TL;DR
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a slower progressing clonal disorder of the hematopoietic stem cells where untreated patients progress to blast crisis stage after 3 – 5 years. It has a peak incidence at 40 – 60 years old.
Signs and symptoms ▾
- Hypermetabolism e.g. weight loss, anorexia or night sweats
- Splenomegaly
- Anemia, bruising, epistaxis or menorrhagia
- Hyperuricemia
Pathogenesis ▾
Laboratory investigations ▾
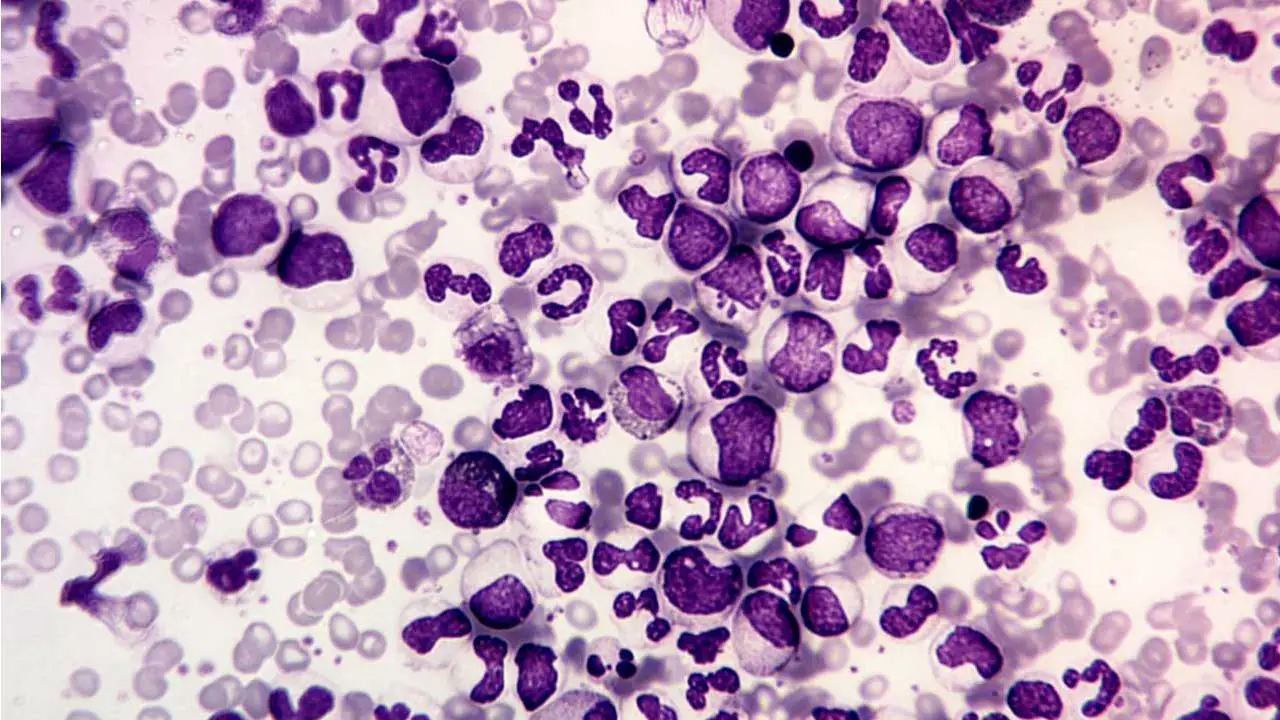
- PBF: Normochromic normocytic anemia and leukocytosis
- BMA: Hypercellular with granulopoietic predominance
- NAP score: Low
- Cytogenetic analysis or qPCR: Presence of Philadelphia chromosome
- ↑ serum acid
Treatment and management ▾
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs)
- Stem cell transplantation
*Click ▾ for more information
What is chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)?
