TL;DR
Red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, are the most common blood cells, small biconcave disks lacking a nucleus and primarily composed of hemoglobin.
- Function ▾: Their main function is to transport oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues back to the lungs, essential for cellular energy production. They also play roles in acid-base balance, blood pressure regulation, immune function, wound healing, and temperature regulation.
- Hematopoiesis ▾: All blood cells, including RBCs, originate from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in the bone marrow (the primary site in adults). The hematopoiesis process involves HSCs differentiating into various progenitor cells that mature into different blood cell types.
- Erythropoiesis ▾: This is the specific process of RBC formation from hematopoietic stem cells. It involves several maturation stages in the bone marrow, regulated primarily by the hormone erythropoietin (EPO), which stimulates erythroid progenitor cells. Mature RBCs are released into circulation after about 4 days in the marrow.
- RBC Metabolism ▾: RBCs rely on pathways like Embden-Meyerhof, Hexose Monophosphate, Methemoglobin Reductase, and Leubering-Rapoport Shunt for energy and to maintain hemoglobin function and cell integrity.
- Oxygen Dissociation Curve (ODC) ▾: The ODC illustrates how hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen changes with partial pressure, facilitating oxygen uptake in the lungs and release in tissues. Factors like PCO2, pH, temperature, and 2,3-DPG regulate this curve, adapting oxygen delivery to the body’s needs.
- Red Blood Cell Membrane ▾: A complex and dynamic structure vital for RBC survival and function, protecting the cell, maintaining its biconcave shape (crucial for efficient oxygen transport), and regulating molecular transport. It’s composed of a lipid bilayer and various proteins (e.g., spectrin, ankyrin) that form a supporting cytoskeleton.
- Hemoglobin ▾: Hemoglobin is a crucial protein found exclusively in RBCs. It’s responsible for binding and transporting oxygen and is composed of heme (iron-containing pigment) and globin chains. Its synthesis is a complex process essential for proper RBC function.
- RBC Lifespan and Destruction ▾: The average lifespan of an RBC is approximately 120 days. Aged or damaged RBCs are primarily destroyed by macrophages in the reticuloendothelial system (e.g., spleen, liver).
- Clinical Relevance & Disorders ▾: Abnormal counts (low or high) or membrane disorders (e.g., hereditary spherocytosis, elliptocytosis, stomatocytosis) can lead to various health issues and diseases like anemia.
*Click ▾ for more information
Introduction
A red blood cell (RBC) is also known as an erythrocyte. Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell in the human body. They are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Red blood cells (RBCs) are small, biconcave disks that lack a nucleus.
Why are red blood cells (RBCs) important?
- They transport oxygen to the tissues. Oxygen is essential for all cellular processes, including energy production, growth, and repair. Red blood cells (RBCs) contain a protein called hemoglobin, which binds to oxygen and transports it to the tissues throughout the body.
- They remove carbon dioxide from the tissues. Carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular respiration. Red blood cells (RBCs) transport carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs, where it is exhaled.
- They maintain the body’s acid-base balance. The body’s acid-base balance is the balance between acids and bases in the blood. Red blood cells (RBCs) help to maintain this balance by acting as buffers, which means that they can absorb or release acids and bases depending on the needs of the body.
- They regulate blood pressure. Red blood cells (RBCs) release a substance called nitric oxide, which helps to relax the blood vessels. This can help to lower blood pressure.
In addition to these essential functions, Red blood cells (RBCs) also play a role in a number of other important physiological processes, such as:
- Immune function: Red blood cells (RBCs) interact with white blood cells to help fight infection.
- Wound healing: Red blood cells (RBCs) deliver oxygen and nutrients to the tissues at the site of a wound, which helps to promote healing.
- Temperature regulation: Red blood cells (RBCs) help to regulate body temperature by absorbing and releasing heat.
How are red blood cells (RBCs) produced?
Hematopoiesis
All blood cells originate from the haematopoietic stem cell. Stem cells are mother cells that can replicate itself as well as differentiate into many types of cell.
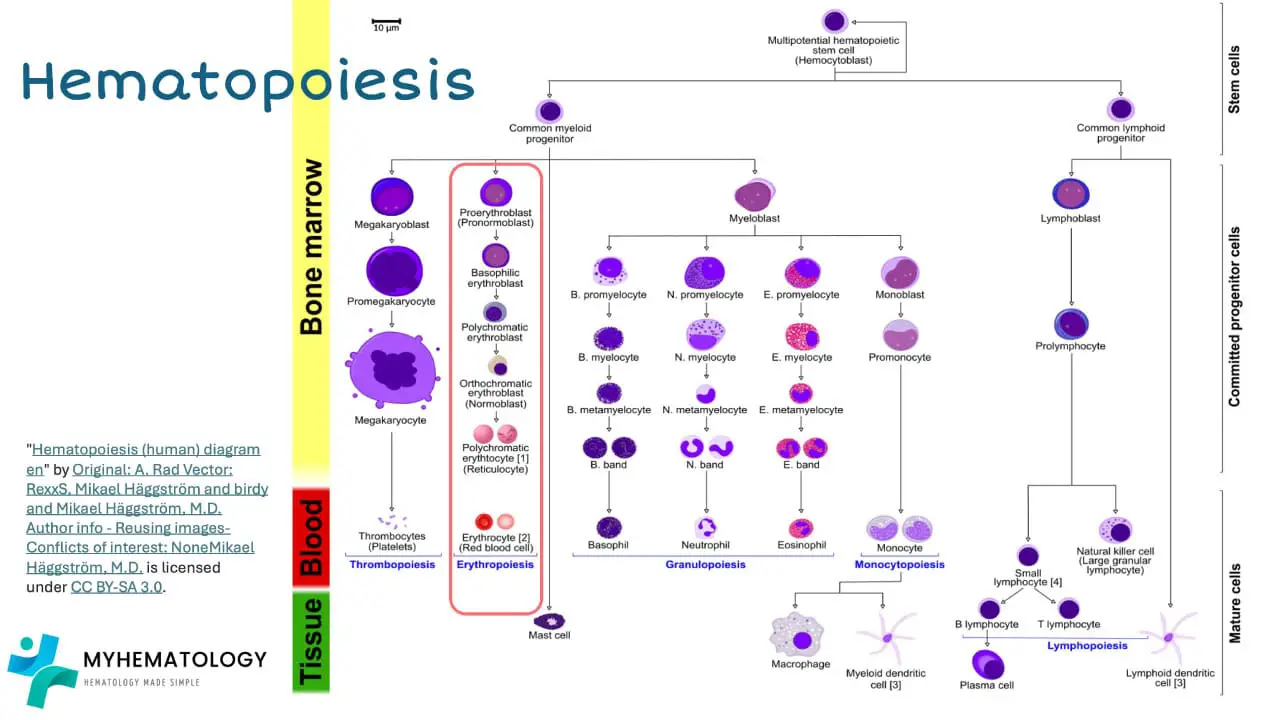
In the bone marrow, the hematopoietic stem cell initially differentiates into myeloid progenitor and lymphoid progenitor cells. Then the lymphoid progenitor cells will differentiate and mature into lymphoblasts and natural killer cells and eventually the lymphoblasts will become functional mature small lymphocytes. Lymphocytes and natural killer cells are part of the immune cells involved in our body immunity.
The myeloid progenitor cell can differentiate into the erythroid lineage by maturing into erythroblasts, then the normoblasts, then reticulocytes and finally functional mature erythrocytes.
The myeloid progenitor cell can also differentiate into megakaryoblast which matures into megakaryocytes that will fragment into thousands of platelets.
Granular white blood cells like the neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils matures from the myeloblasts. While monocytes and macrophages develop from monoblasts.
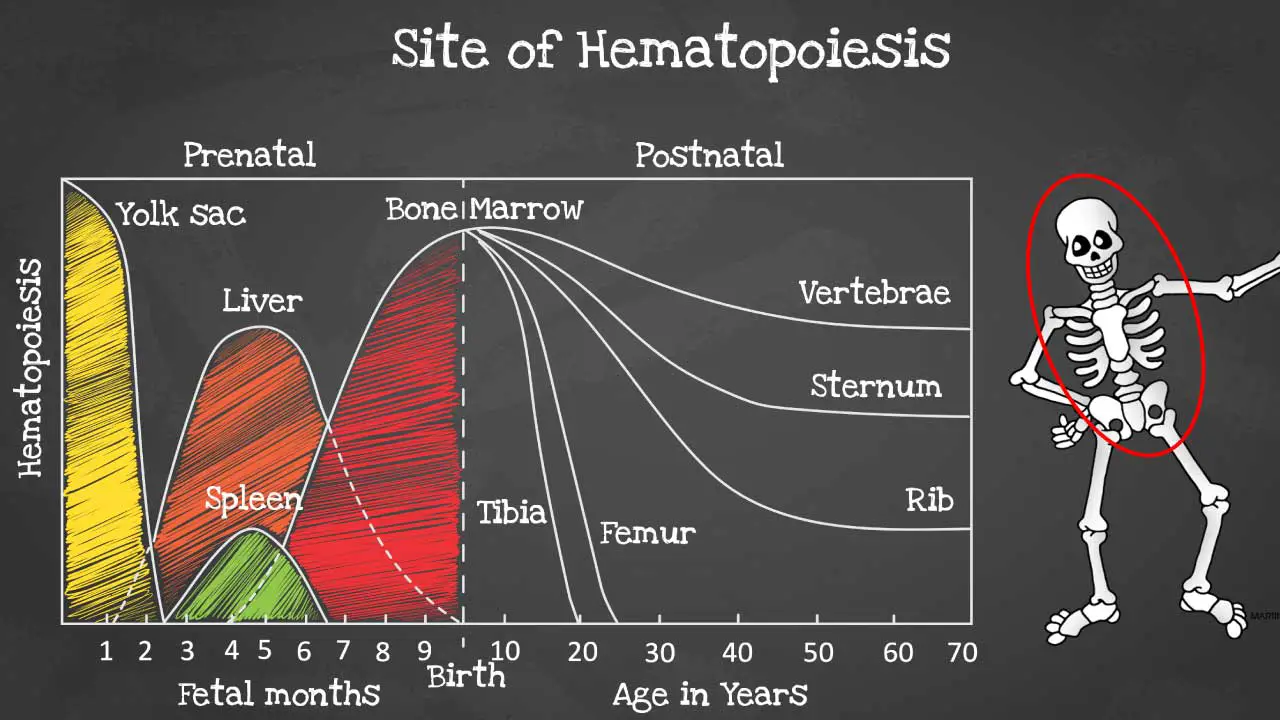
Hematopoiesis sites
Hematopoiesis is produced initially in the yolk sac when we are formed as an embryo before migrating to the liver and spleen in the fetus.
By 6 months onwards the bone marrow takes over as the main hematopoietic site and all bones are able to produce blood cells at birth. However, these sites become more and more restricted as we age and by the time we are adults, hematopoiesis occurs mainly in the pelvis, cranium, sternum, and the vertebrae.
Hematopoiesis within the bone marrow is termed intramedullary. The term extramedullary hematopoiesis describes hematopoiesis outside the bone marrow environment primarily the liver and the spleen because these organs play major roles in early fetal hematopoiesis, thus they retain their hematopoietic memory and capability.
If extramedullary hematopoiesis develops, the liver and spleen becomes enlarged due to the extra burden and the enlargement is known as hepatosplenomegaly.
Importance of the bone marrow environment
The bone marrow environment plays a vital role in hematopoiesis. It provides a supportive niche for hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and progenitor cells, and it helps to regulate their proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
The bone marrow microenvironment is a complex and dynamic system that is composed of a variety of cell types, including stromal cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, endothelial cells, and macrophages. These cells interact with each other and with HSCs and progenitor cells to create a favorable environment for hematopoiesis.
