
by MH Team | Apr 14, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Polycythemia is an abnormally high increase in red blood cells, leading to elevated hemoglobin and hematocrit. It can be absolute (true increase in RBC mass) or relative (due to decreased plasma volume). Classification ▾: Absolute polycythemia includes...

by MH Team | Apr 11, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Neutropenia is a quantitative deficiency of neutrophils, crucial for the innate immune system. Diagnosis relies on the absolute neutrophil count (ANC), classified by severity (mild, moderate, severe) and duration (acute, chronic). Causes ▾: Decreased bone...

by MH Team | Apr 9, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Infectious mononucleosis is an acute viral illness (primarily EBV) with classic triad: pharyngitis, fever, lymphadenopathy. Epidemiology ▾: Common in adolescents/young adults, spread globally, primarily via saliva. Causes ▾: Primarily Epstein-Barr...

by MH Team | Apr 7, 2025 | White Blood Cells
TL;DR Eosinophilia (high eosinophils), defined as an elevated eosinophil count above 500 cells/µL, is a laboratory finding, not a disease itself, that signals a potential underlying medical issue requiring investigation based on its severity and the...

by MH Team | Apr 6, 2025 | White Blood Cells
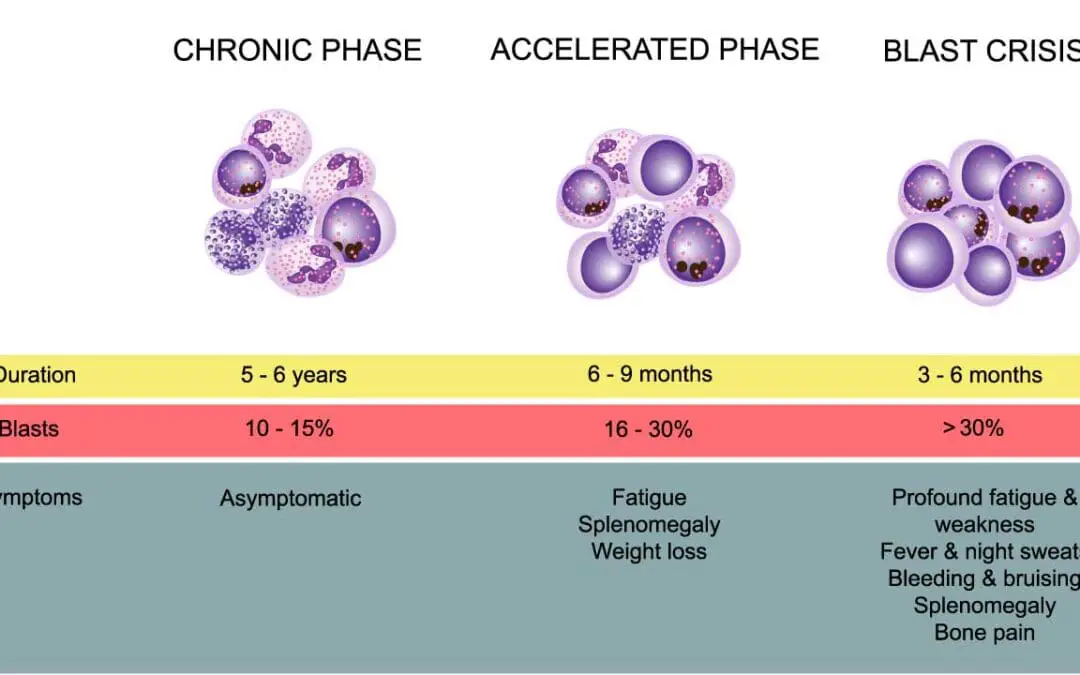
This blog post provides an overview of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) and its treatment strategies based on the most recent guideline (2025) from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). TL;DR Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are the primary treatment...


Recent Comments