Procedure At A Glance
The Periodic Acid-Schiff stain (PAS staining) is a cost-effective method to primarily used to identify and characterize various hematological disorders, especially leukemias.
- Fix air-dried blood/bone marrow films for 1 minute at room temperature.
- Rinse slides thoroughly in slowly running tap water for 1 minute.
- Immerse slides in Periodic Acid Solution for 10 minutes at room temperature.
- Rinse slides well.
- Immerse slides in Schiff’s Reagent for 20 minutes at room temperature (in the dark if possible, as Schiff’s is photosensitive).
- Wash slides in running tap water for 5-10 minutes.
- Counterstain with methyl green.
- Wash slides.
- Mount with a suitable mounting medium (e.g., DPX) and coverslip.
Introduction
The periodic acid Schiff stain or also known as PAS staining assay is a histochemical stain used to identify carbohydrates, including glycogen, mucopolysaccharides, and basement membranes. It is a simple and inexpensive stain that is widely used in pathology laboratories to diagnose a variety of diseases and conditions, including leukemia.
When used on peripheral blood, the periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) can be used to identify leukemic cells that contain increased amounts of glycogen or mucopolysaccharides. This can be helpful in differentiating between different types of leukemia, such as acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Principle of Periodic Acid Schiff Stain (PAS staining)
Periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) is a method used to identify glycogen in tissues. Periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) works by selectively oxidizing carbohydrate radicals, such as those found in glycols and related compounds, to produce dialdehydes. These dialdehydes react with Schiff’s reagent to produce a purple-magenta color. Periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) is helpful in diagnosing acute lymphoblastic leukemia and some cases of erythroleukemia.
Method differs slightly according to the manufacturer’s protocol.

Materials
- Absolute methanol
- Schiff’s reagent
- Period acid 1% w/v with distilled water
- Methyl green 4% with distilled water
- Unstained peripheral blood smear slide
Protocol
- Fix slides in absolute methanol for 5 – 10 minutes.
- Rinse the slide with slow running tap water for 1 minute.
- Submerge in periodic acid for 10 minutes.
- Rinse the slide with slow running tap water.
- Wipe the back of the slide and edges with Kim wipes. Be careful not to touch the smear.
- Submerge in Schiff’s reagent for 20 minutes.
- Rinse the slide with slow running tap water for 5 minutes.
- Counterstain with methyl green for 3 minutes.
- Rinse the slide with slow running tap water.
- Wipe the back of the slide and edges with Kim wipes. Be careful not to touch the smear.
- Dry the slide using the hair dryer on the lowest speed or air dry in a tilted position.
- Mount the slide with Depex and cover the zone of morphology with a cover slip.
- This slide is now ready for viewing.
Interpretation

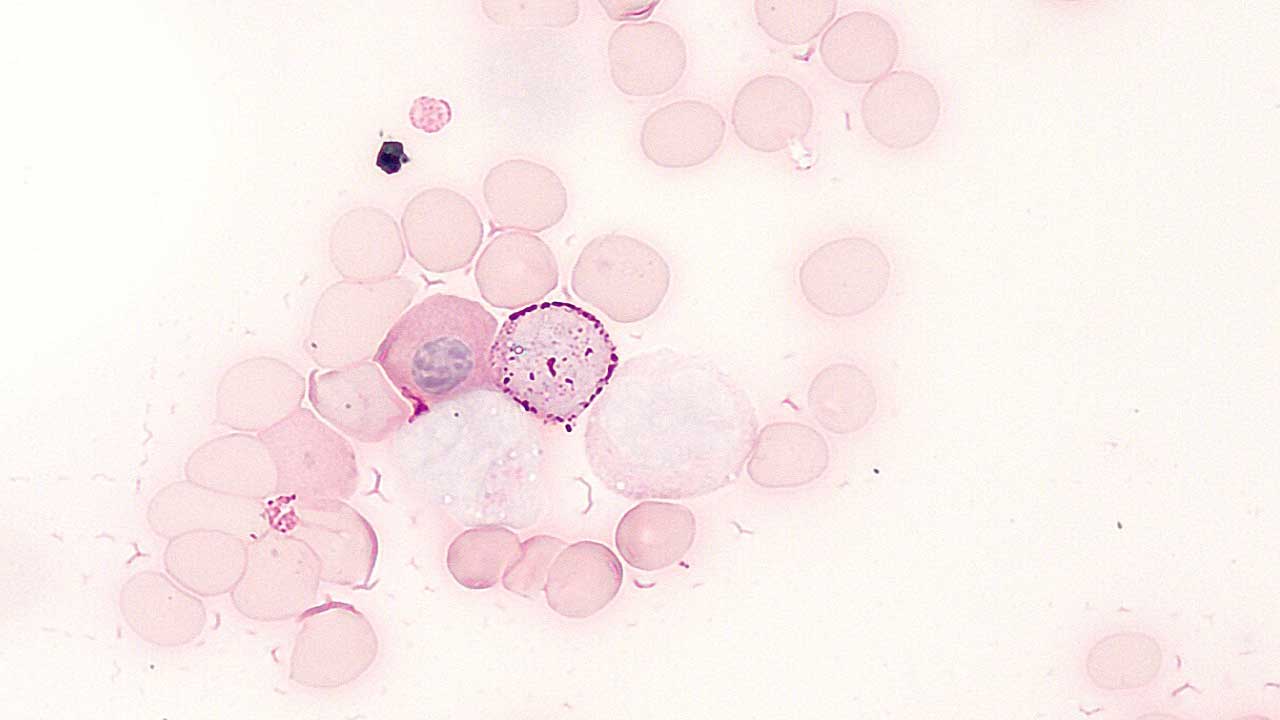
Periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) is used to identify glycogen in tissues. PAS positive cells stain magenta (red) in the cytoplasm, while the nucleus stains green.
