To detect the presence of antibodies or complement proteins bound to red blood cells (RBCs) in vivo, indicating potential immune-mediated hemolysis.
Rh Typing using Tube Method
Unraveling the Rh code! Mix blood with anti-sera in tubes. Incubate, centrifuge, & observe. Clumping reveals antigen presence, guiding safe transfusions.
IHC – Immunohistochemistry Staining
This immunohistochemistry protocol guides you step-by-step through visualizing specific proteins in tissue sections, aiding in accurate diagnosis of various diseases.
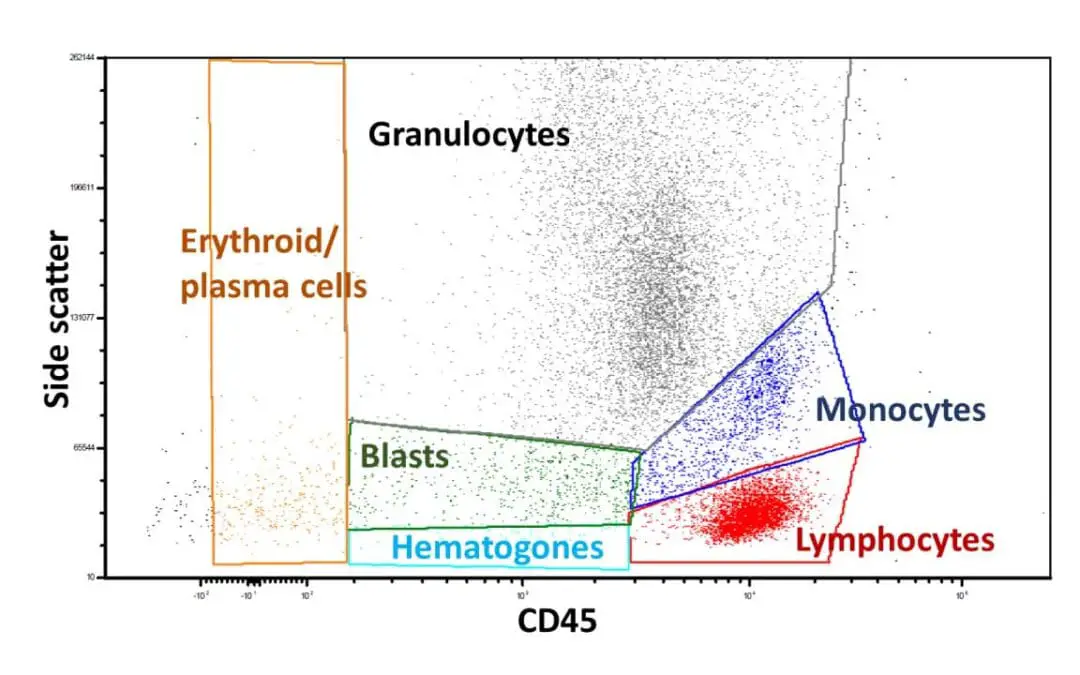
Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping of Blood
Blood cells stained with fluorescent antibodies reveal hidden markers, like a cellular fingerprint. Flow cytometry analyzes millions of cells, painting a detailed picture of immune health, disease clues, and treatment insights.
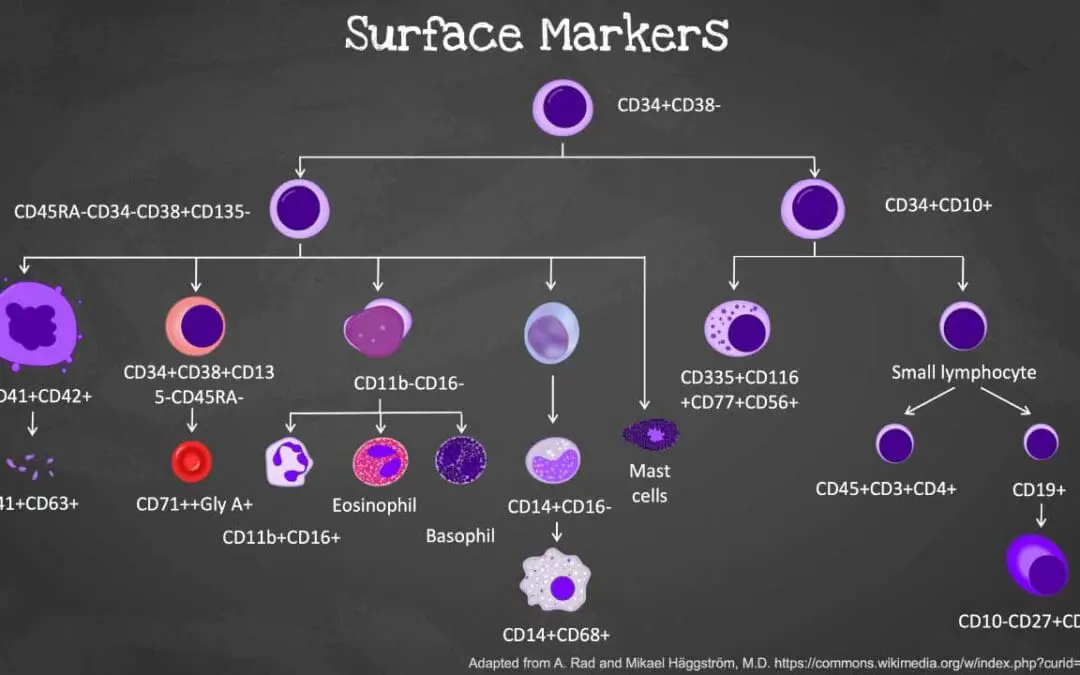
Hematopoietic cell surface markers (CD34 and more)
Explore hematopoietic cell markers & CD34: identification, functions, flow cytometry, and clinical uses in hematology and leukemia.