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a type of cancer (a clonal disorder) that starts in the myeloid cells in the bone marrow. Myeloid cells are immature blood cells that develop into different types of mature blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
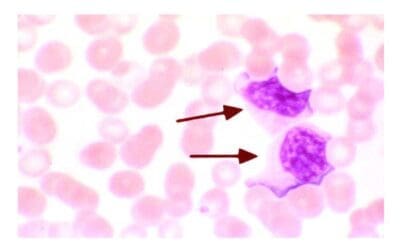
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) differs from most of the other myeloproliferative neoplasms in 2 important ways: 1) virtually all untreated patients progress to a phase identical to acute leukemia or also known as blast crisis usually within a period of 3 – 5 years from diagnosis and 2) the acute leukemia of blast crisis may resemble acute myeloid leukemia or the myeloid blast crisis or acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the lymphoid blast crisis. The ability of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) to progress to either acute myeloid or lymphoid leukemia is good evidence that the tumor originates in a multipotent hematopoietic stem cell. Prior to the blast crisis, some patients experienced an accelerated phase by increased resistance to therapy, falling platelet counts and increasing numbers of basophils and blasts.
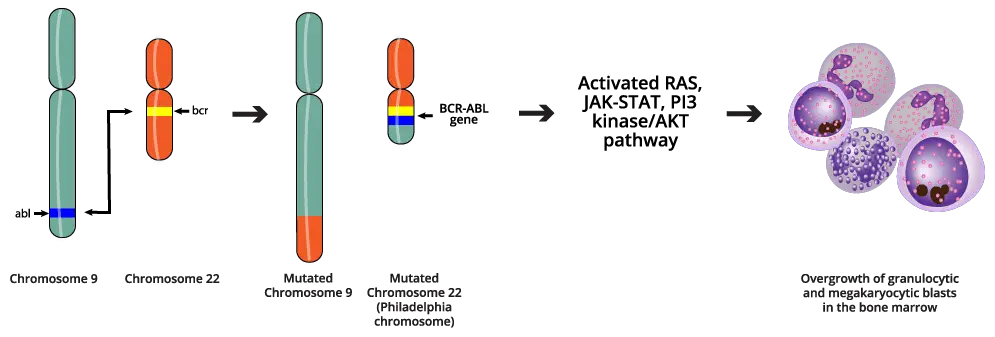
The diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is rarely difficult and is assisted by the characteristic presence of the Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome. This is a somatic mutation that produces a BCR-ABL fusion gene, usually a balanced translocation between chromosome 9, where ABL kinase is encoded, and the breakpoint cluster region (BCR) on chromosome 22 that can be identified by staining of metaphase chromosome preparations. The BCR-ABL kinase activates the RAS, JAK-STAT and PI3 kinase/AKT pathways, the same pathways that are stimulated by hematopoietic growth factors in normal progenitors. As a result, there is an overgrowth of granulocytic and megakaryocytic precursors in the bone marrow.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) Symptoms
Early stages of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
Many people with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) do not have any symptoms when they are first diagnosed. In the early stages of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), the abnormal white blood cells may not cause any problems. However, as the disease progresses, the abnormal white blood cells can crowd out the healthy blood cells in the bone marrow. This can lead to a variety of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) symptoms, including:
- Fatigue: Fatigue is one of the most common chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) symptom. It is caused by a shortage of healthy red blood cells.
- Weight loss: Weight loss can occur due to a variety of factors, including fatigue, loss of appetite, and increased metabolism.
- Night sweats: Night sweats are another common chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) symptom. They are caused by the body’s attempt to cool down.
- Fever: Fever can be a sign of infection or inflammation. It can also occur in people with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) due to the release of chemicals from the abnormal white blood cells.
- Shortness of breath: Shortness of breath can occur due to a shortage of healthy red blood cells or due to pressure on the lungs from an enlarged spleen.
Later stages of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
As chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) progresses, the abnormal white blood cells can accumulate in the organs and tissues of the body. This can lead to a variety of other chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) symptoms, including:
- Easy bleeding and bruising: Easy bleeding and bruising can occur due to a shortage of platelets. Platelets are responsible for blood clotting.
- Abdominal fullness: Abdominal fullness can be caused by an enlarged spleen. The spleen is an organ located in the upper left abdomen that helps to filter the blood.
- Bone pain: Bone pain can be caused by pressure on the nerves from the abnormal white blood cells or by the spread of the disease to the bones.
- Gout or renal impairment: Is caused by hyperuricemia from excessive purine breakdown may be a problem.
What causes chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)?
The pathogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is characterized by the acquisition of the Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome, a cytogenetic abnormality that results in the constitutive activation of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase. This oncogene encodes a chimeric protein that is formed by the fusion of the BCR and ABL genes. The BCR-ABL protein has increased tyrosine kinase activity, which leads to uncontrolled growth and proliferation of myeloid cells.