Key functions of bone marrow microenvironment
- Hematopoiesis (Blood Cell Production): This is the primary and most vital function. The bone marrow environment is the main site where hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) differentiate and mature into all types of blood cells, including:
- Red blood cells (Erythrocytes): Responsible for oxygen transport.
- White blood cells (Leukocytes): Crucial for the immune system, fighting infections.
- Platelets (Thrombocytes): Essential for blood clotting.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell (HSC) Maintenance: The microenvironment provides specialized niches that support the self-renewal and quiescence (resting state) of HSCs. This ensures a lifelong supply of these multipotent cells. It protects HSCs from premature differentiation or depletion.
- Regulation of Cell Proliferation and Differentiation: Through a complex network of stromal cells (like fibroblasts, mesenchymal stem cells, adipocytes, osteoblasts, endothelial cells, and macrophages), extracellular matrix proteins, and signaling molecules (cytokines, growth factors, hormones), the bone marrow precisely regulates the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of HSCs and their progenitor cells.
- Immune System Support: Beyond producing immune cells, the bone marrow environment actively participates in immune responses. Stromal cells can interact with immune cells to promote tolerance and prevent autoimmune reactions. B lymphocytes also mature in the bone marrow before migrating to secondary lymphoid tissues.
- Protection of Hematopoietic Cells: The microenvironment helps protect HSCs and progenitor cells from damage by secreting factors that suppress apoptosis (programmed cell death) and promote DNA repair.
- Energy Storage (Yellow Bone Marrow): Yellow bone marrow, which largely consists of fat cells, serves as an energy reserve for the body. While primarily involved in fat storage, it can convert back to red marrow under conditions of increased demand for blood cell production (e.g., severe blood loss or anemia).
- Bone Remodeling and Metabolism: The bone marrow environment, particularly through its osteolineage cells (osteoblasts and osteoclasts), is intricately linked to bone tissue homeostasis, contributing to bone formation and resorption.
Erythropoiesis
In erythropoiesis, the hematopoietic stem cell differentiates into proerythroblasts before developing further as early erythroblast where the ribosomes are synthesized.
As hemoglobins are synthesized and accumulated, the nucleus condenses and the cell becomes a normoblast. When the nuclear chromatin is fully condensed, then the nucleus is extruded and the cell becomes an immature erythrocyte also known as a reticulocyte.
Less than 1% of the reticulocytes can be found in the peripheral blood circulation. A reticulocyte still has some RNA available which are lost when the cell develops into a mature erythrocyte.
The maturation of the red blood cell (RBC) takes about 4 days in the bone marrow before it is released into the circulation. Very young red blood cells (RBCs) like the normoblasts are only found in the bone marrow for healthy individuals and morphologically it is very similar to the juvenile cells of other lineages, other than the deeper bluish staining cytoplasm.
The mechanisms of chromatin condensation during erythropoiesis are still unclear. Erythroid cells become smaller as they mature so that mature erythrocytes are small enough to pass through small capillaries at the arterioles and ventrioles. The lifespan of a red blood cell (RBC) is approximately 120 days before its destruction in the reticuloendothelial system (RES) by macrophages.
Regulation of Erythropoiesis
EPO is a glycoprotein hormone that primarily stimulates the production of red blood cells (RBCs). It does this by binding to receptors on erythroid progenitor cells in the bone marrow and triggering a cascade of signaling events that lead to cell proliferation and differentiation.
EPO plays a vital role in maintaining oxygen homeostasis in the body.
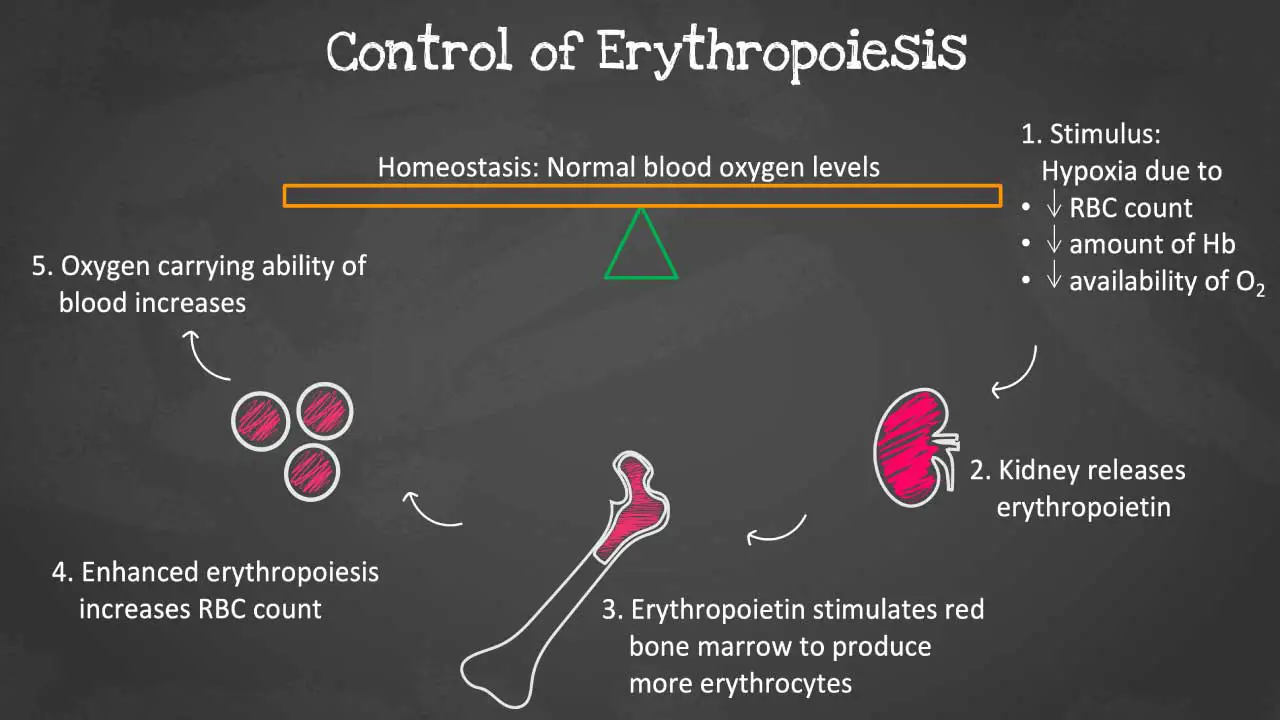
As oxygen levels in the blood decline, specialized cells in the kidneys, known as juxtaglomerular (JAG) cells, detect the hypoxia and release EPO into the bloodstream. EPO travels to the bone marrow, where it binds to receptors on erythroid progenitor cells, initiating a cascade of signaling events that trigger the differentiation and maturation of these cells into red blood cells.
EPO production is regulated by a number of factors, including oxygen levels in the blood, iron levels in the blood, and inflammatory cytokines. When oxygen levels are low, the kidneys produce more EPO to elevate the red blood cell count. Iron is also essential for the production of hemoglobin. When iron levels are low, EPO production is increased. Inflammatory cytokines can also increase EPO production.
The EPO gene is located on chromosome 7q21 and is primarily produced by the kidneys. However, it is also produced in smaller amounts by the liver and other tissues.
How it travels to the bone marrow for erythropoiesis: EPO is released into the bloodstream from the kidneys. It then circulates through the bloodstream and binds to receptors on erythroid progenitor cells in the bone marrow. This binding triggers a cascade of signaling events that lead to cell proliferation and differentiation into mature RBCs thereby increasing the red blood cell count.
Characteristics of red blood cells (RBCs)
Red blood cells (RBCs) have a lifespan of approximately 120 days, and during that time, they must be able to withstand a variety of stresses, including physical trauma, oxidative damage, and changes in pH. A number of elements are responsible for the survival of RBCs, including their metabolism, hemoglobin, and membrane apart from essential nutrients and a good bone marrow environment.
Red blood cell (RBC) metabolism
Red blood cells (RBCs) are the most abundant cell type in the human body, and they play a vital role in oxygen transport. To meet this high demand for oxygen, red blood cells (RBCs) have a unique metabolism that is highly specialized for energy production.
Red blood cells (RBCs) are anucleate cells, meaning they do not have a nucleus. This lack of a nucleus allows red blood cells (RBCs) to contain more hemoglobin and pass through small spaces. However, it also means that red blood cells (RBCs) do not have the ability to synthesize new proteins or DNA.
The metabolism of red blood cells (RBCs) is tightly regulated to ensure that they have enough energy to meet the body’s oxygen demands. Red blood cells (RBCs) are constantly being produced and destroyed, and their metabolism must be able to adapt to changes in the environment, such as oxygen levels and pH.
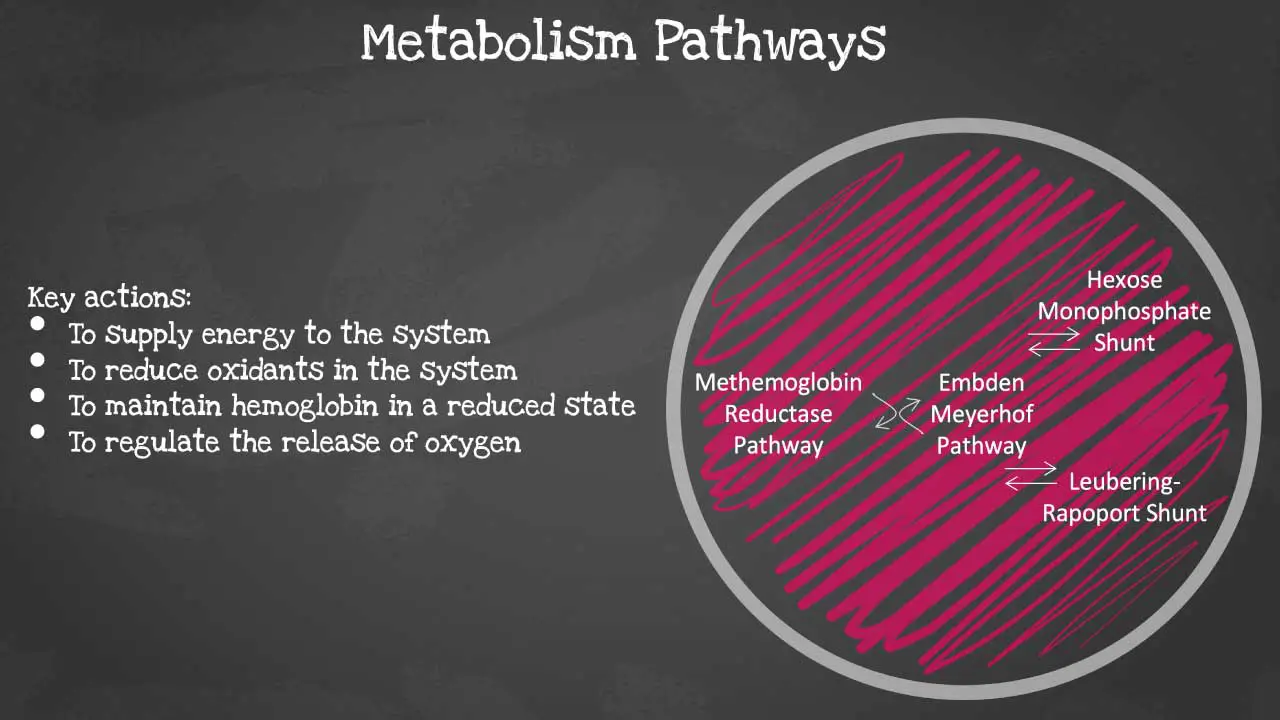
There are 4 major pathways involved and they are interconnected. The pathways are Embden-Meyerhof pathway, hexose monophosphate shunt, methaemoglobin reductase pathway and Leubering-Rapoport shunt. The key actions of these pathways include energy supply to the system, oxidant reduction of the cell, maintaining haemoglobin in a reduced state and regulation of oxygen release. Let’s look at each pathway in more detail.