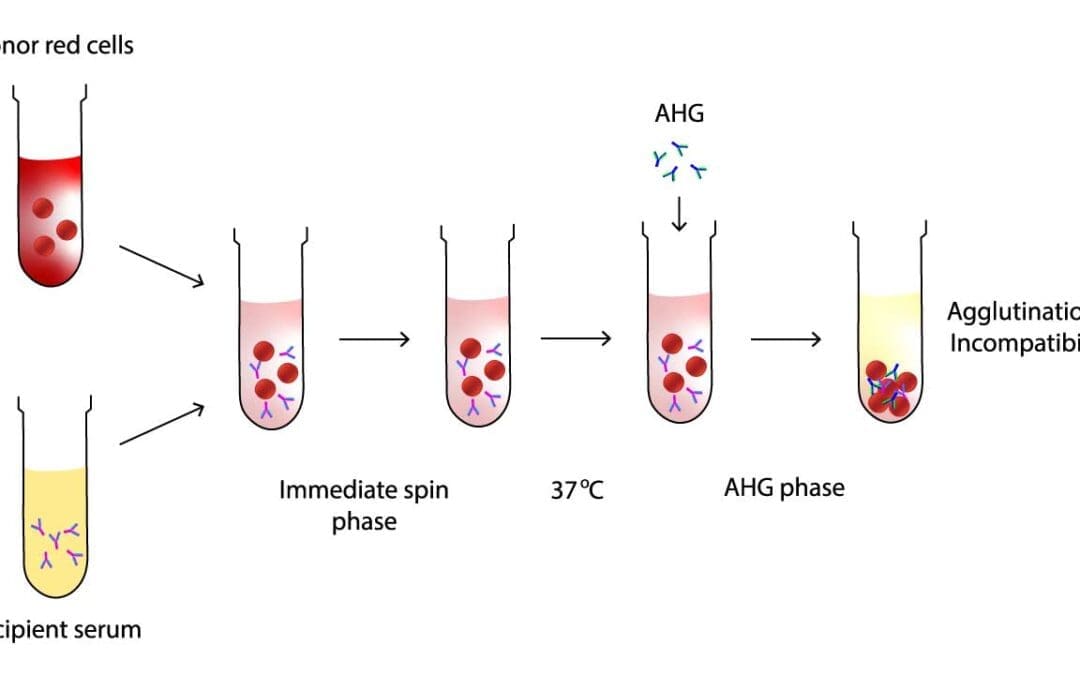
Serologic Crossmatching (Blood Compatibility Test)
Cross-matching mimics transfusion by mixing recipient serum & donor cells. Clumping (agglutination) indicates incompatibility, preventing transfusion reactions.
Myeloperoxidase Reaction (MPO) Stain
A stain mainly used to differentiate AML from ALL and gives a bluish to brownish tinge in cells with lysosomal enzyme.
May-Grünwald Giemsa (MGG) Stain
May-Grünwald Giemsa (MGG) stain is an intense Romanovsky stain to help with the visualisation of bone marrow smears.
Perls’ Prussian Blue Staining
Perls’ Prussian blue stain helps in identifying presence of iron stores in the bone marrow aspirate smear.
Leishman Stain for Peripheral Blood Smear
Leishman stain is used commonly for the identification of different cells present in the peripheral blood smear. It has acidic and basic properties.