
by MH Team | Mar 9, 2026 | White Blood Cells
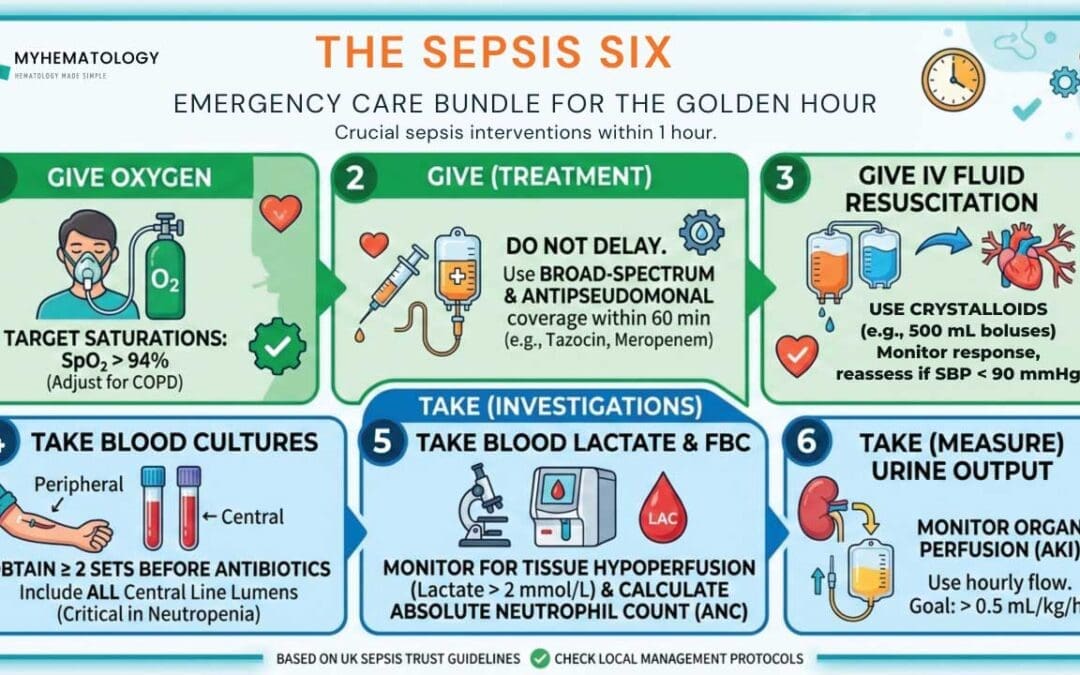
TL;DR Neutropenic sepsis is a medical emergency defined by a fever (≥ 38.3°C (101°F)) and an ANC < 0.5 X 109/L. It requires a “door-to-needle” time of < 60 minutes for the first dose of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Pathophysiology...

by MH Team | Nov 7, 2025 | White Blood Cells
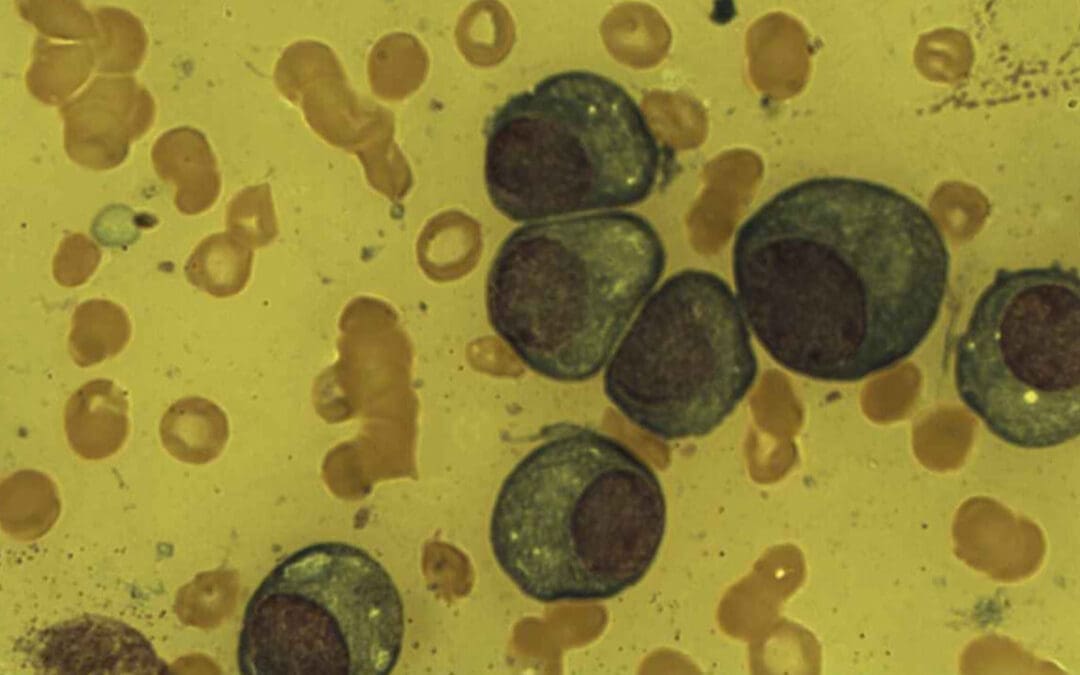
TL;DR The plasma cell is the terminal, non-proliferating B-lymphocyte dedicated to antibody secretion. Plasma cells originate from B-cells via the Germinal Center (GC) reaction in lymphoid organs. Morphology ▾: Plasma cells has an eccentric nucleus with...