Embden-Meyerhof Pathway
The Embden-Meyerhof pathway (EMP), also known as glycolysis, is the major pathway to produce energy for the membrane ion pumps. It supplies 90-95% of the energy for the red blood cell (RBC). It is an anaerobic glucose metabolism which converts 1 molecule of glucose into 2 molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the absence of oxygen. It is the primary energy source for most cells, including red blood cells (RBCs).
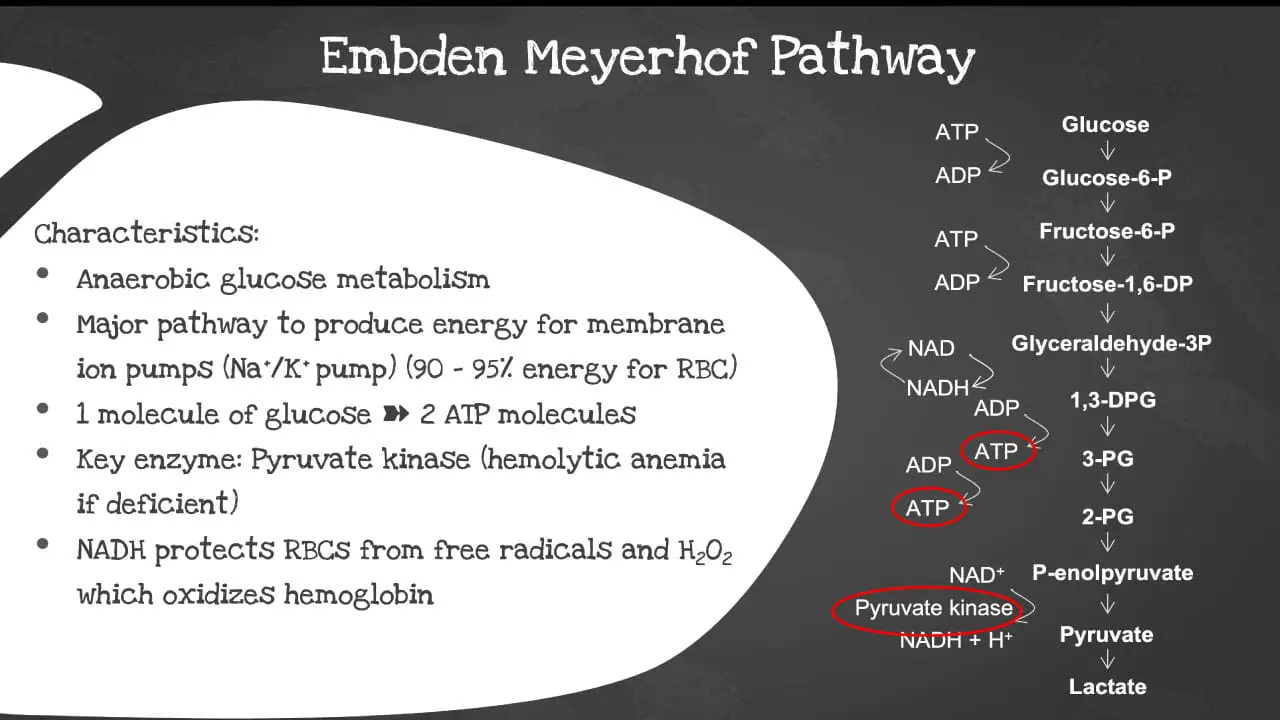
The key enzyme involved is the pyruvate kinase. The pyruvate kinase deficiency causes a shortage of ATPs in the red blood cells (RBCs) and increased levels of other molecules produced earlier in the glycolytic process. The abnormal cells are prematurely destroyed leading to hemolytic anemia, a low red blood cell count. The NADH also protects the red blood cells (RBCs) from free radical and hydrogen peroxide which oxidizes the hemoglobin.
Substrates involved in the EMP
- Glucose
- Fructose-6-phosphate
- Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
- 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG)
- 3-phosphoglycerate
- 2-phosphoglycerate
- Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
- Pyruvate
Enzymes are involved in the EMP
- Hexokinase: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate.
- Phosphofructokinase: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
- Aldolase: Cleaves fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and G3P.
- Triose phosphate isomerase: Interconverts DHAP and G3P.
- Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase: Catalyzes the oxidation of G3P to 1,3-BPG.
- Phosphoglycerate kinase: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of 1,3-BPG to 3-phosphoglycerate.
- Phosphoglyceromutase: Interconverts 3-phosphoglycerate and 2-phosphoglycerate.
- Enolase: Catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to PEP.
- Pyruvate kinase: Catalyzes the conversion of PEP to pyruvate.
Pyruvate kinase is the enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the EMP, the conversion of PEP to pyruvate. It is a key regulatory enzyme in the EMP and plays an important role in maintaining energy homeostasis in the red blood cell (RBC).
Pyruvate kinase deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that affects the production of the pyruvate kinase enzyme. This can lead to a number of problems, including anemia (low red blood cell count), muscle weakness, and exercise intolerance.
In red blood cells (RBCs), pyruvate kinase deficiency can lead to a decrease in ATP production and an increase in lactate production. This can make it difficult for red blood cells (RBCs) to transport oxygen to the tissues and can lead to anemia (low red blood cell count).
In muscle cells, pyruvate kinase deficiency can lead to muscle weakness and exercise intolerance. This is because muscle cells need ATP to function properly, and pyruvate kinase deficiency reduces the amount of ATP that muscle cells can produce.
There is no cure for pyruvate kinase deficiency, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms. Treatment typically involves taking supplements, such as iron and vitamin B12, and avoiding strenuous activity.
Hexose monophosphate (pentose phosphate) pathway
Hexose monophosphate pathway (HMP), also known as the pentose phosphate pathway, is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into ribose-5-phosphate and NADPH.
It is a parallel pathway to glycolysis, but it is not dependent on oxygen. The hexose monophosphate shunt prevents oxidative stress by converting hydrogen peroxide into water.
The key enzyme in this pathway is the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD). In G6PD deficiency, the red blood cells (RBCs) become susceptible to oxidative stress causing acute hemolytic anemia (low red blood cell count) when triggered.

Substrates involved in the HMP
- Glucose
- Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P)
- 6-phosphogluconate (6PG)
- Ribulose-5-phosphate (R5P)
- Ribose-5-phosphate (Ru5P)
- Fructose-6-phosphate
G6PD is the key regulatory enzyme in the HMP. It is responsible for the production of NADPH, which is a cofactor for many important enzymes, including glutathione reductase. Glutathione reductase helps to protect cells from oxidative damage.
G6PD deficiency is a genetic disorder that affects the production of the G6PD enzyme. It is one of the most common genetic disorders in the world, affecting about 400 million people.
G6PD deficiency can lead to a number of problems, including anemia (low red blood cell count), jaundice, and hemolysis (the destruction of red blood cells). This is because G6PD deficiency reduces the amount of NADPH that cells can produce. NADPH is needed to protect cells from oxidative damage, and a lack of NADPH can lead to cell death.
G6PD deficiency is typically triggered by an event, such as an infection or exposure to certain chemicals. In people with G6PD deficiency, these events can lead to a sudden and severe decrease in the number of red blood cells (RBCs).
There is no cure for G6PD deficiency, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms. Treatment typically involves avoiding triggers and taking medications to prevent or treat hemolysis.
Methemoglobin reductase pathway
The methemoglobin reductase pathway is a metabolic pathway that reduces methemoglobin (MetHb) to hemoglobin (Hb). The methaemoglobin reductase pathway prevents the ferrous iron from being oxidised into ferric iron as the environment is highly oxidative.
Ferric iron (MetHb) is not able to transport oxygen. The methemoglobin reductase pathway is important for maintaining normal levels of MetHb in the blood. Deficiency of the key enzyme methaemoglobin reductase will lead to decreased oxygen carrying capacity. The disorder can be acquired or inherited.
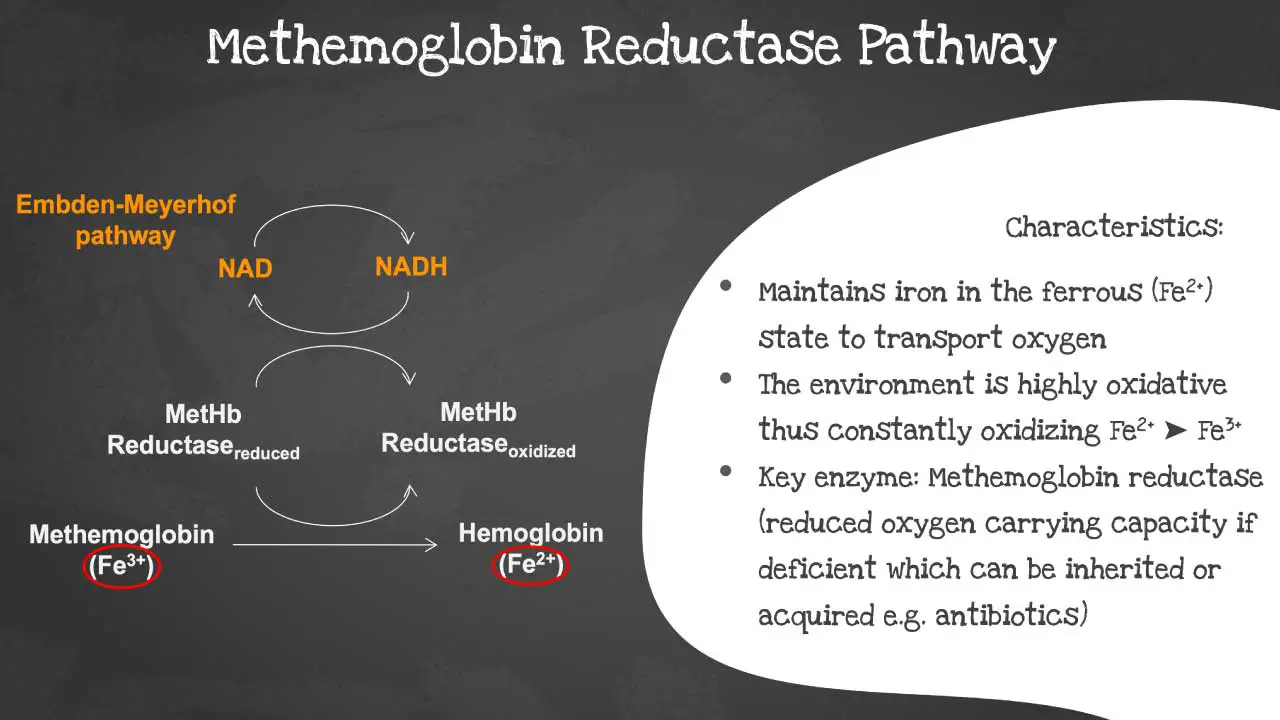
The following substrates are involved in the methemoglobin reductase pathway:
- Methemoglobin (MetHb)
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)
- Cytochrome b5
The key enzyme in the methemoglobin reductase pathway is methemoglobin reductase. This enzyme is responsible for transferring electrons from NADPH to MetHb, reducing MetHb to Hb.
