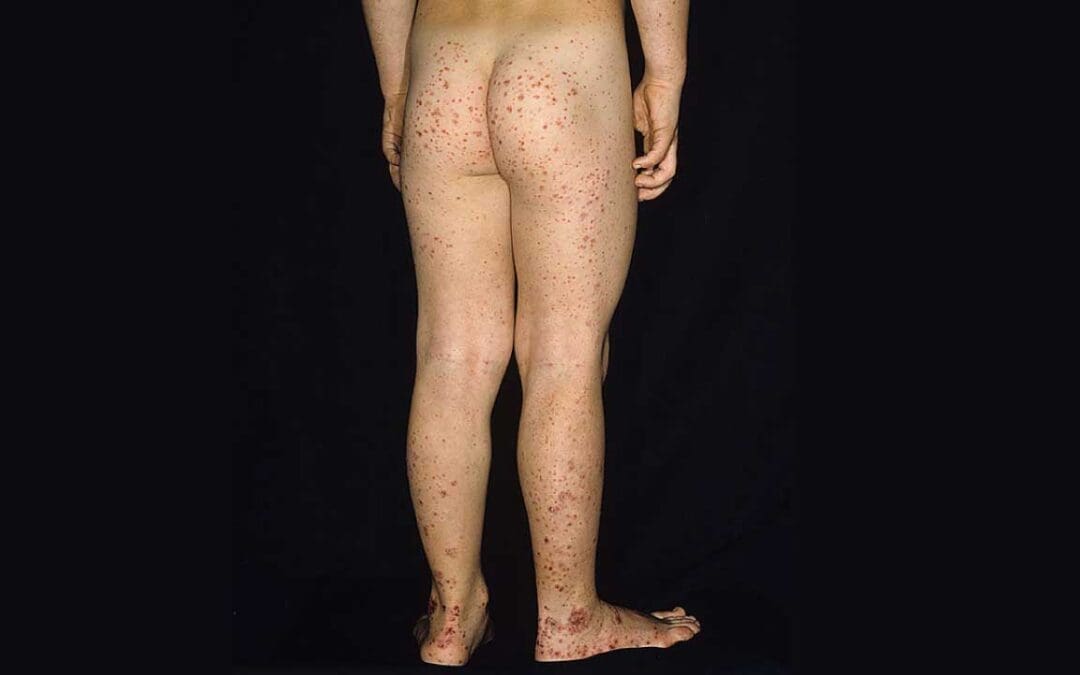
TL;DR Vascular bleeding disorders encompass a diverse range of conditions marked by easy bruising and minor vessel bleeds. Inherited Vascular Disorders ▾ Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia Connective tissue disorders e.g. Ehlers-Danlos syndromes and...

by MH Team | May 13, 2024 | Platelet Disorders
TL;DR Dengue Virus and Transmission ▾ Dengue is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes, particularly Aedes mosquitoes. There are four serotypes of the dengue virus, and infection with one serotype provides only temporary immunity to that specific type. Clinical...


Recent Comments