- Neutrophils are a positive control for periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining). They show intense, confluent granular positivity.
- In acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the lymphoblasts are stained block positivity.
- Myeloblasts contain a few small PAS-positive granules.
- Monocytes and their precursors show variable diffuse positivity.
- The reaction in megakaryocytes and platelets is variable.
- Erythroleukemia and erythroid precursors of some thalassemia are periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) positive.
- Normal erythroid precursors and red blood cells are negative.
Periodic Acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) of blood cells
| Cell Type | PAS Staining | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Erythrocytes | Negative | Lack significant glycogen or other polysaccharide stores. |
| Neutrophils | Granular positivity | Neutrophils contain specific granules rich in glycoproteins and proteoglycans, which readily react with PAS stain, leading to intense, confluent granular positivity in the cytoplasm. This easily distinguishable staining pattern makes them good indicators of proper stain function. |
| Eosinophils | Negative | Granules primarily composed of proteins, not polysaccharides. |
| Basophils | Negative | Granules contain proteoglycans, but PAS staining typically yields negative results. |
| Lymphocytes | Weakly positive | Some lymphocytes, particularly activated ones, may exhibit faint cytoplasmic staining due to glycogen stores. |
| Megakaryoblasts | Negative | Lack significant glycogen or other PAS-positive structures. |
| Megakaryocytes | Negative | Similar to megakaryoblasts. |
| Platelets | Negative | Lack nuclei and cytoplasm, essential for PAS staining. |
| Lymphoblasts | Weakly positive | Similar to lymphocytes, can exhibit faint cytoplasmic staining due to glycogen. |
| Erythroblasts | Negative | Lack significant glycogen or other PAS-positive structures. |
| Monoblasts | Weakly positive | May exhibit faint cytoplasmic staining due to glycogen stores. |
| Macrophages | Variable | Can be positive depending on their activation state and glycogen content. Some types, like Kupffer cells in liver, are typically positive. |
| Myeloblasts | Negative | Lack significant glycogen or other PAS-positive structures. |
| Common lymphoid progenitor cells (CLPs) | Weakly positive | May show faint cytoplasmic staining due to developing glycogen stores. |
| Common myeloid progenitor cells (CMPs) | Negative | Similar to myeloblasts, lack significant PAS-positive structures. |
| HSCs (Hematopoietic stem cells) | Negative | Lack significant glycogen or other PAS-positive structures. |
Periodic Acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) positive hematological disorders
While periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) plays a role in hematological diagnosis, not all PAS-positive cases necessarily indicate disease. However, several hematological conditions exhibit PAS positivity, often serving as a clue for further investigation and diagnosis.
