
by MH Team | Jan 31, 2025 | Red Blood Cells, Tests
Homocysteine is an amino acid naturally produced in the body. It’s broken down with the help of B vitamins. If your body doesn’t have enough of these vitamins, homocysteine levels can rise. Elevated homocysteine levels (hyperhomocysteinemia) are associated...

by MH Team | Jan 26, 2025 | Red Blood Cells
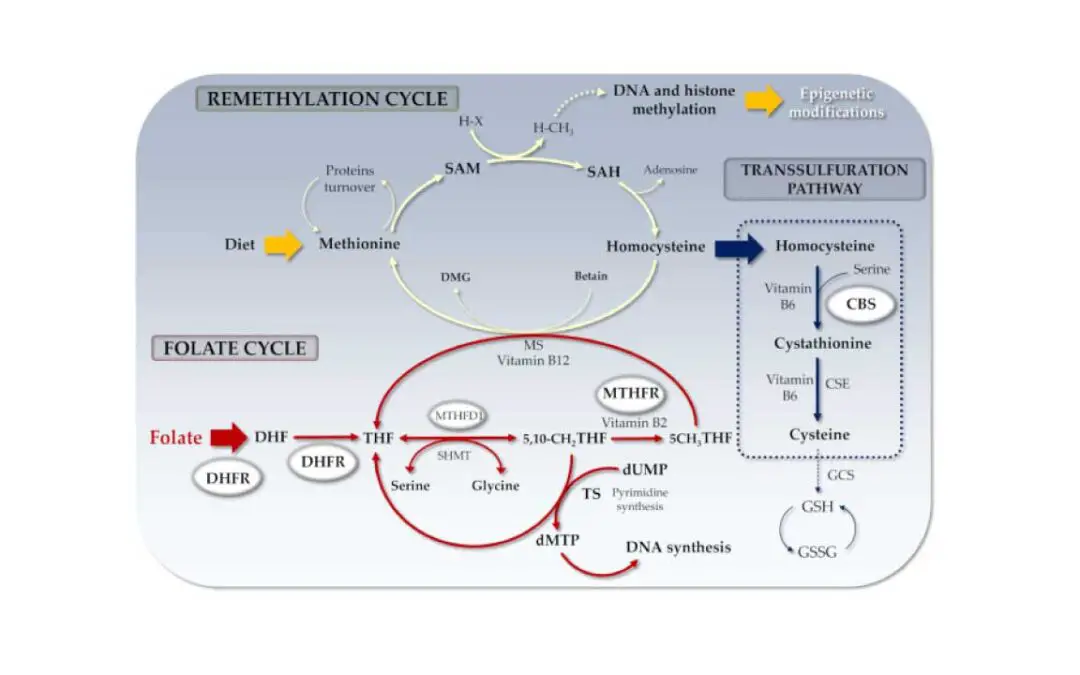
TL;DR Homocysteine is an amino acid, a building block of proteins, naturally produced in the body. It undergoes two main metabolic pathways: remethylation (requiring folate, vitamin B12, or betaine) and transsulfuration (requiring vitamin B6). Biomarker for...

by MH Team | Jan 25, 2025 | Red Blood Cells, Tests
You’re constantly tired, even after a good night’s sleep. You feel sluggish, forgetful, and your mood seems off. Could it be something more than just stress? Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an essential nutrient that the human body cannot produce...

by MH Team | Jan 24, 2025 | Red Blood Cells, Tests
Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is an essential water-soluble B vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It is involved in the production of DNA and RNA, the genetic material in every cell, and is essential for cell growth and development....

by MH Team | Jan 23, 2025 | Tests
Lead is a toxic heavy metal that can cause serious health problems, especially in children. Toxic effects can be classified into six main categories: gastrointestinal, central nervous system, neuromuscular, hematologic, renal, and constitutional. Lead poisoning in the...






Recent Comments