
by MH Team | Aug 10, 2025 | White Blood Cells
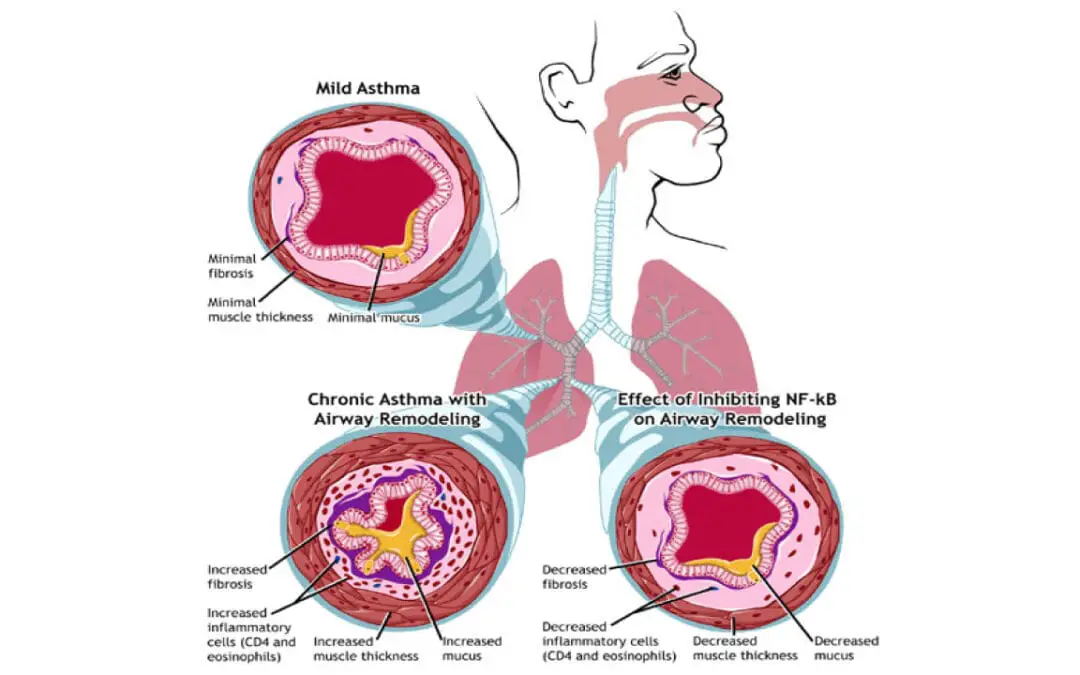
TL;DR Eosinophilic asthma is a severe, late-onset type of asthma characterized by a high number of eosinophils, which drives chronic airway inflammation that is often resistant to standard treatments and responds best to targeted biologic therapies. Symptoms and Signs...

by MH Team | Aug 2, 2025 | White Blood Cells
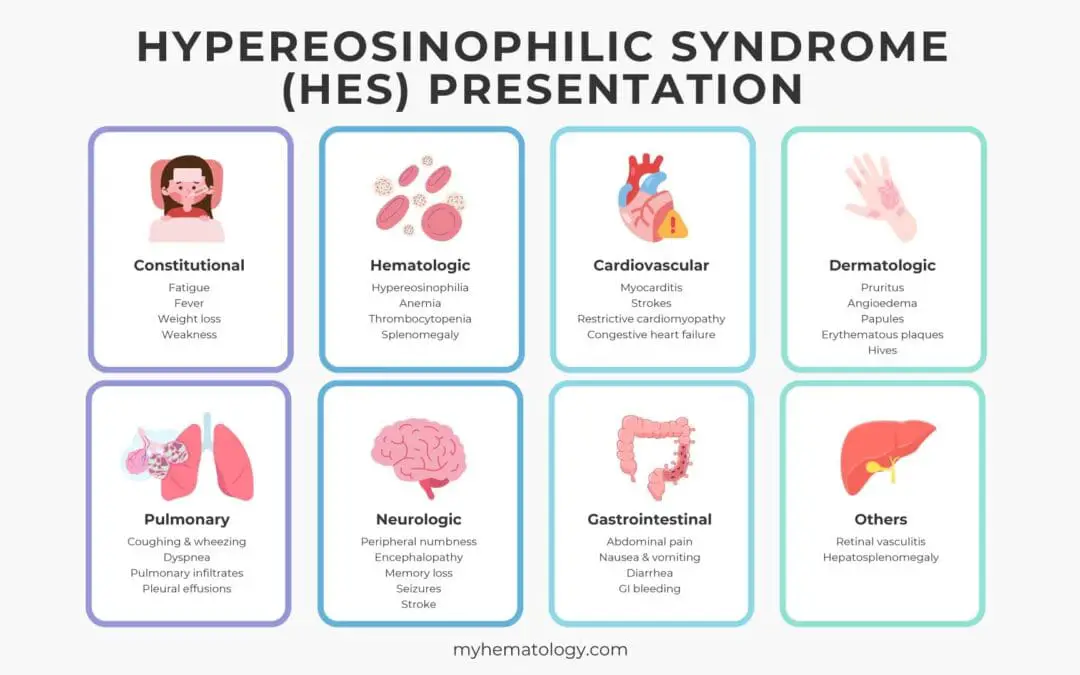
TL;DR Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is a rare group of disorders characterized by persistently high blood eosinophils (≥1,500/μL), leading to inflammation and organ damage. Pathophysiology ▾: Caused by eosinophil overproduction and toxic granule...

