
by MH Team | Sep 16, 2025 | Red Blood Cells
TL;DR Pancytopenia is the reduction of all three major blood cell lines: red blood cells (anemia), white blood cells (leukopenia), and platelets (thrombocytopenia). It is a clinical finding, not a disease itself, indicating an underlying issue. Causes ▾ : The...

by MH Team | Sep 13, 2025 | Red Blood Cells
TL;DR Shwachman-Diamond syndrome or SDS is a rare, autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the SBDS gene on chromosome 7. Cause ▾: Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome (SDS) is a rare, inherited genetic disorder. It is an autosomal recessive...

by MH Team | Sep 11, 2025 | Red Blood Cells
TL;DR Bone marrow failure is the inability of the bone marrow to produce enough mature blood cells, leading to low counts (pancytopenia). Causes ▾: The causes are broadly divided into acquired and inherited. Acquired causes include immune-mediated attacks...

by MH Team | Sep 8, 2025 | Red Blood Cells
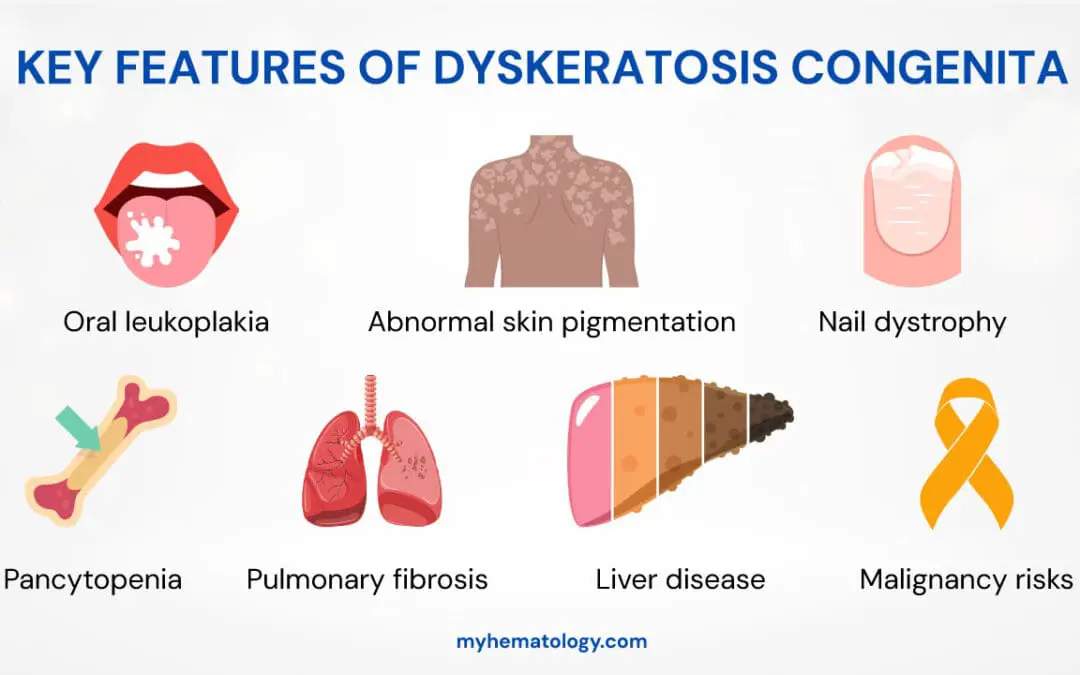
TL;DR Dyskeratosis congenita is a rare, inherited bone marrow failure syndrome caused by defects in telomere maintenance. This leads to abnormally short telomeres and premature cellular aging, primarily affecting rapidly dividing cells. Key Clinical Manifestations...

by MH Team | Sep 5, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Chediak-Higashi syndrome is a rare, autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by defects in lysosomal trafficking. Cause: A mutation in the LYST gene. Pathophysiology ▾: The LYST gene defect leads to the formation of abnormally large,...





Recent Comments