
by MH Team | Sep 5, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Chediak-Higashi syndrome is a rare, autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by defects in lysosomal trafficking. Cause: A mutation in the LYST gene. Pathophysiology ▾: The LYST gene defect leads to the formation of abnormally large,...

by MH Team | Sep 1, 2025 | Red Blood Cells
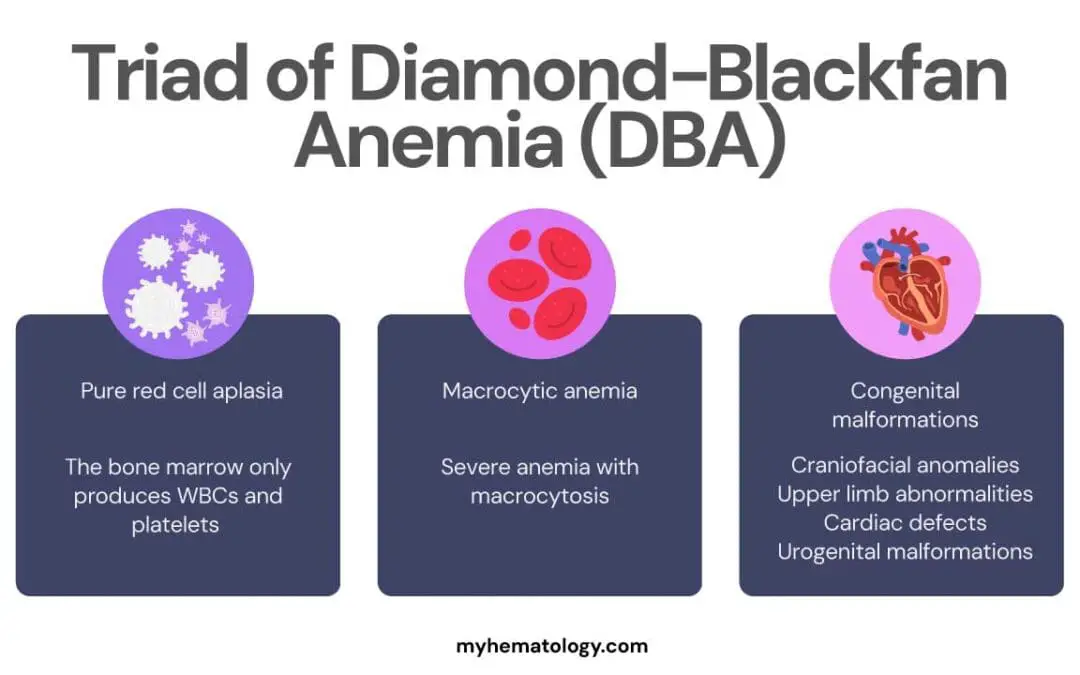
TL;DR Diamond-Blackfan Anemia or DBA is a rare, congenital blood disorder where the bone marrow fails to produce red blood cells. It is also known as congenital hypoplastic anemia. Causes ▾: The core cause is a defect in ribosome biogenesis, primarily due to...

by MH Team | Aug 26, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common and aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, a fast-growing cancer of B-lymphocytes. Epidemiology ▾: It is the most common non-Hodgkin lymphoma worldwide, with incidence increasing with age. Risk...

by MH Team | Aug 17, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL disease) is a rare and aggressive type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that originates from B-cells in the “mantle zone” of the lymph nodes. Pathogenesis ▾: The hallmark of MCL is a specific genetic mutation called a...

by MH Team | Aug 15, 2025 | Platelet Disorders
TL;DR Factor V Leiden thrombophilia is a genetic condition caused by a mutation in the F5 gene that results in a defective Factor V protein, making it resistant to inactivation by activated protein C (APC). Pathophysiology ▾: Because the mutated Factor V...





Recent Comments