by MH Team | Jul 29, 2025 | White Blood Cells
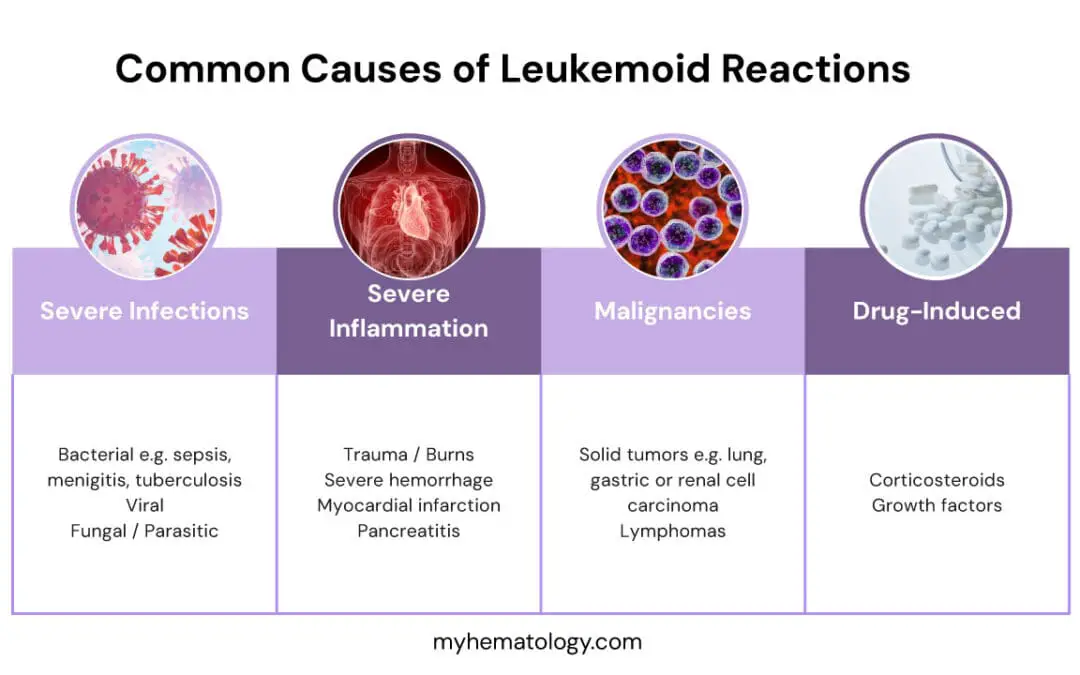
TL;DR A leukemoid reaction is a benign, reactive process characterized by a marked increase in white blood cells (leukocytosis, often >50,000/µL) with immature myeloid forms (left shift), but it is not a malignancy. Physiological Basis ▾: It represents an...

by MH Team | Jun 13, 2025 | Red Blood Cells
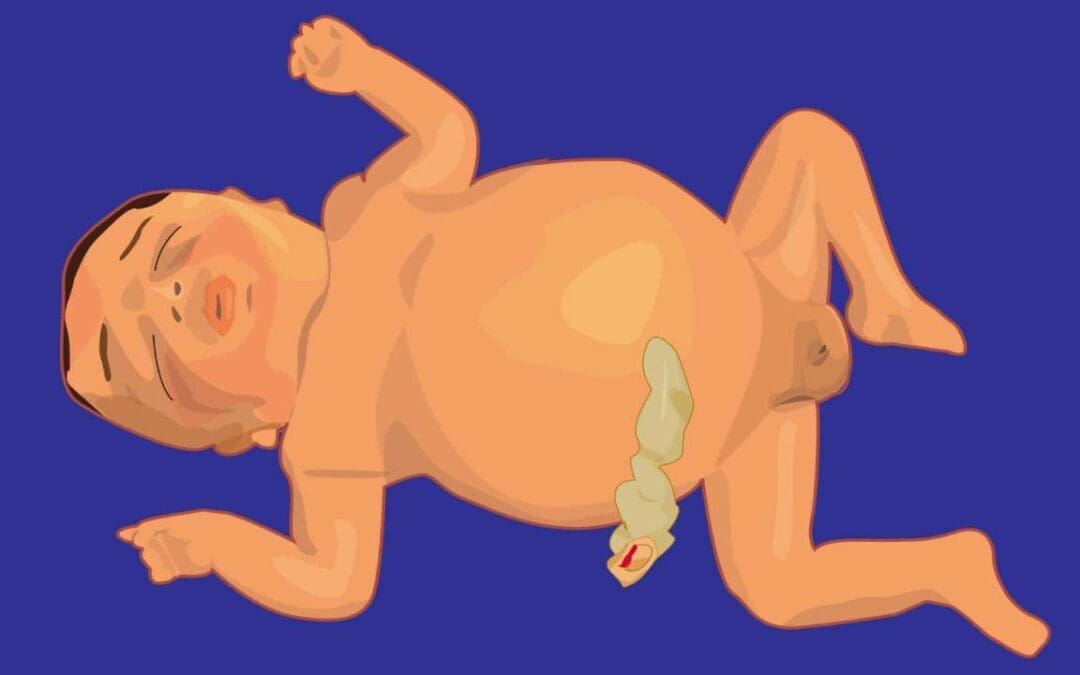
TL;DR Hydrops fetalis is excessive fluid accumulation in at least two fetal compartments (skin edema, pleural/pericardial effusion, ascites). Types: Immune (IHF, rare due to RhIG) and Non-Immune (NIHF, ~90% of cases). Pathophysiology ▾: Imbalance in fluid...

by MH Team | Jun 10, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Atypical lymphocytes are reactive, morphologically altered lymphocytes (mainly activated T cells) that appear in the peripheral blood. They indicate an active immune response, not necessarily malignancy. Common Causes ▾: The most frequent triggers are...



Recent Comments