Leukemias
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): As previously discussed, ALL, particularly B-cell subtypes, frequently shows strong PAS positivity due to glycogen accumulation, altered membrane composition, and vacuoles.
- Erythroleukemia: This rare leukemia affects red blood cell precursors. Some types, like M6a and M7 in the French-American-British (FAB) classification, exhibit PAS-positive erythroblasts.
- Hairy Cell Leukemia: The neoplastic cells in this chronic lymphocytic leukemia subtype often stain weakly positive with PAS due to cytoplasmic inclusions.
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN)
- Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML): Some CMML patients show PAS-positive monocytes in the bone marrow.
- Mastocytosis: In systemic mastocytosis, bone marrow mast cells may exhibit weak PAS positivity due to their heparin content.
Other hematological conditions
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS): This group of bone marrow disorders can sometimes show PAS-positive erythroblasts, potentially indicating dyserythropoiesis (abnormal red blood cell development).
- Late Onset Pompe Disease: This genetic disorder can cause PAS-positive lymphocytes due to glycogen accumulation.
- Gaucher Disease: Certain subtypes of this lysosomal storage disorder can show PAS-positive Gaucher cells in the bone marrow.
Important Points
- PAS positivity alone is not diagnostic of any specific disease. It requires integration with other tests and clinical context for accurate diagnosis.
- The intensity and pattern of PAS staining can vary within a disease and across different cell types.
- PAS staining is not routinely used for primary diagnosis but can be helpful in certain situations, especially when combined with other techniques.
Troubleshooting
- Positive and Negative Controls: Always run a known positive control (e.g., kidney, liver with glycogen) and a negative control (e.g., a section treated with diastase for glycogen demonstration, or a blank slide) with each batch. This helps determine if the reagents are working correctly and if the staining is specific.
- Record Keeping: Document reagent lot numbers, preparation dates, incubation times, and any observations. This helps in tracing problems.
- Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always strictly follow the manufacturer’s instructions for commercially prepared reagents and kits, as formulations can vary.
- Fresh Reagents: Prepare fresh working solutions daily or as recommended.
- Clean Glassware: Ensure all glassware is meticulously clean and free of contaminants.
- Temperature Control: Maintain recommended temperatures for reagents and incubation steps.
| Problems | Cause | Solution |
| Weak or absent magenta/red color | Incorrect Reagent Preparation/Expiration Schiff’s Reagent: This is the most sensitive reagent. If it’s old, exposed to light/air, or improperly stored (should be refrigerated in a dark bottle), it can lose its reactivity. | Test the Schiff’s reagent by adding a few drops to 10ml of 37% formalin. A good reagent will rapidly turn red-purple. A deteriorating one will give a delayed or weak reaction, or turn deep blue-purple. If it fails the test, replace it. Store tightly capped in the refrigerator (2-8°C) away from light. |
| Incorrect Reagent Preparation/Expiration Periodic Acid: Ensure the periodic acid solution is fresh and at the correct concentration (e.g., 0.5% or 1%). Old or contaminated periodic acid can lose its oxidizing power. | Prepare fresh periodic acid solution for each batch of slides, or at least regularly according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. | |
| Insufficient Oxidation (Periodic Acid Step) | Increase periodic acid incubation time (e.g., from 5 to 10 minutes) or ensure the solution is fresh. | |
| Insufficient Schiff’s Reagent Incubation | Increase Schiff’s reagent incubation time (e.g., from 15 to 30 minutes). | |
| Over-washing after Schiff’s Reagent | Ensure washing is thorough but not prolonged (e.g., 5 minutes in running tap water). If tap water is heavily chlorinated, consider using distilled or deionized water for rinsing or a sulfite rinse as an alternative (though modern protocols often omit this). | |
| Insufficient Schiff’s Reagent Incubation | Increase Schiff’s reagent incubation time (e.g., from 15 to 30 minutes). | |
| Improper Fixation | Use recommended fixatives like 10% neutral buffered formalin. If glutaraldehyde was used, consider an appropriate blocking step (e.g., aniline-acetic aldehyde block) before PAS staining. Prompt fixation is important for glycogen demonstration. | |
| Poor Tissue Quality/Handling | Ensure proper and timely tissue processing and fixation. Use freshly prepared or properly stored sections. | |
| Excessive or Non-specific Staining (too dark, diffuse, or background staining). | Over-oxidation by Periodic Acid | Reduce periodic acid incubation time or confirm the correct concentration. |
