Introduction
Peripheral blood smears are usually ordered together with a full blood count. A full blood count is able to give the quantitative results of the blood cells whereas morphological abnormalities of the blood cells are viewed from the blood smear. Using different stains on the smears allow viewing of the different blood components including inclusion bodies and even parasites.
Principle of peripheral blood smear
The peripheral blood smear, a deceptively simple technique, allows for the visualization of the various blood cells found in whole blood. Its core principle lies in the creation of a thin, uniform film of blood cells spread upon a glass slide. Asmall drop of blood is carefully “smeared” across the surface using another slide held at a specific angle. This spreading action forces the blood cells into a single layer, without overlapping of cells, allowing for individual examination under a microscope. However, simply spreading the blood wouldn’t be enough; uncontrolled spreading would result in distorted and overlapping cells, hindering accurate analysis
Materials
- EDTA preserved whole blood
- Glass slide and spreader
- Lens paper
- Hair dryer
Protocol
- Make sure the glass slide and spreader are clean using the lens paper.
- Place 1 drop of well-mixed EDTA blood approximately 1 cm from the end of the glass slide, in the center.
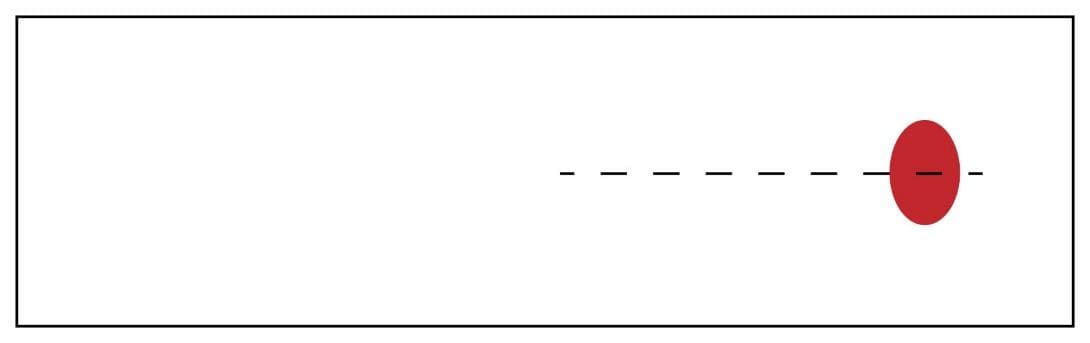
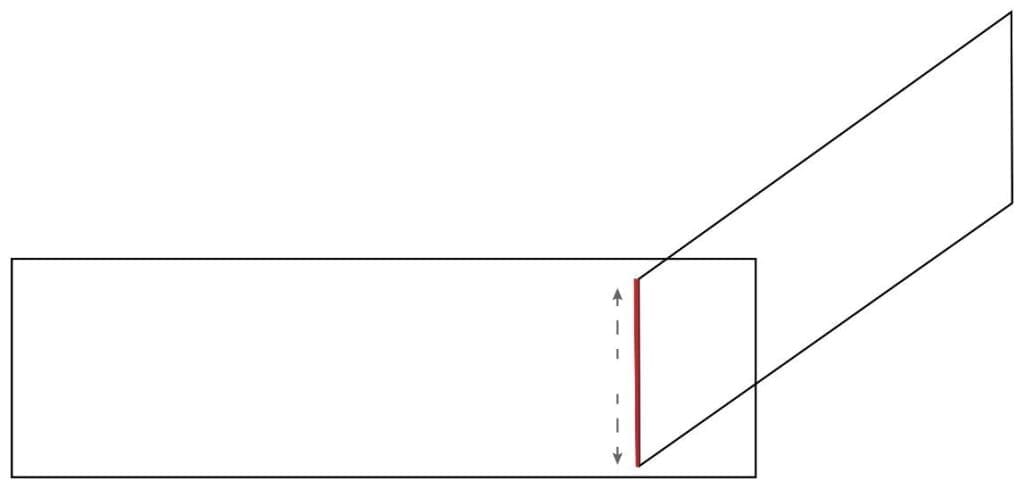
3. Hold the clean spreader at a 30° angle (in relation to the slide) just in front of the blood drop.
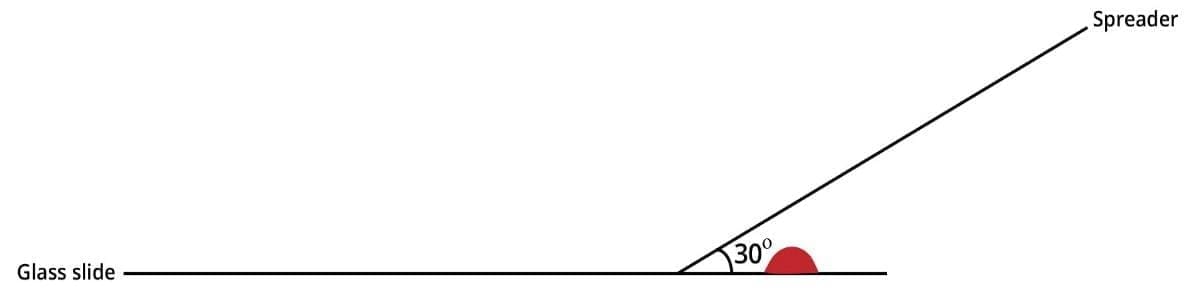
4. Move the spreader backwards to touch the blood drop.
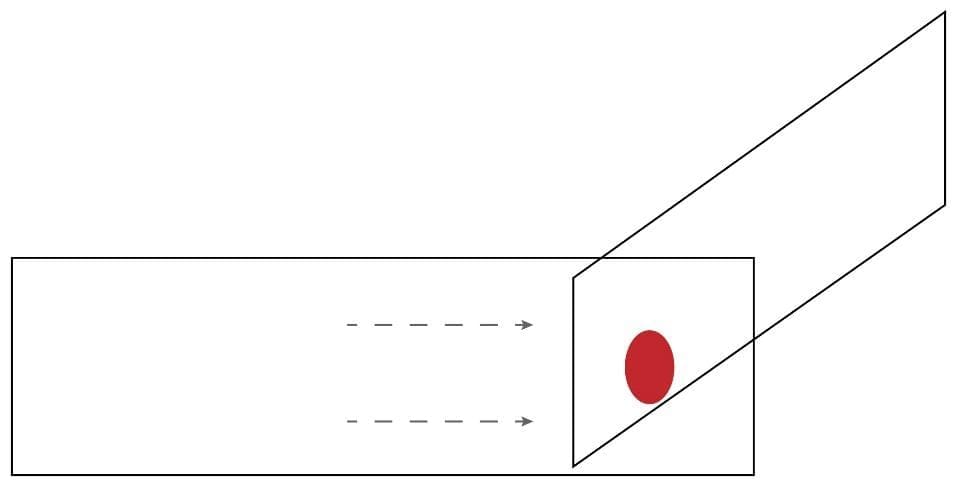
5. Allow the blood to spread the entire width of the spreader.
6. Push the spreader rapidly and smoothly across the glass slide while maintaining the angle of the spreader. The blood should spread across 2/3 of the entire glass slide.
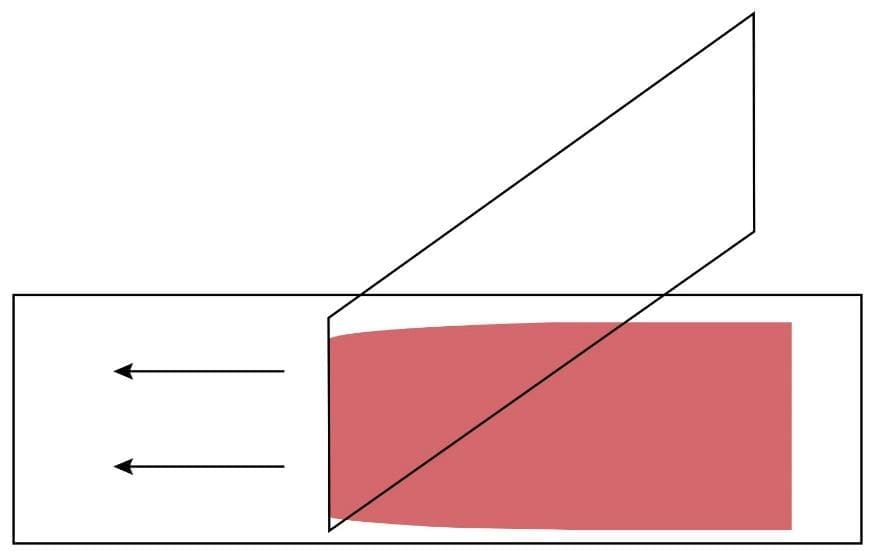
7. Dry the slide using a hair dryer at the lowest speed. The smear can also be air-dried.
8. The blood smear can now be used for staining.
Interpretation
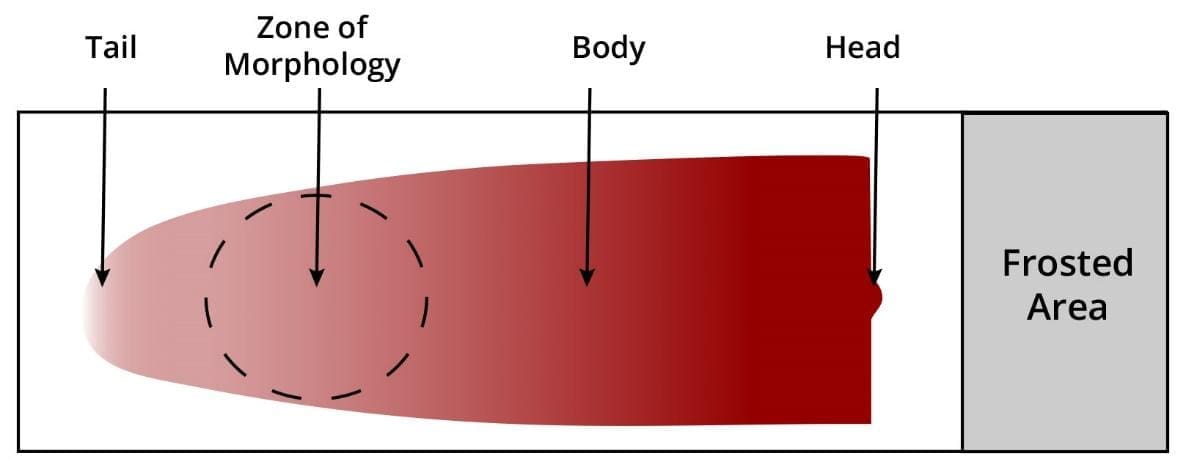
Fast spreading will result in longer and thinner films.
Angles more than 30° will result in thicker smear.
Large blood drops will cause the smear to extend beyond the length of the slide.
Disclaimer: This protocol is intended for informational purposes only and may need to be modified depending on the specific laboratory procedures and patient circumstances. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for guidance. See additional information.