
by MH Team | Apr 26, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Leukopenia is defined as a decrease in total white blood cells (leukocytes) below the normal range, increasing infection susceptibility. Normal Count: Typically 4,000-11,000 cells/µL; leukopenia is generally <4,000 cells/µL. Classification ▾:...

by MH Team | Apr 23, 2025 | Platelet Disorders
TL;DR Thrombocytosis or high platelet count is defined as elevated platelet count above the normal range (typically >450,000/μL). Reactive Thrombocytosis ▾: More common, caused by underlying conditions like infection, inflammation, iron deficiency,...

by MH Team | Apr 21, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Lymphadenopathy refers to the swelling or enlargement of lymph nodes, which are part of the lymphatic system, a crucial component of the immune system. Causes of Lymphadenopathy ▾: The causes are diverse, with infections being the most common, followed by...

by MH Team | Apr 19, 2025 | White Blood Cells
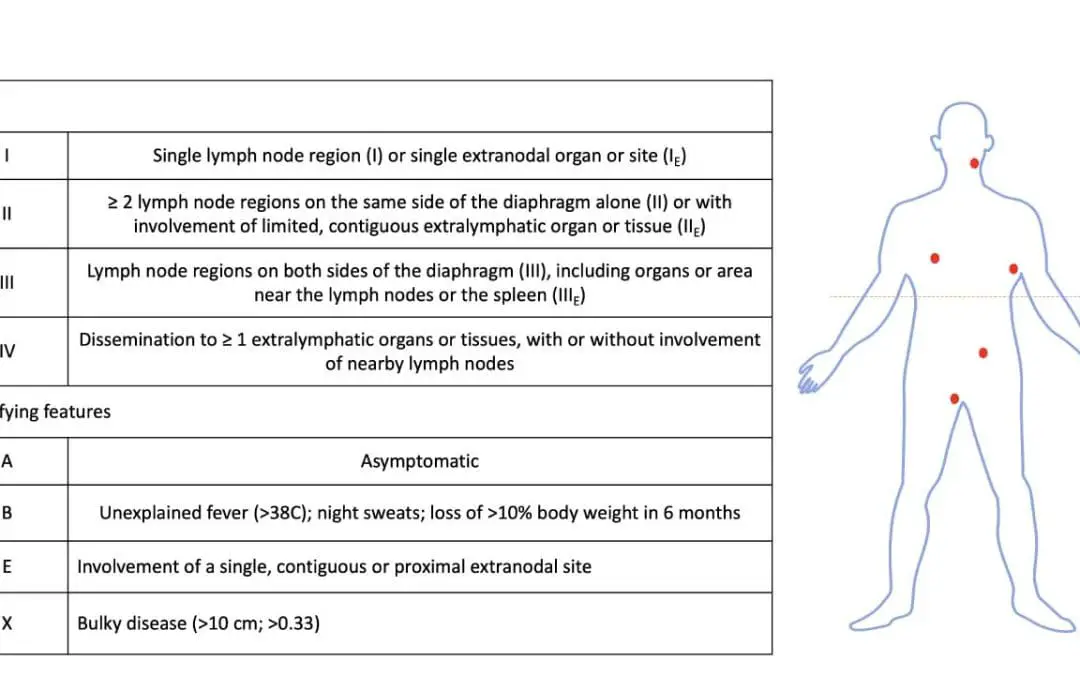
TL;DR Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma is primarily treated with systemic therapy (chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy) and sometimes radiation therapy. Early-Stage Treatment ▾: Early-stage (Stage 1-2) treatment is tailored based on whether the disease is...

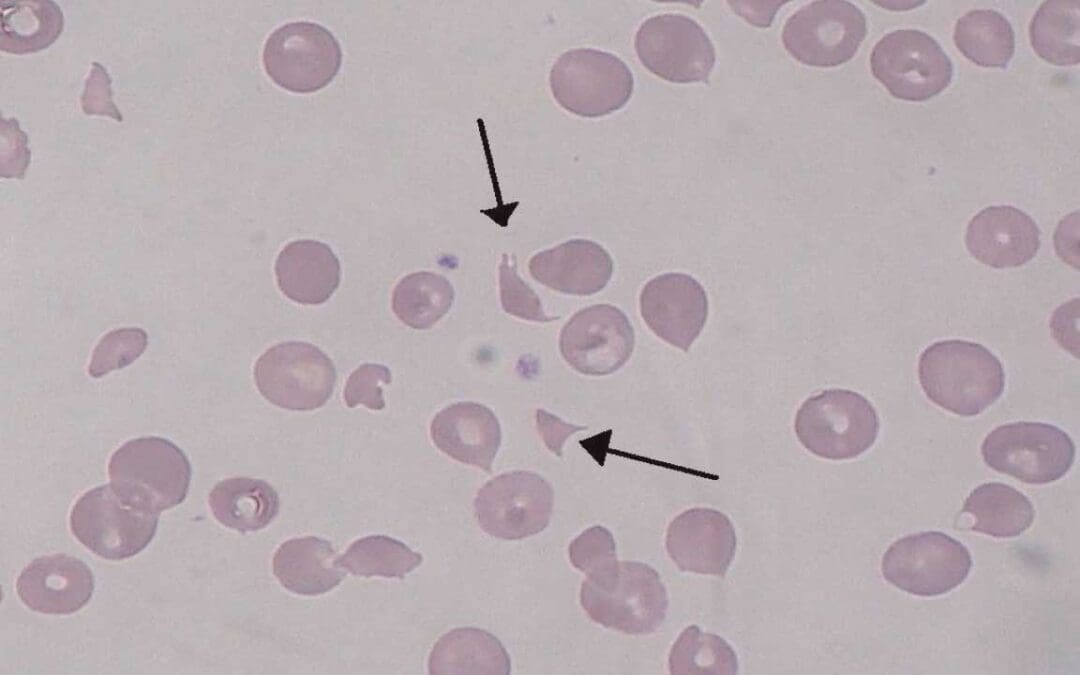
by MH Team | Apr 18, 2025 | Red Blood Cells
TL;DR Hemolytic uremic syndrome is defined by the triad of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, acute kidney injury, and thrombocytopenia. It’s a serious, potentially life-threatening condition. Classification ▾: Primarily classified as STEC-HUS (typical,...


Recent Comments