| Contaminated Schiff’s Reagent | Filter the Schiff’s reagent or replace it if it’s discolored or heavily precipitated. | |
| Insufficient Washing after Periodic Acid or Schiff’s Reagent | Ensure thorough rinsing in distilled water after the periodic acid step. Wash thoroughly in running tap water after the Schiff’s reagent step until the water runs clear and the desired magenta color develops. | |
| Contaminated Water | Use deionized or distilled water for rinses and reagent preparation. | |
| Starch-based Adhesives on Slides | Use poly-L-lysine or silane-coated slides, or ensure any adhesive is non-reactive with PAS. | |
| Inadequate Counterstaining or Bluing | Adjust the counterstain concentration or incubation time. Ensure proper bluing (e.g., in tap water or a bluing reagent) after hematoxylin. | |
| Uneven Staining | Uneven Reagent Coverage | Ensure all sections are fully submerged. Gently agitate slides or solutions during incubation steps. Use proper staining racks and containers. |
| Air Bubbles | Gently tap slides or ensure smooth immersion to dislodge air bubbles. | |
| Inconsistent Water Flow (Washing) | Ensure a consistent, gentle flow of running water during washes | |
| Sections floating off slides | Inadequate Adhesion | Use appropriately coated slides for challenging tissues. Ensure slides are thoroughly dried before commencing the staining protocol. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why does PAS stain positive in ALL?
While most mature blood cells stain negative or weakly positive for periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining), Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) cells frequently show strong PAS positivity. This positivity arises from various factors:
- Glycogen accumulation: ALL blasts often have increased glycogen stores compared to normal lymphocytes. Glycogen, being a polysaccharide, readily reacts with the periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining), leading to visible color development.
- Increased glycoproteins and glycolipids: The cell membranes and cytoplasm of ALL blasts may contain higher levels of glycoproteins and glycolipids compared to normal lymphocytes. These molecules also possess sugars that react with the periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining), contributing to positive results.
- Presence of vacuoles: Some subtypes of ALL, particularly B-cell ALL, are associated with cytoplasmic vacuoles. These vacuoles can contain accumulated carbohydrates, leading to strong PAS positivity.
- Importance in diagnosis: The strong PAS positivity observed in ALL plays a significant role in diagnosis and classification. It helps differentiate ALL from other types of acute leukemia, like Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), which typically stains negative or weakly positive with periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining).
- Not universally positive: Not all ALL cases exhibit strong PAS positivity. The degree of positivity can vary depending on the specific subtype, individual cell features, and technical aspects of the staining procedure.
Additional notes:
- PAS alone doesn’t confirm ALL: While helpful, PAS positivity alone isn’t definitive for ALL diagnosis. Other tests, such as immunophenotyping and cytogenetic analysis, are crucial for confirmation.
- Subtypes with stronger positivity: B-cell ALL, particularly common ALL, tends to show stronger PAS positivity compared to T-cell ALL.
Why is erythroleukemia PAS positive?
The strong PAS positivity observed in certain types of erythroleukemia (particularly M6a and M7 in the FAB classification) arises from several factors:
1. Increased Glycogen Stores: Compared to normal erythroblasts, erythroleukemic blasts often accumulate more glycogen due to:
- Abnormal metabolic pathways: Dysregulation of enzymes involved in glycogen synthesis or breakdown can lead to elevated glycogen levels.
- Impaired maturation: Immature blasts might not utilize glycogen efficiently, leading to its accumulation.
2. Altered Membrane Composition: The cell membranes of erythroleukemic blasts may contain:
- More glycoproteins and glycolipids: These molecules possess sugars that readily react with the PAS stain, contributing to positive results.
- Abnormal glycosylation patterns: Changes in how sugars are attached to membrane molecules can enhance their reactivity with the PAS stain.
3. Cytoplasmic Vacuoles: Some subtypes of erythroleukemia, particularly B-cell ALL, are associated with cytoplasmic vacuoles. These vacuoles can contain:
- Accumulated carbohydrates: These stored carbohydrates, including glycogen, readily react with the PAS stain and contribute to positivity.
- Other PAS-positive substances: In some cases, the vacuoles might contain other molecules like mucin, further enhancing PAS positivity.