by MH Team | Nov 3, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS) is an asymptomatic premalignant plasma cell or lymphoplasmacytic disorder. Classification ▾: Divided into Non-IgM MGUS (most common, precursor to Multiple Myeloma, MM), IgM MGUS (precursor to...

by MH Team | Nov 1, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Smoldering Multiple Myeloma (SMM) is an intermediate, asymptomatic stage between Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS) (low-risk) and Active Multiple Myeloma (MM) (symptomatic, requiring treatment). Pathophysiology ▾: Smoldering...

by MH Team | Oct 25, 2025 | Platelet Disorders
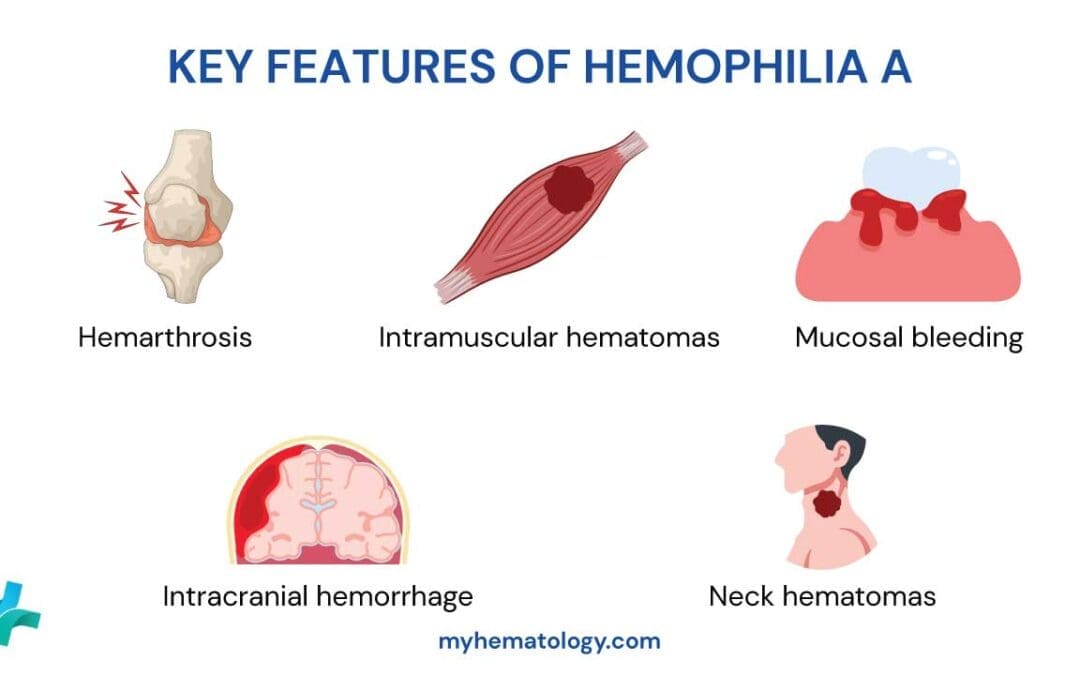
TL;DR Hemophilia A (Classic Hemophilia) is an inherited bleeding disorder defined by a quantitative or qualitative deficiency of Factor VIII (FVIII). Etiology & Inheritance: Hemophilia A is an X-linked recessive disorder caused by mutations in the F8 gene on the X...




Recent Comments