Methemoglobin reductase deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that affects the production of the methemoglobin reductase enzyme. This can lead to a number of problems, including cyanosis (a bluish tint to the skin), shortness of breath, and headache.
In people with methemoglobin reductase deficiency, even small amounts of exposure to oxidizing agents, such as nitrates and nitrites, can lead to a sudden and severe increase in MetHb levels. This can cause a life-threatening condition called methemoglobinemia.
There is no cure for methemoglobin reductase deficiency, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms. Treatment typically involves taking medications to reduce MetHb levels and preventing complications.
Leubering-Rapoport shunt
The Luebering-Rapoport shunt is a metabolic pathway that is found in mature erythrocytes (red blood cells). The Leubering-Rapoport pathway involves the formation of 2,3-DPG (2,3-diphosphoglycerate) which regulates oxygen release from hemoglobin and delivery to tissues.
It allows the red blood cells (RBCs) to regulate oxygen transportation during conditions of hypoxia or acid-base imbalance. 2,3-DPG decreases the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin so when there is more 2,3-DPG in the red blood cells (RBCs), means more oxygen will be delivered to body tissues.
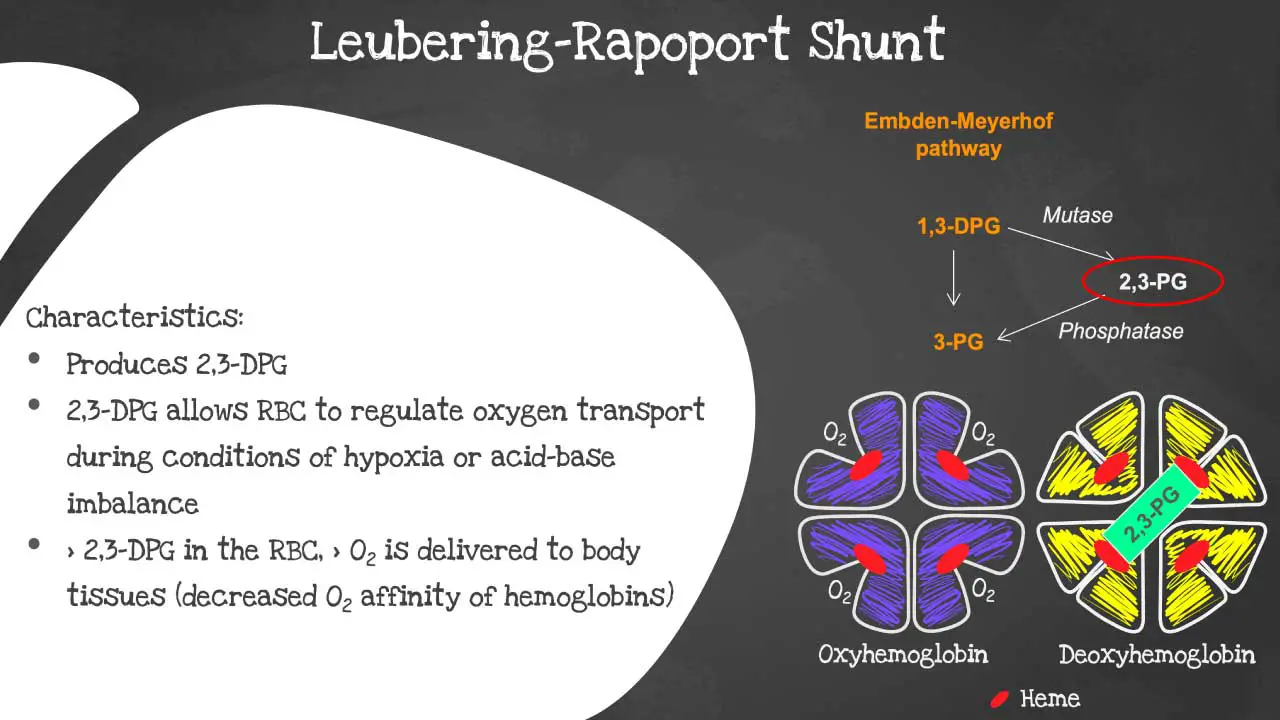
The following substrates are involved in the Luebering-Rapoport shunt:
- 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG)
- 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG)
- 3-phosphoglycerate
The key metabolism enzyme in the Luebering-Rapoport shunt is bisphosphoglycerate mutase (BPGM). This enzyme is responsible for converting 1,3-BPG to 2,3-DPG.
2,3-DPG is a key regulator of oxygen release from hemoglobin. It binds to hemoglobin and reduces its affinity for oxygen. This means that 2,3-DPG helps to promote the release of oxygen in the tissues, where it is needed most.
2,3-DPG deficiency can occur as a result of a number of factors, including:
- High altitude
- Chronic lung disease
- Congestive heart failure
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Hypophosphatemia
- Certain medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen
2,3-DPG deficiency can lead to a number of problems, including:
- Decreased oxygen delivery to the tissues
- Increased risk of lactic acidosis
- Impaired exercise tolerance
Treatment for 2,3-DPG deficiency typically involves addressing the underlying cause. For example, if 2,3-DPG deficiency is caused by high altitude, treatment may involve moving to a lower altitude or taking medications to increase oxygen levels in the blood.
Oxygen dissociation curve
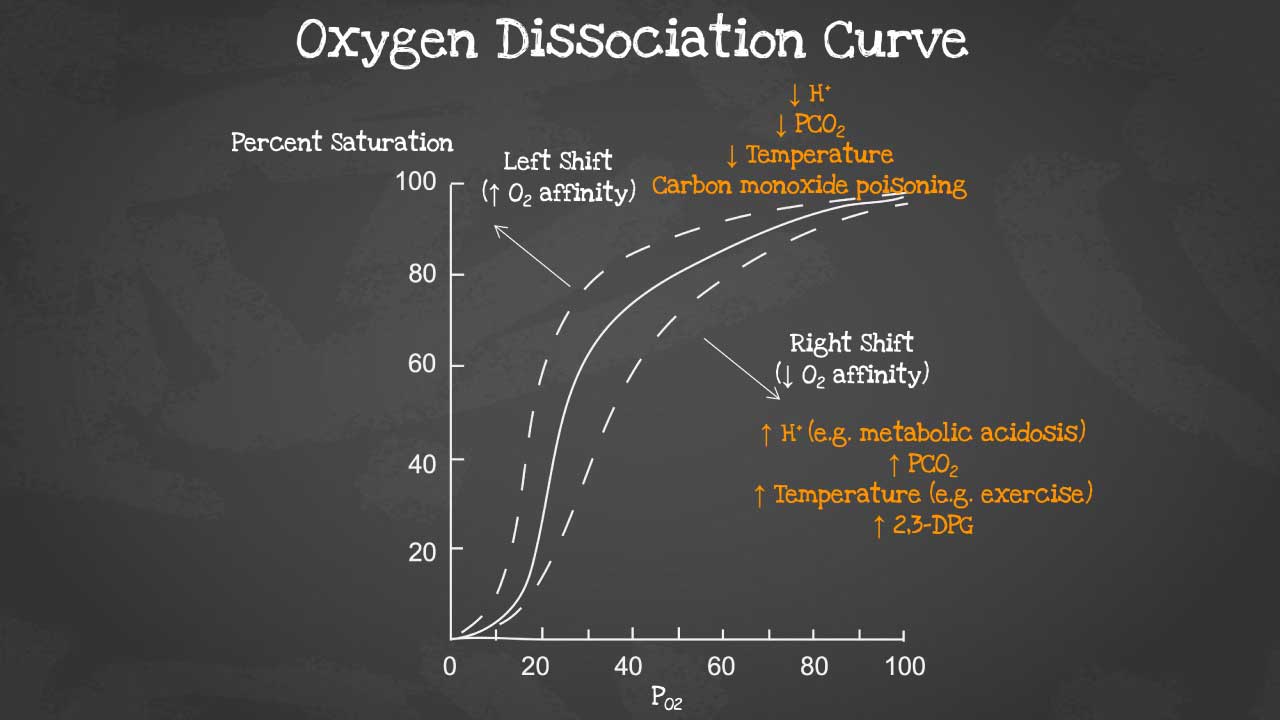
The oxygen dissociation curve (ODC) is a graph that shows the relationship between the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) and the percentage of hemoglobin that is saturated with oxygen (HbO2 saturation). The ODC is a sigmoid curve, which means that it has a steep slope at low and high PO2 values, and a flatter slope in the middle range.
Function of oxygen dissociation curve
The ODC is an important tool for understanding how oxygen is transported and released in the body. In the lungs, where PO2 is high, hemoglobin becomes saturated with oxygen. As the blood circulates through the body, oxygen diffuses from the blood into the tissues, where PO2 is lower. The ODC shows that hemoglobin has a lower affinity for oxygen at lower PO2 values, which means that oxygen is more easily released to the tissues.
Factors that regulate the oxygen dissociation curve
The ODC can be regulated by a number of factors, including:
- PCO2: Higher PCO2 values lead to more oxygen release, while lower PCO2 values lead to lower oxygen release.
- pH: A lower pH (more acidic environment) shifts the ODC to the right, which means that hemoglobin has a lower affinity for oxygen. This is important because it helps to promote the release of oxygen in the tissues, which are typically more acidic than the blood.
- 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG): 2,3-DPG is a molecule that binds to hemoglobin and reduces its affinity for oxygen. This is also important for promoting the release of oxygen in the tissues.
- Temperature: Temperature also has an effect on the ODC. A higher temperature shifts the ODC to the right, which means that hemoglobin has a lower affinity for oxygen. This is because higher temperatures increase the rate of metabolism, which increases the demand for oxygen.
A right shift of the oxygen dissociation curve (ODC) means that hemoglobin has a lower affinity for oxygen, and therefore releases oxygen more easily to the tissues. A left shift of the ODC means that hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen, and therefore holds on to oxygen more tightly.
For example, when a person runs a marathon, the muscles will have an increased metabolic rate and consequently need more oxygen. Not only that, carbon dioxide and lactic acid are produced and body temperature increases too. So when this condition occurs, there will be a right-shift in the oxygen dissociation curve to release more oxygen from the RBCs to the tissue as required.
Factors that cause a right shift of the ODC:
- Increased PCO2
- Decreased pH
- Increased 2,3-DPG levels
- Increased temperature
Factors that cause a left shift of the ODC:
- Decreased PCO2
- Increased pH
- Decreased 2,3-DPG levels
- Decreased temperature
Physiological significance of right and left shifts of the ODC:
- A right shift of the ODC promotes oxygen release to the tissues, which is important in areas of the body where oxygen levels are low, such as during exercise or in high altitudes.
- A left shift of the ODC promotes oxygen loading in the lungs, which is important in areas of the body where oxygen levels are high.
Clinical significance of right and left shifts of the ODC:
- A right shift of the ODC can be seen in patients with anemia (low red blood cell count), chronic lung disease, and heart failure.
- A left shift of the ODC can be seen in patients with polycythemia vera (elevated red blood cell count) and sickle cell anemia.
Examples of right and left shifts of the ODC in real life:
- A high-altitude climber would experience a right shift of their ODC, as their body would need to release more oxygen to the tissues to meet the increased demand.
- A patient with sickle cell anemia would experience a left shift of their ODC, as their abnormal hemoglobin molecules have a higher affinity for oxygen.
Overall, the right and left shifts of the oxygen dissociation curve are important physiological mechanisms that help to ensure that the body’s tissues receive the oxygen they need.
Clinical significance of the oxygen dissociation curve
The ODC is a useful tool for clinicians in assessing and managing patients with a variety of conditions, such as anemia (low red blood cell count), respiratory failure, and heart failure.