The pathophysiology of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is complex and involves a variety of cellular and molecular mechanisms. The BCR-ABL protein disrupts normal hematopoietic signaling pathways, leading to increased cell proliferation, decreased apoptosis, and enhanced stem cell self-renewal. It also promotes angiogenesis and increased vascular permeability, which contributes to the development of splenomegaly and other clinical features of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
The following are some of the key pathophysiological mechanisms involved in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML):
- Increased cell proliferation: The BCR-ABL protein activates a variety of signaling pathways that promote cell proliferation, including the RAS/MAPK, JAK/STAT, and PI3K/AKT pathways. This leads to increased expression of cyclin D1 and c-myc, which are key regulators of the cell cycle.
- Decreased apoptosis: The BCR-ABL protein inhibits apoptosis by upregulating anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2 and Mcl-1. This allows the abnormal myeloid cells to survive longer than normal.
- Enhanced stem cell self-renewal: The BCR-ABL protein promotes stem cell self-renewal by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This leads to an increased pool of abnormal stem cells, which can further contribute to the development and progression of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
- Angiogenesis and increased vascular permeability: The BCR-ABL protein promotes angiogenesis and increased vascular permeability by upregulating the expression of pro-angiogenic factors such as VEGF and MMP-9. This leads to the development of splenomegaly and other chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) symptoms.
In addition to the above mechanisms, the BCR-ABL protein also disrupts the normal function of the immune system. This can lead to a variety of immunological abnormalities, including impaired T cell function, increased B cell activity, and autoimmunity.
The pathophysiological mechanisms involved in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) are complex and not fully understood. However, significant progress has been made in recent years in understanding the role of the BCR-ABL protein in the development and progression of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). This knowledge has led to the development of more effective and targeted therapies for this disease.
How is chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) investigated?
Laboratory investigations play an important role in the diagnosis and monitoring of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). The following tests are commonly used:
Complete blood count (CBC) with differential
A CBC is a blood test that quantitatively measures the different parameters of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood.
People with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) often have a high increased white blood cell count (leukocytosis). They may also have a decreased red blood cell count (anemia) and platelet (thrombocytopenia) count.
Peripheral blood smear
A peripheral blood smear is a blood test that examines the different types of blood cells under a microscope. This test can help to identify abnormal blood cells, such as leukemic blast cells.
People with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) often have immature myeloid cells (blast cells) in their peripheral blood smear. Leukocytosis with a complete spectrum of myeloid cells. Normochromic, normocytic anemia is usual. NAP score is low as opposed to those during infections.
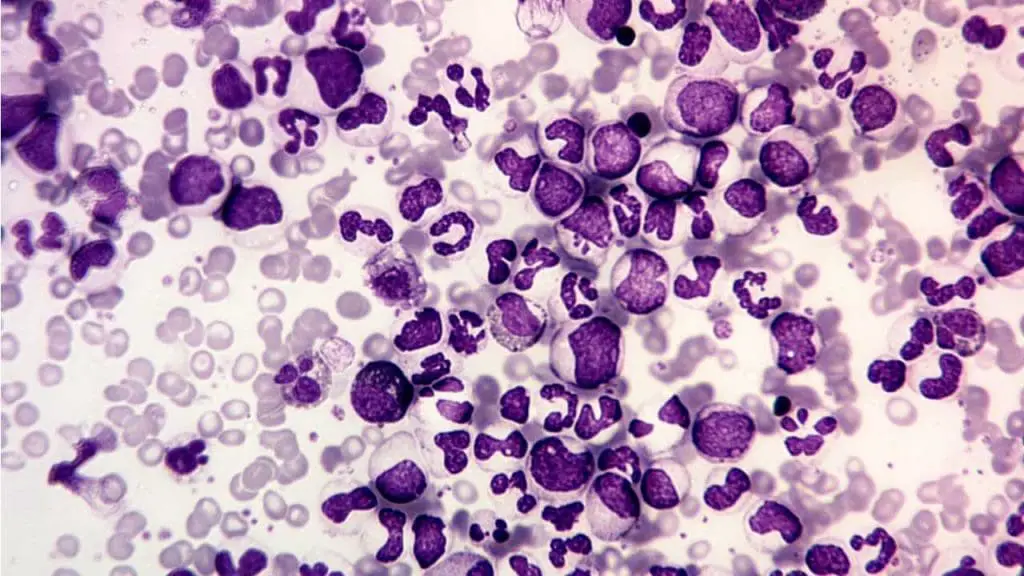
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
A bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are procedures that remove a sample of bone marrow for examination under a microscope. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside the bones where blood cells are made.
In chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), the bone marrow is usually hypercellular, meaning that it contains more cells than normal. There is also an increased number of myeloblasts in the bone marrow (granulopoietic predominance).
Cytogenetic analysis
Cytogenetic analysis is a laboratory test that examines the chromosomes in cells. This test can identify chromosomal abnormalities, such as the Philadelphia chromosome.
The Philadelphia chromosome is a chromosomal abnormality that is found in the bone marrow cells of almost all people with CML. It is formed when two chromosomes, chromosome 9 and chromosome 22, exchange material.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
FISH is a laboratory test that uses fluorescent probes to identify specific genes or chromosomal sequences. This test can be used to detect the Philadelphia chromosome.
Molecular testing
Molecular testing like quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) can be used to detect the BCR-ABL gene fusion, which is the genetic abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Molecular testing is more sensitive than cytogenetic analysis and FISH, and it can be used to detect chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells even when the Philadelphia chromosome is not present.
Current treatment and management for CML
The current treatment and management of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is focused on targeting the BCR-ABL protein with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). TKIs are oral medications that block the BCR-ABL protein from signaling, which prevents the leukemia cells from growing and dividing.
There are six TKIs that are currently approved for the chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) treatment:
- Imatinib (Gleevec)
- Nilotinib (Tasigna)
- Dasatinib (Sprycel)
- Bosutinib (Bosulif)
- Ponatinib (Iclusig)
- Asciminib (Scemblix)
Imatinib was the first TKI to be developed for the chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) treatment, and it remains the first-line treatment for most patients. However, some patients may not respond to imatinib, or they may develop resistance to it over time. In these cases, a second- or third-generation TKI may be used.
TKIs have revolutionized the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), and they have led to significant improvements in survival rates. In fact, most patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who are treated with TKIs can now expect to live a normal lifespan.
Treatment goals
The primary goal of treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is to achieve complete molecular remission (CMR). CMR is defined as the absence of detectable BCR-ABL transcripts in the blood.
Achieving CMR is important because it is associated with the best long-term outcomes for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Patients who achieve CMR have a very low risk of relapse and progression to the more aggressive blastic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
Treatment options
The specific chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) treatment options will depend on the patient’s individual disease characteristics, such as the phase of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and their response to previous treatments.
For most patients with newly diagnosed chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), the first-line treatment is imatinib. Imatinib is a very effective TKI, and it can achieve CMR in up to 90% of patients.
However, some patients may not respond to imatinib, or they may develop resistance to it over time. In these cases, a second- or third-generation TKI may be used.
Second-generation TKIs, such as nilotinib and dasatinib, are more potent than imatinib and can achieve CMR in a higher percentage of patients. Third-generation TKIs, such as ponatinib and asciminib, are even more potent than second-generation TKIs and can be used to treat patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who are resistant to other TKIs.
In addition to TKIs, other chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) treatment options include:
- Stem cell transplant: A stem cell transplant is a procedure in which the patient’s own stem cells are harvested and then reinfused into the body after high-dose chemotherapy. Stem cell transplants can be curative, but they are associated with significant risks.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a type of medication that kills cancer cells. Chemotherapy is not curative, but it can be used to control the disease in patients who are not responding to TKIs or who are not eligible for a stem cell transplant.
Management of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
Once a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has achieved CMR, they need to continue taking their TKI indefinitely. This is because the BCR-ABL gene fusion is still present in the patient’s body, even if they are in remission. If the patient stops taking their TKI, the leukemia cells can return.
In addition to taking their TKI, patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) also need to be monitored closely for any signs of relapse. This typically involves regular blood tests and bone marrow biopsies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is CML life expectancy?
CML life expectancy has significantly improved due to advancements in treatment, particularly tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). With effective treatment, many patients with CML can live long, near-normal lives. However, factors such as the stage of the disease at diagnosis, response to treatment, and the development of resistance can influence individual outcomes. Regular monitoring and adherence to treatment plans are crucial for managing CML and maximizing life expectancy.
Can CML be cured?
While there is no definitive cure for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), modern treatments, particularly tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), have significantly improved outcomes. Many patients with CML can live long, near-normal lives. With ongoing advancements in research and treatment, the goal of curing CML remains a focus for medical professionals.