4. Significance of PAS Positivity:
- Diagnostic Clue: Although not diagnostic alone, strong PAS positivity in erythroblasts can raise suspicion of erythroleukemia, prompting further investigation with other tests like immunophenotyping and cytogenetics for definitive diagnosis.
- Differentiating from Other Leukemias: Strong PAS positivity often helps differentiate erythroleukemia from other leukemias like AML, which typically show negative or weak periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) in blasts.
What are the disadvantages of periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining)?
Despite its valuable applications, periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) has some disadvantages to consider:
Non-specificity
- Stains multiple carbohydrate structures: Periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) reacts with various polysaccharides like glycogen, mucins, and glycoproteins, making it difficult to pinpoint specific targets within a tissue.
- False positives: Other substances, like hemosiderin and basement membranes, can also stain positive, potentially leading to misinterpretations.
Sensitivity limitations
- May miss low-level carbohydrate targets: The periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) might not be sensitive enough to detect small amounts of polysaccharides, potentially overlooking early disease signs.
- Variability in staining intensity: The intensity of PAS positivity can vary across different cell types and tissues, making interpretation challenging.
Technical considerations
- Time-consuming and multi-step procedure: Performing the periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) properly requires multiple steps and precise timing, increasing potential for errors.
- Subjectivity in interpretation: Assessing periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) intensity and patterns can be subjective, introducing potential observer bias.
- Susceptibility to artifacts: Improper fixation, processing, or staining technique can lead to artifacts that mimic or obscure true PAS positivity.
Additional limitations
- Not diagnostic alone: PAS positivity needs integration with other tests and clinical context for accurate diagnosis.
- Environmental concerns: Some reagents used in the periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) are considered hazardous materials, requiring special handling and disposal.
What are the common counterstains used for Periodic Acid Schiff stain?
Periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) typically requires a counterstain to provide contrast and better visualize the structures highlighted by the PAS reaction. Here are some commonly used counterstains:
Nuclear counterstains
- Hematoxylin: The most widely used counterstain, providing blue or purple nuclei, creating a classic blue-magenta contrast with PAS-positive structures.
- Methyl blue: Produces a blue counterstain, particularly useful for highlighting nuclei and collagen.
Cytoplasmic counterstains
- Light green SF: Offers cytoplasmic counterstaining, highlighting non-PAS-positive areas in green.
- Neutral red: Another cytoplasmic counterstain, producing a pink-red color for non-PAS-positive regions.
- Orange G: Offers an orange counterstain, often used in combination with hematoxylin for a contrasting appearance.
| Counterstain | Color | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hematoxylin | Blue/purple | Classic contrast, highlights nuclei | Can obscure subtle PAS positivity |
| Methyl blue | Blue | Highlights nuclei and collagen | Less vibrant contrast than hematoxylin |
| Light green SF | Green | Good cytoplasmic counterstain | May fade over time |
| Neutral red | Pink/red | Clear cytoplasmic counterstain | Not as widely used as light green SF |
| Orange G | Orange | Contrasting with hematoxylin, highlights cytoplasm | Less specific than other counterstains |
- Some specialized counterstains are used for specific applications:
- Alcian blue: Can be used before periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining) to differentiate between different types of acidic mucins.
- Fast green: Commonly used for fungal stains with periodic acid Schiff stain (PAS staining).
Disclaimer: This protocol is intended for informational purposes only and may need to be modified depending on the specific laboratory procedures and patient circumstances. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for guidance. See additional information.
References
- Bain BJ. A Practical Guide. 6th Edition (Wiley). 2022.
- Bain BJ, Bates I, Laffan MA. Dacie and Lewis Practical Haematology: Expert Consult: Online and Print 12th Edition (Elsevier). 2016.
- Carr JH. Clinical Hematology Atlas 6th Edition (Elsevier). 2021.
- Tabatabaei Shafiei, M., Carvajal Gonczi, C. M., Rahman, M. S., East, A., François, J., & Darlington, P. J. (2014). Detecting glycogen in peripheral blood mononuclear cells with periodic acid schiff staining. Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE, (94), 52199. https://doi.org/10.3791/52199
- Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) Staining: A Useful Technique for Demonstration of Carbohydrates. (2020). Medico Legal Update, 20(2), 353-357. https://doi.org/10.37506/mlu.v20i2.1129