For example, in a patient with anemia (low red blood cell count), the ODC can be used to assess the severity of the anemia and to guide treatment decisions. In a patient with respiratory failure, the ODC can be used to assess the effectiveness of oxygen therapy.
Red blood cell (RBC) membrane
The red blood cell (RBC) is a biconcave shaped cell of approximately 7.5 um in diameter and 2 um thick. The biconcave shape allows it to have a high surface to volume ratio for optimal gaseous exchange as well as to be able to be deformed to pass through microcapillaries of 3 um in diameter.
What makes up the red blood cell membrane?
The red blood cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer that surrounds the red blood cell (RBC). It is made up of a lipid bilayer, a membrane skeleton, and a glycocalyx.
The phospholipid bilayer has an asymmetric phospholipid distribution. This layer is also where glycolipids that carry red blood cell (RBC) antigens and Rh antigens are embedded. Phospholipid molecules have a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail. The hydrophilic heads face the outside and inside of the cell, while the hydrophobic tails face each other. It is semi-permeable and forms a barrier between the cytoplasm within the cell from the extracellular environment.
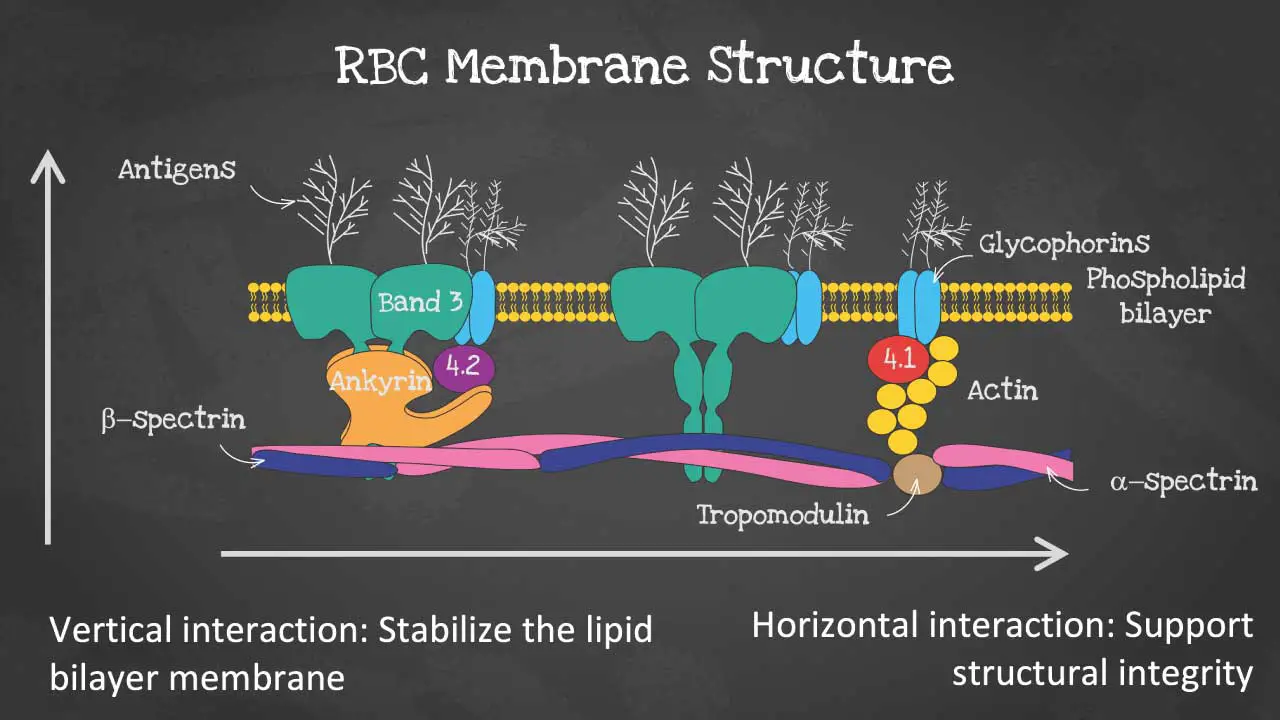
The membrane skeleton is a network of proteins that lies on the inside of the lipid bilayer. The membrane skeleton helps to maintain the shape of the red blood cell (RBC) and to protect it from damage. The membrane structure also provides permeability to allow water and electrolytes to exchange via the cation pumps.
As for the membrane proteins, there are transmembrane proteins also known as integral proteins making up the ion transport channels like the Band 3 proteins, the glycophorins and aquaporins which transport water.
The cytoskeleton are peripheral proteins which are located on the cytoplasmic surface of the lipid bilayer. The cytoskeleton is responsible for membrane elasticity and stability. It is anchored to the integral proteins via actin, spectrin, protein 4.1, band 4.2, ankyrin and other proteins that form nodes called the junctional complexes.
The glycocalyx is a layer of carbohydrates that is attached to the outside of the lipid bilayer. The glycocalyx helps to protect the RBC from the immune system and to promote cell-cell adhesion.
Functions of the red blood cell membrane
The red blood cell membrane has a number of important functions, including:
- Protection: The red blood cell membrane protects the red blood cell (RBC) from damage from the immune system and from other environmental factors.
- Shape maintenance: The red blood cell membrane helps to maintain the red blood cell’s biconcave shape. This shape is important for efficient oxygen transport.
- Transport: The red blood cell membrane contains proteins that transport oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other molecules across the membrane.
- Cell-cell interactions: The red blood cell membrane contains proteins that allow red blood cells (RBCs) to interact with other cells, such as the cells of the blood vessel wall.
Red blood cell membrane proteins
The red blood cell membrane is regulated by a number of factors, including the cytoskeleton, spectrin, ankyrin, actin, band 4.1, and protein 4.2.
- Cytoskeleton: A network of proteins that lies on the inside of the lipid bilayer. The cytoskeleton helps to maintain the shape of the red blood cell (RBC) and to protect it from damage.
- Spectrin: A major protein of the cytoskeleton. It is responsible for the biconcave shape of the RBC.
- Ankyrin: A protein that links the cytoskeleton to the lipid bilayer. It is essential for maintaining the integrity of the membrane.
- Actin: A protein that is involved in cell movement and cell shape. It also plays a role in the regulation of the red blood cell membrane.
- Band 4.1 and protein 4.2 are proteins that link the cytoskeleton to the glycocalyx. They are essential for maintaining the integrity of the membrane and for promoting cell-cell adhesion.
Disorders of the red blood cell membrane
There are a number of disorders that can affect the red blood cell membrane. These disorders can be caused by genetic mutations or by environmental factors.
Some of the most common red blood cell membrane disorders include:
- Hereditary spherocytosis: This disorder is caused by a mutation in a gene that encodes a protein of the cytoskeleton. The mutation leads to the production of defective proteins, which results in the formation of spherical red blood cells (RBCs).
- Elliptocytosis: This disorder is caused by a mutation in a gene that encodes a protein of the cytoskeleton. The mutation leads to the production of defective proteins, which results in the formation of elliptical red blood cells (RBCs).
- Stomatocytosis: This disorder is caused by a mutation in a gene that encodes a protein that transports ions across the lipid bilayer, causing the red blood cells (RBCs) to become more fragile and prone to developing the stomatocyte (mouth-like slit or indentation in the center) shape. This can lead to hemolytic anemia, where red blood cells are destroyed prematurely.
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and removes carbon dioxide from the tissues. It is a complex protein made up of four globin chains and four heme groups. Heme groups contain iron, which is essential for oxygen binding.
Why is hemoglobin important?
Hemoglobin is important because it allows the body to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently. Oxygen is essential for the production of energy, and carbon dioxide is a waste product that must be removed from the body.
Where is hemoglobin found?
Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells. Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow and are released into the bloodstream. They circulate throughout the body, carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Hemoglobin can also be found in other tissues, such as the muscles and the liver. However, the highest concentration of hemoglobin is found in red blood cells.
Composition of hemoglobin
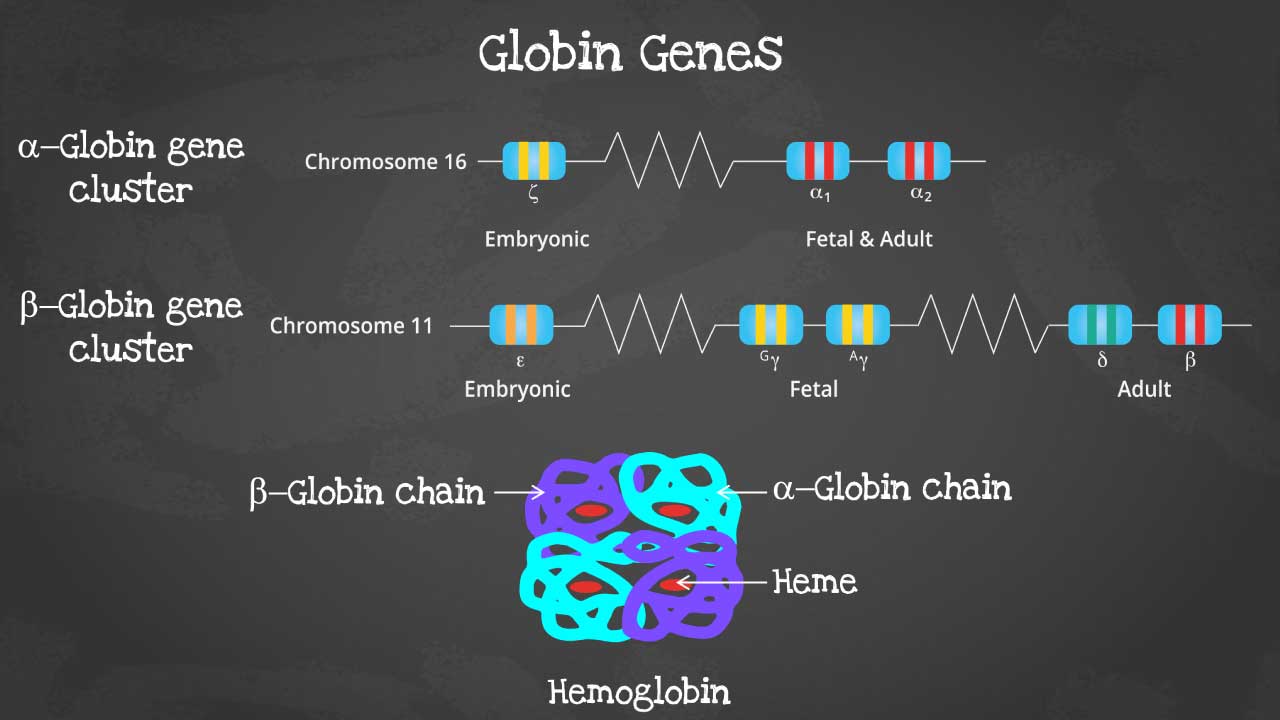
This captivating image unveils the intricate arrangement of genes within each cluster, highlighting the embryonic and fetal globin genes including zeta, epsilon and gamma globin genes that contribute to hemoglobin’s developmental diversity.
Hemoglobin is a complex protein made up of four globin chains and four heme groups. Heme groups contain iron, which is essential for oxygen binding.
Globin chains are polypeptide chains that are made up of amino acids. There are two types of globin chains in hemoglobin: alpha-like chains and beta-like chains. Adult hemoglobin (HbA) has two alpha chains and two beta chains.
Heme groups are flat, ring-shaped molecules that contain iron. The iron atom in the heme group binds to oxygen.
The four globin chains and four heme groups of hemoglobin are arranged in a tetrahedral structure. This structure allows hemoglobin to bind to four molecules of oxygen.