What are the three stages of CML?
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is typically divided into three phases.
- Chronic phase: This is the initial stage, characterized by a gradual increase in abnormal white blood cells. Symptoms may be mild or absent during this phase.
- Accelerated phase: As the disease progresses, the number of abnormal white blood cells increases rapidly. Symptoms may become more severe, including fatigue, weight loss, and easy bleeding or bruising.
- Blast crisis: This is the most advanced stage, characterized by a high number of immature white blood cells (blasts) in the blood and bone marrow. Symptoms can be severe and life-threatening, including fever, infections, and bleeding.
What happens if CML is not treated?
If chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is not treated, the disease can progress through three phases: chronic, accelerated, and blast crisis. As the disease advances, symptoms become more severe, including fatigue, weight loss, easy bleeding, and infections. In the blast crisis stage, the disease can be life-threatening. Early diagnosis and treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are crucial for managing CML and improving outcomes.
Does CML run in families?
CML is not typically inherited. While a small number of cases may be linked to inherited genetic factors, most cases of CML occur spontaneously. However, certain genetic mutations, such as the Philadelphia chromosome, are common in CML and can be detected through genetic testing.
Can CML spread to other organs?
Yes, CML can spread to other organs. As the disease progresses, abnormal white blood cells can accumulate in various organs, including the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. This can lead to organ enlargement, pain, and dysfunction. However, with effective treatment, the spread of CML can be controlled, and complications can be minimized.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and is specifically targeted towards medical students. It is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. While the information presented here is derived from credible medical sources and is believed to be accurate and up-to-date, it is not guaranteed to be complete or error-free. See additional information.
References
- Alaggio R, Amador C, Anagnostopoulos I, Attygalle AD, Araujo IBO, Berti E, Bhagat G, Borges AM, Boyer D, Calaminici M, Chadburn A, Chan JKC, Cheuk W, Chng WJ, Choi JK, Chuang SS, Coupland SE, Czader M, Dave SS, de Jong D, Du MQ, Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Ferry J, Geyer J, Gratzinger D, Guitart J, Gujral S, Harris M, Harrison CJ, Hartmann S, Hochhaus A, Jansen PM, Karube K, Kempf W, Khoury J, Kimura H, Klapper W, Kovach AE, Kumar S, Lazar AJ, Lazzi S, Leoncini L, Leung N, Leventaki V, Li XQ, Lim MS, Liu WP, Louissaint A Jr, Marcogliese A, Medeiros LJ, Michal M, Miranda RN, Mitteldorf C, Montes-Moreno S, Morice W, Nardi V, Naresh KN, Natkunam Y, Ng SB, Oschlies I, Ott G, Parrens M, Pulitzer M, Rajkumar SV, Rawstron AC, Rech K, Rosenwald A, Said J, Sarkozy C, Sayed S, Saygin C, Schuh A, Sewell W, Siebert R, Sohani AR, Tooze R, Traverse-Glehen A, Vega F, Vergier B, Wechalekar AD, Wood B, Xerri L, Xiao W. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022 Jul;36(7):1720-1748. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01620-2. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Erratum in: Leukemia. 2023 Sep;37(9):1944-1951. PMID: 35732829; PMCID: PMC9214472.
- Carr JH. Clinical Hematology Atlas 6th Edition (Elsevier).
- Jabbour E, Kantarjian H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2022 update on diagnosis, therapy, and monitoring. Am J Hematol. 2022 Sep;97(9):1236-1256. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26642. Epub 2022 Jul 6. PMID: 35751859.
- Jabbour EJ, Sasaki K, Haddad FG, Issa GC, Garcia-Manero G, Kadia TM, Jain N, Yilmaz M, DiNardo CD, Patel KP, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Champlin R, Khouri IF, Dellasala S, Pierce SA, Kantarjian H. The outcomes of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with third-line BCR::ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Am J Hematol. 2023 Apr;98(4):658-665. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26852. Epub 2023 Jan 31. PMID: 36683287.
- https://www.lls.org/booklet/chronic-myeloid-leukemia
- Javidi-Sharifi N, Hobbs G. Future Directions in Chronic Phase CML Treatment. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2021 Dec;16(6):500-508. doi: 10.1007/s11899-021-00658-w. Epub 2021 Oct 14. PMID: 34648120.