Hemoglobin subtypes
There are different subtypes of hemoglobin according to different stages of development. The hemoglobin is a tetrameric structure of 2 alpha-like and 2 beta-like globin chains interconnected by specific points and each folded globin chain carries a heme peptide with an iron atom in the center. Each iron atom can carry 1 molecule of oxygen.
The alpha globin gene cluster is found on chromosome 16 while the beta globin gene cluster is found on chromosome 11. The genes in the cluster are arranged according to the order of development and at different stages of development, different hemoglobins subtypes are formed to have different oxygen affinities.
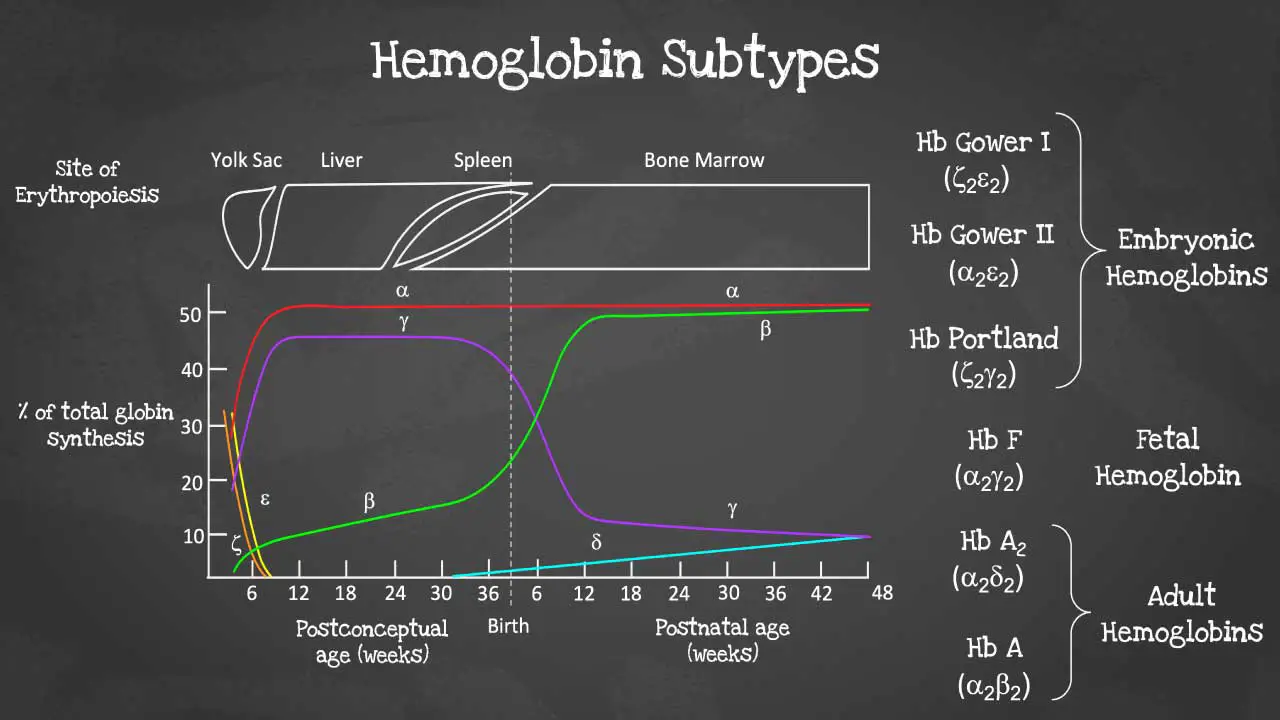
Different gene expressions are predominant at different times during fetal development especially for gamma and beta expression. These facilitate the formation of different subtypes of hemoglobin. These different hemoglobin subtypes have different oxygen affinity.
For example, fetal hemoglobin or Hb F have a higher oxygen affinity compared to Hb A to allow for oxygen exchange between the mother and the developing fetus and is predominant during fetal development. However, Hb F switches to Hb A which is more efficient in oxygen delivery once the baby is born at around 6 months after birth. In a healthy adult, approximately 96 – 98 % of the hemoglobins are Hb A, with some Hb A2 and less than 1% of Hb F.
Functions of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin has a number of important functions, including:
Oxygen transport: Hemoglobin is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. It does this by binding to oxygen in the lungs and releasing it in the tissues.
Carbon dioxide transport: Hemoglobin also helps to transport carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. It does this by binding to carbon dioxide in the tissues and releasing it in the lungs.
Regulation of blood pH: Hemoglobin helps to regulate blood pH by acting as a buffer. This means that it can absorb or release hydrogen ions depending on the pH of the blood.
Nitric oxide signaling: Hemoglobin also plays a role in nitric oxide signaling. Nitric oxide is a molecule that helps to regulate blood pressure and blood flow.
Hemoglobin synthesis
Hemoglobin synthesis is the process by which hemoglobin is produced. It occurs in the late stages of red blood cell development, called erythropoiesis, and takes place primarily in the bone marrow.
Hemoglobin synthesis pathway
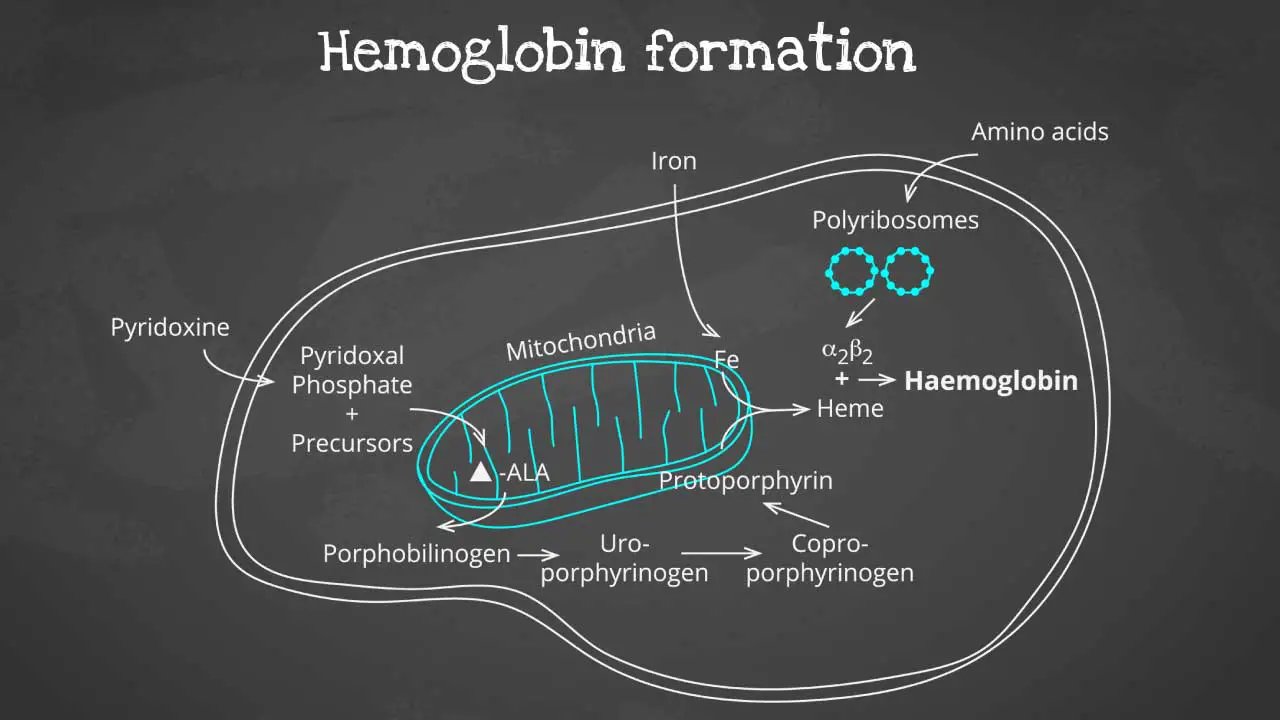
Hemoglobin synthesis is a complex process that involves multiple steps, including:
- Production of globin chains: Globin chains are the protein subunits of hemoglobin. There are two types of globin chains: alpha chains and beta chains. Adult hemoglobin (HbA) has two alpha chains and two beta chains.
- Production of heme groups: Heme groups are non-protein molecules that contain iron. Iron is essential for oxygen binding.
- Assembly of hemoglobin: The globin chains and heme groups are assembled into the final hemoglobin molecule.
The heme part is synthesized in a series of steps in the mitochondria and cytosol of immature RBC, while the globin protein parts are synthesized by ribosomes in the cytosol. These then come together to form the hemoglobin.
Production of globin chains
Globin chains are produced in the ribosomes of red blood cells. The ribosomes are tiny organelles that read genetic information from mRNA and translate it into proteins.
The genetic information for globin chains is encoded in the DNA of the red blood cell nucleus. When a red blood cell is maturing, its DNA is transcribed into mRNA. The mRNA is then transported to the ribosomes, where it is translated into globin chains.
Production of heme
Heme is produced in the mitochondria of red blood cells. The mitochondria are organelles that produce energy for the cell.
The production of heme is a complex process that involves multiple steps. One of the key steps is the insertion of iron into a protoporphyrin ring. Protoporphyrin is a molecule that is synthesized in the mitochondria.
Once the iron has been inserted into the protoporphyrin ring, the heme is complete. Heme is then transported out of the mitochondria and into the cytoplasm of the red blood cell.
Assembly of hemoglobin
The globin chains and heme groups are assembled into the final hemoglobin molecule in the cytoplasm of the red blood cell.
The globin chains first assemble into a dimer. The heme groups are then inserted into the dimer to form the complete hemoglobin molecule.
Once the hemoglobin molecule is formed, it is packaged into vesicles and transported to the surface of the red blood cell. The vesicles then fuse with the cell membrane, releasing the hemoglobin into the bloodstream.
Heme synthesis
Heme is a non-protein molecule that contains iron. It is an essential component of hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells. Heme is also found in other proteins, such as myoglobin, cytochromes, and catalase. Heme is a porphyrin ring complexed with ferrous iron and protoporphyrin IX. The porphyrin ring is a cyclic compound formed by fusion
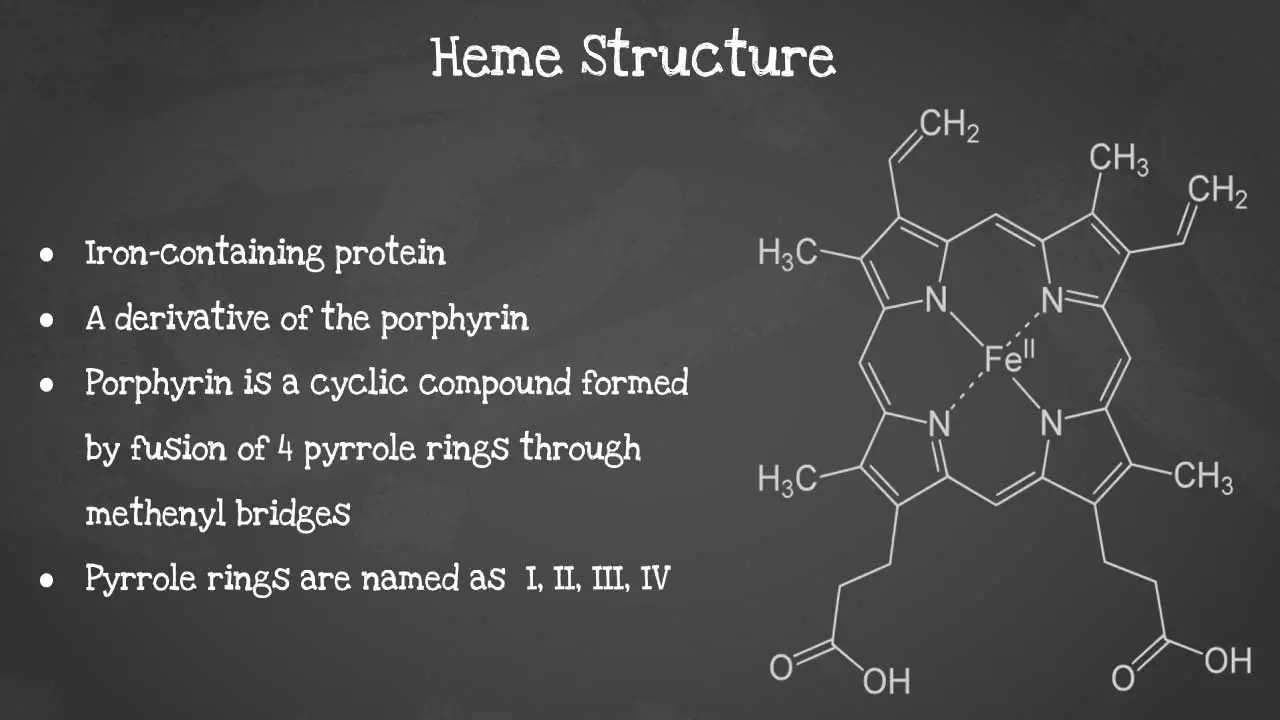
This captivating image unveils the intricate arrangement of atoms, revealing the iron-containing porphyrin ring at the heart of heme’s remarkable functionality including its characteristics
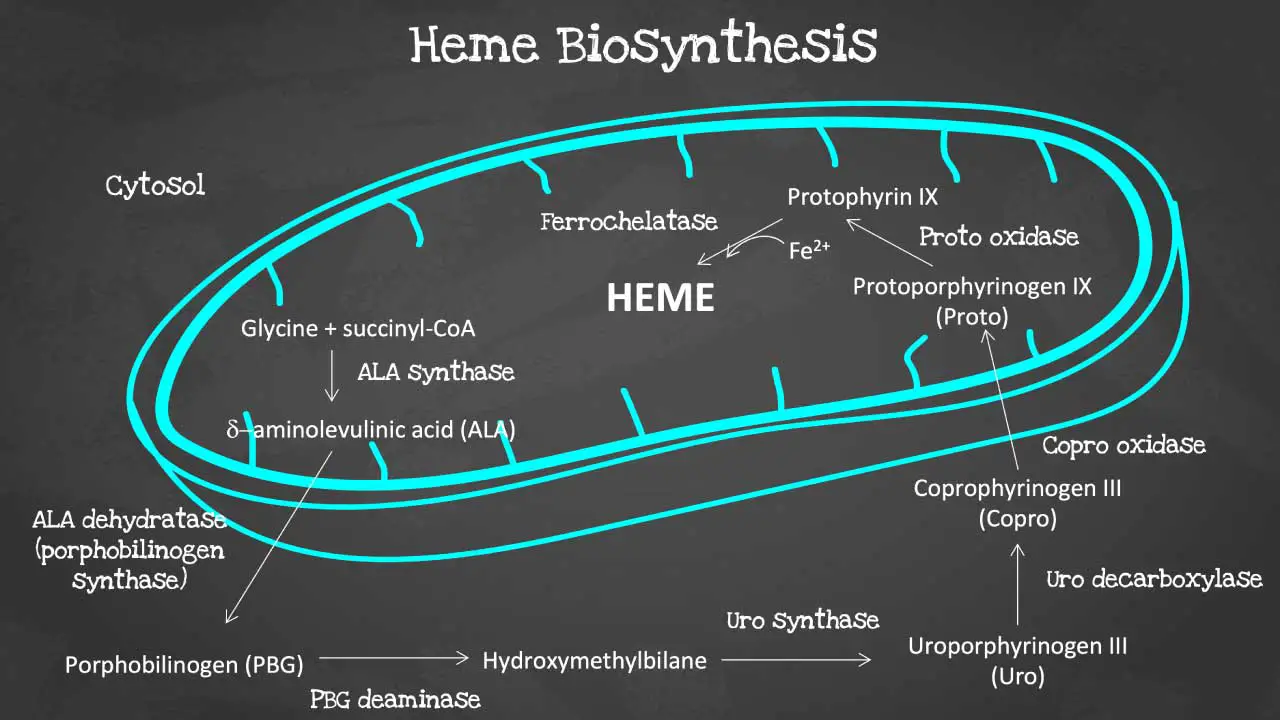
Porphyrin synthesis is the process that produces heme. Heme synthesis occurs partly in the mitochondria and partly in the cytosol. The biosynthesis involves an 8-step enzymatic pathway, including:
- Condensation of glycine and succinyl-CoA to form ALA: The first step in heme synthesis is the condensation of glycine and succinyl-CoA to form 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA). ALA is synthesized by the enzyme ALA synthase.
- Formation of PBG: Two molecules of ALA condense to form porphobilinogen (PBG). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme ALA dehydratase.
- Formation of HMB: Four molecules of PBG condense to form hydroxymethylbilane (HMB). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme PBG deaminase.
- Cyclization of HMB to form URO: HMB cyclizes to form uroporphyrinogen III (URO). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme uroporphyrinogen III synthase.
- Decarboxylation of URO to form CPO: URO is decarboxylated to form coproporphyrinogen III (CPO). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase.
- Oxidation of CPO to form PP: CPO is oxidized to form protoporphyrin IX (PP). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase.
- Insertion of iron into PP to form heme: Iron is inserted into PP to form heme. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme ferrochelatase.
Disorders of heme synthesis
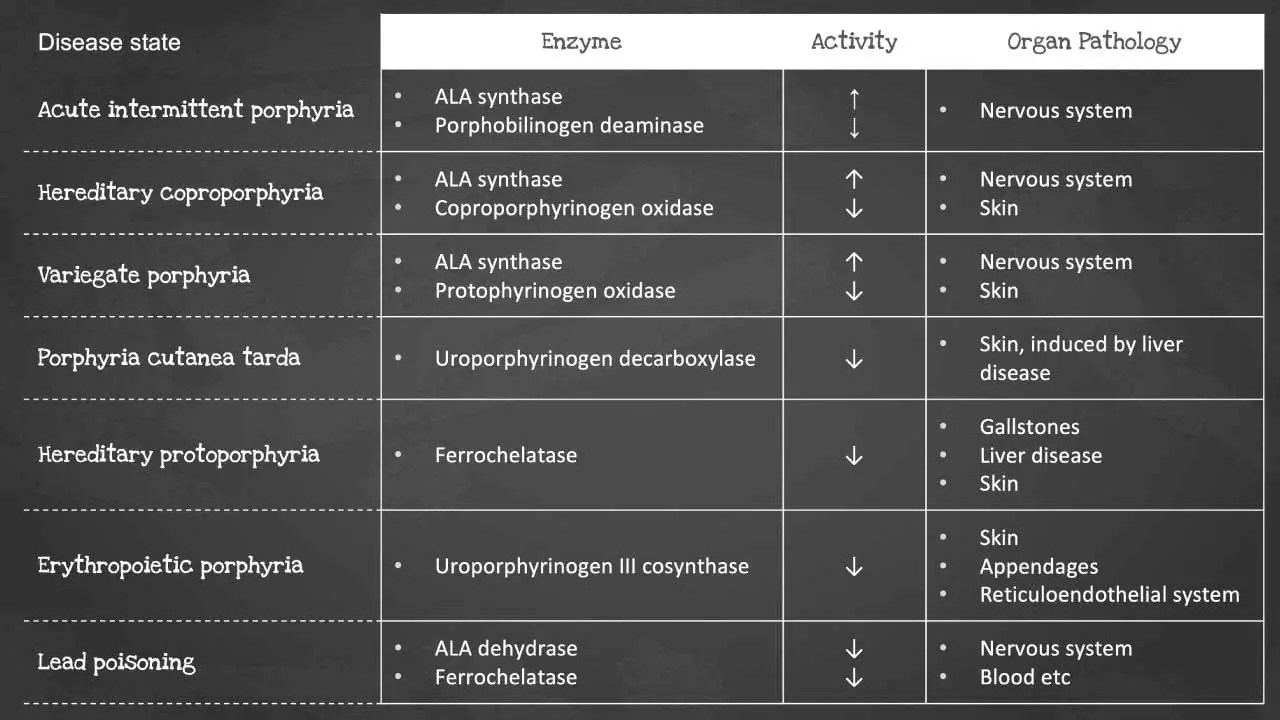
Heme synthesis is a biochemical pathway which requires a number of steps, substrates and enzymes. A deficiency in an enzyme or substrate leads to accumulation of intermediates of heme synthesis in blood, tissues, and urine leading to a clinically significant outcome of a group of disorders called porphyrias.
There are a number of disorders that can affect heme synthesis. Porphyrias are hepatic or erythropoietic. They can be acute or chronic, leading to neurologic dysfunction, mental disturbance or photosensitivity.
Acute intermittent porphyria occurs due to a mutation in the PBG deaminase, which leads to an accumulation of ALA and porphobilinogen. It does not affect erythroblasts. The disease presents as severe abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation, abdominal distention and behavioural changes.
Porphyria cutanea tarda on the other hand is the most common type of porphyria. It is due to a deficiency or decreased activity in uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase. It can be acquired or hereditary. Uroporphyrin accumulates in the urine. Symptoms include photosensitivity leading to blisters developing in sun-exposed areas and hyperpigmentation and hepatic injury.
Erythropoietic porphyria occurs due to a deficiency in ferrochelatase. Deficiency leads to an accumulation of protoporphyrin IX in erythrocytes. Symptoms include painful photosensitivity like swelling, burning and itching in sun-exposed areas. Lead interacts with zinc cofactors for ALA dehydratase and ferrochelatase leading to inhibition of these 2 enzymes in lead poisoning. This inhibition leads to mostly ALA and some protoporphyrin IX accumulating in the urine. Symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, fatigue, irritability and developmental disability in children.
Some of the most common disorders of heme synthesis include:
- Acute intermittent porphyria
- Congenital erythropoietic porphyria
- Hereditary coproporphyria
- Variegate porphyria
Aging and destruction of red blood cells (RBCs)
Aging of red blood cells (RBCs)
Red blood cells (RBCs) have a lifespan of about 120 days, after which they are removed from the circulation and about 90% of the red blood cells (RBCs) are destroyed in the reticuloendothelial system and the rest in the lumen of the vascular system.
The aging of red blood cells (RBCs) is a complex process that is not fully understood. Red blood cells (RBCs) age when there is a physiological decrease of ATP generation for the ion pumps, reduced cholesterol and phospholipid amounts leading to loss of selective permeability, declining methaemoglobin reductase activity causing increased oxidative stress and accumulation of IgG on the RBC surface prompting the destruction of the RBC by enzymatic degradation or macrophage phagocytosis.
However, it is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Oxidative stress: Red blood cells (RBCs) are constantly exposed to oxidative stress, which is damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can damage the red blood cell (RBC) membrane, proteins, and DNA.
- Glycation: Glycation is the process by which glucose molecules bind to proteins. This can damage the red blood cell (RBC) membrane and proteins.
- Proteolysis: Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins. Proteolysis of red blood cell (RBC) proteins can lead to loss of function and cell death.
As red blood cells (RBCs) age, they undergo a number of changes, including:
- Decreased deformability: Red blood cells (RBCs) become less deformable as they age. This makes it more difficult for them to pass through small capillaries.
- Increased density: Red blood cells (RBCs) become more dense as they age. This makes them more likely to be removed from the circulation by the spleen.
- Loss of surface proteins: Red blood cells (RBCs) lose surface proteins as they age. This can make them more susceptible to attack by the immune system.
- Changes in hemoglobin: Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells (RBCs) that carries oxygen. Hemoglobin undergoes changes as red blood cells (RBCs) age, which can reduce its ability to carry oxygen.
The aging of red blood cells (RBCs) is a normal process that occurs in everyone. However, there are a number of conditions that can accelerate the aging process, such as:
- Anemia: Anemia is a condition in which the red blood cells do not have enough hemoglobin. This can lead to premature cell death causing low red blood cell count.
- Diabetes: Diabetes is a condition that causes high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can damage red blood cells (RBCs) and accelerate the aging process.
- Sickle cell anemia: Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder that causes red blood cells (RBCs) to be abnormally shaped. Sickle cells are more likely to be destroyed by the spleen and have a shorter lifespan.
- Thalassemia: Thalassemia is a genetic disorder that reduces the production of hemoglobin. This can lead to anemia and premature cell death causing low red blood cell count.
The aging of red blood cells (RBCs) can also be accelerated by certain lifestyle factors, such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Destruction of red blood cells (RBCs)
When the RBC ruptures, the hemoglobin is ingested by the macrophage. The globin chains are then broken down to form amino acids and are then reused for protein synthesis.
Iron is released from the heme of hemoglobin. Iron is then transported by transferrin into different tissues to be stored in ferritin. It can also be transported into the bone marrow for making new hemoglobin.
The remaining structure is converted into biliverdin. Then converted into bilirubin. Free bilirubin is transported by albumin into the liver. Liver cells will conjugate the bilirubin which is then excreted as part of the bile into the small intestine. Intestinal bacteria convert the bilirubin into bilirubin derivatives. Some of the bilirubin derivatives are absorbed into the blood and excreted in the kidneys as urobilin in the urine. Other bilirubin derivatives are converted into stercobilin and excreted in the feces.
Clinical Significance of the Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
Any impairment in oxygen delivery due to issues with RBCs directly impacts organ function and overall bodily processes. Symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, and pallor are common indicators of inadequate oxygenation, often pointing to underlying RBC disorders.
A complete blood count (CBC), which includes an RBC count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and red blood cell indices (MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW), is a cornerstone of diagnostic medicine.
Blood Disorders (Anemias and Polycythemias)
- Anemia (Low RBCs/Hemoglobin): This is the most common RBC-related disorder. A low RBC count, hemoglobin, or hematocrit indicates anemia, meaning the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity is reduced. The specific type of anemia can often be identified by examining the RBC indices.
- Microcytic Anemia (small RBCs, low MCV): Often due to iron deficiency (most common), thalassemia, or chronic disease.
- Macrocytic Anemia (large RBCs, high MCV): Commonly caused by Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, liver disease, or certain medications.
- Normocytic Anemia (normal size RBCs): Can be due to acute blood loss, chronic kidney disease (due to low erythropoietin), bone marrow failure (e.g., aplastic anemia), or inflammation.
- Hemolytic Anemia: Characterized by premature destruction of RBCs, which can be due to autoimmune conditions, genetic defects (e.g., sickle cell disease, G6PD deficiency), or infections.
- Polycythemia/Erythrocytosis (High RBCs): An elevated RBC count can lead to thicker blood, increasing the risk of blood clots, heart attack, and stroke. Causes can be:
- Primary Polycythemia Vera: A myeloproliferative disorder where the bone marrow produces too many RBCs (and often other blood cells).
- Secondary Polycythemia: Often a physiological response to chronic low oxygen levels (hypoxia), such as in:
- Chronic lung diseases (COPD, pulmonary fibrosis)
- Congenital heart disease
- High altitude living
- Sleep apnea
- Certain kidney or liver tumors that produce excess erythropoietin.
- Relative Polycythemia: Due to dehydration, where the blood plasma volume is low, making the RBCs appear more concentrated.
Monitoring Disease Progression and Treatment Effectiveness
- Chronic Diseases: RBC parameters are vital in monitoring the progression of chronic conditions like kidney disease (anemia is common), chronic inflammatory diseases, and certain cancers that affect bone marrow function.
- Cancer Treatment: Chemotherapy and radiation can suppress bone marrow activity, leading to anemia. Monitoring RBC counts helps manage these side effects and guide supportive care, including blood transfusions or erythropoietin-stimulating agents.
- Nutritional Status: RBC indices help identify nutritional deficiencies (iron, B12, folate) that impact red blood cell production.
- Blood Loss: Rapid drops in hemoglobin and hematocrit indicate acute blood loss, guiding immediate intervention.
Specialized RBC Parameters
Beyond the basic counts, other RBC-related parameters offer specific clinical insights.
- Reticulocyte Count: Measures immature RBCs. A high count indicates the bone marrow is actively producing more RBCs (e.g., in response to anemia or blood loss), while a low count suggests impaired bone marrow function.
- Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW): Measures the variation in RBC size. An elevated RDW (anisocytosis) often points to nutritional deficiencies (iron, B12, folate) or certain anemias where new cells are different in size from existing ones. It’s also increasingly recognized as a prognostic marker in various cardiovascular and inflammatory conditions.
- Blood Grouping and Cross-matching: The antigens on the surface of RBCs determine blood type (A, B, O, Rh). This is critically important for safe blood transfusions, preventing life-threatening hemolytic transfusion reactions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a normal blood count?
A “normal blood count” refers to the typical range of values for various components measured in a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test. Normal ranges can vary slightly between different laboratories and also depend on factors like age, sex, and even altitude.
General normal ranges for the key components of a CBC for adults
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
- Men: 4.35 to 5.65 trillion cells/L (or 4.35 to 5.65 million cells/mcL)
- Women: 3.92 to 5.13 trillion cells/L (or 3.92 to 5.13 million cells/mcL)
- Hemoglobin (Hb or Hgb)
- Men: 13.2 to 16.6 grams/dL (132 to 166 g/L)
- Women: 11.6 to 15.0 grams/dL (116 to 150 g/L)
- Hematocrit (Hct): The percentage of blood volume that is made up of red blood cells.
- Men: 38.3% to 48.6%
- Women: 35.5% to 44.9%
- White Blood Cells (WBCs)
- Adults: 3.4 billion to 9.6 billion cells/L (or 3,400 to 9,600 cells/mcL)
- Platelets
- Adults: 150 billion to 400 billion cells/L (or 150,000 to 400,000 cells/mcL)
What level of RBC is dangerously low?
“Dangerously low” RBC levels aren’t solely determined by a single numerical value, but rather by the patient’s clinical status, symptoms, the rate of the drop, and underlying health conditions.
While healthcare providers primarily focus on hemoglobin (Hb) levels and hematocrit (Hct) as key indicators of anemia (low RBC count), here’s a general guideline for what is considered dangerously low.
Hemoglobin (Hb) Levels
- Life-threatening Anemia: A hemoglobin level of less than 6.5 g/dL (or 65 g/L) is generally considered life-threatening and typically requires immediate medical intervention, often including blood transfusions, especially if the patient is symptomatic or hemodynamically unstable.
- Severe Anemia: Hemoglobin levels between 6.5 to 7.9 g/dL (or 65 to 79 g/L) are considered severe. At this level, patients are usually highly symptomatic, and transfusions are often indicated, especially if symptoms of tissue hypoxia (lack of oxygen) are present.
- Moderate Anemia: Hemoglobin levels between 8.0 to 10.0 g/dL (or 80 to 100 g/L) are considered moderate. While not immediately life-threatening for everyone, symptoms can be significant, and treatment (which may or may not include transfusion, depending on the cause and symptoms) is necessary.
Symptoms of Dangerously Low RBCs/Hemoglobin
When RBCs are dangerously low, the body’s tissues and organs don’t receive enough oxygen. This can lead to severe and potentially life-threatening symptoms, which worsen with the severity and rapidity of the hemoglobin drop:
- Extreme Fatigue and Weakness: Profound lack of energy that impairs daily activities.
- Severe Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea): Difficulty breathing, even at rest or with minimal exertion.
- Dizziness, Lightheadedness, or Fainting (Syncope): Due to insufficient oxygen to the brain.
- Chest Pain (Angina) or Palpitations: The heart works harder to compensate for the lack of oxygen, leading to strain. This is particularly concerning for individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
- Pallor: Extremely pale skin, lips, and nail beds.
- Rapid or Irregular Heartbeat (Tachycardia): The heart beats faster to try and deliver more oxygen.
- Confusion or Altered Mental Status: In severe cases, due to brain hypoxia.
- Cold Hands and Feet: Poor circulation.
- Headaches: Often severe.
When are Blood Transfusions Indicated?
The decision to transfuse packed red blood cells (PRBCs) is a critical clinical judgment. While there are general guidelines, it’s highly individualized.
- Hemoglobin < 7 g/dL: For most stable, hospitalized patients, a restrictive transfusion strategy is often recommended, meaning transfusion if Hb falls below 7 g/dL.
- Hemoglobin < 8 g/dL with specific conditions: A higher threshold of 8 g/dL is often used for patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease (e.g., coronary artery disease, heart failure) or those experiencing active bleeding, or who are symptomatic despite a higher Hb level (e.g., chest pain, orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia unresponsive to fluids).
- Hemodynamically Unstable Patients: In cases of acute, massive blood loss (e.g., trauma, severe gastrointestinal bleeding), transfusions may be necessary regardless of the initial Hb level if the patient shows signs of shock (tachycardia, hypotension, altered mental status).
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and is specifically targeted towards medical students. It is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. While the information presented here is derived from credible medical sources and is believed to be accurate and up-to-date, it is not guaranteed to be complete or error-free. See additional information.
References
- Peter Klinken S. Red blood cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;34(12):1513-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00087-0.PMID: 12379271.
- Mohandas N, Gallagher PG. Red cell membrane: past, present, and future. Blood. 2008 Nov 15;112(10):3939-48. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-07-161166.
- Huisjes Rick, Bogdanova Anna, van Solinge Wouter W., Schiffelers Raymond M., Kaestner Lars, van Wijk Richard (2018). Squeezing for Life – Properties of Red Blood Cell Deformability . Frontiers in Physiology, 9. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2018.00656.
- Delaunay J. The molecular basis of hereditary red cell membrane disorders. Blood Rev. 2007 Jan;21(1):1-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2006.03.005. Epub 2006 May 30. PMID: 16730867.
- Daniels G. Functions of red cell surface proteins. Vox Sang. 2007 Nov;93(4):331-40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1423-0410.2007.00970.x. PMID: 18070278.
- D’Alessandro A, Anastasiadi AT, Tzounakas VL, Nemkov T, Reisz JA, Kriebardis AG, Zimring JC, Spitalnik SL, Busch MP. Red Blood Cell Metabolism In Vivo and In Vitro. Metabolites. 2023; 13(7):793. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070793.
- Franco RS. Measurement of red cell lifespan and aging. Transfus Med Hemother. 2012 Oct;39(5):302-7. https://doi.org/10.1159/000342232. Epub 2012 Aug 27. PMID: 23801920; PMCID: PMC3678251.
- Bain, B.J., Bates I., Laffan M. A. (2016). Dacie and Lewis practical haematology. Elsevier.
- Bain, B.J. (2017). A beginner’s guide to blood cells. Wiley Blackwell.
- Bain, B.J. (2022). Blood cells: A practical guide. Wiley.
- Dean L. Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2005. Chapter 1, Blood and the cells it contains. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2263/
- Barbalato L, Pillarisetty LS. Histology, Red Blood Cell. [Updated 2022 Nov 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539702/