Warm AIHA: Immune system attacks red blood cells, causing anemia. Symptoms include fatigue, pallor, and jaundice. Treatment targets immune suppression.
Cold Agglutinin Disease
Cold Agglutinin Disease (CAD) is a rare autoimmune anemia. Cold-reactive antibodies destroy red blood cells, causing fatigue, cold sensitivity, and anemia.
Homocysteine Test
A homocysteine blood test measures the level of homocysteine in your blood. Elevated levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. This simple test can help identify potential vitamin deficiencies and guide personalized treatment plans
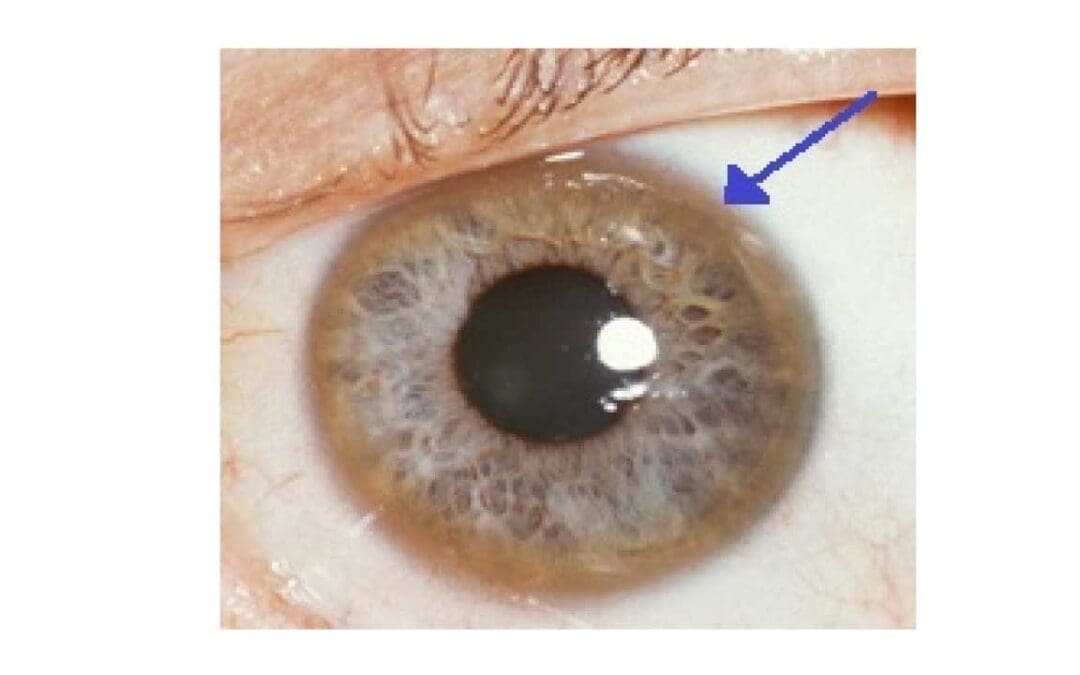
Wilson’s Disease
Wilson’s disease: A rare genetic disorder causing toxic copper buildup in the liver and brain. Early diagnosis and lifelong treatment are crucial.
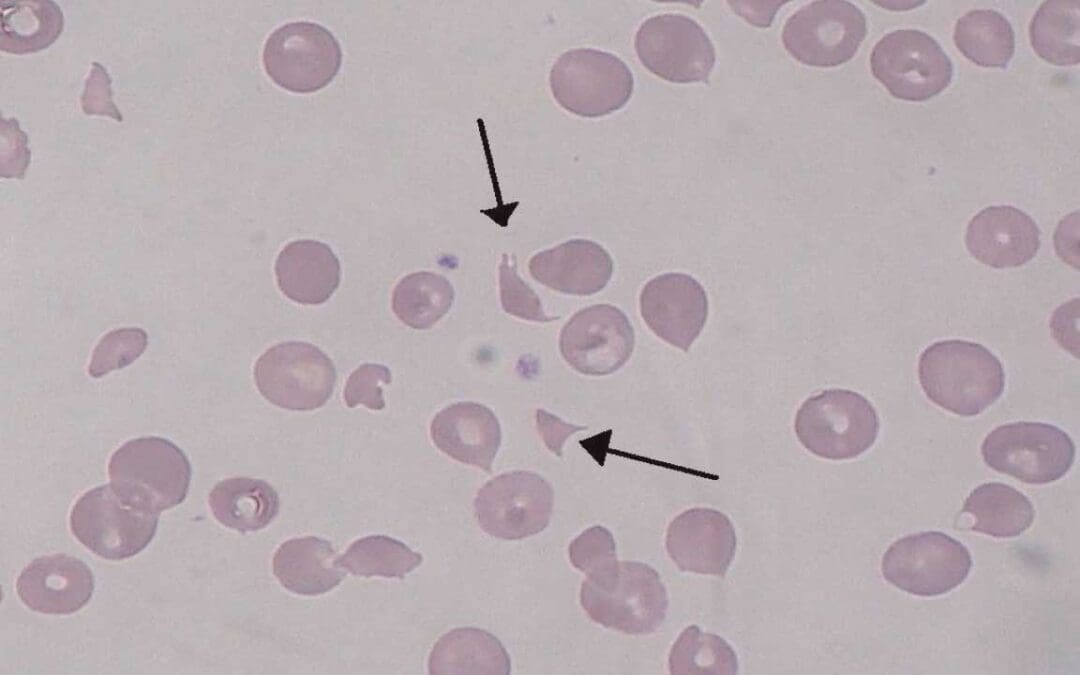
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS): A rare but serious condition causing red blood cell damage, low platelets, and kidney failure. Early diagnosis is key.
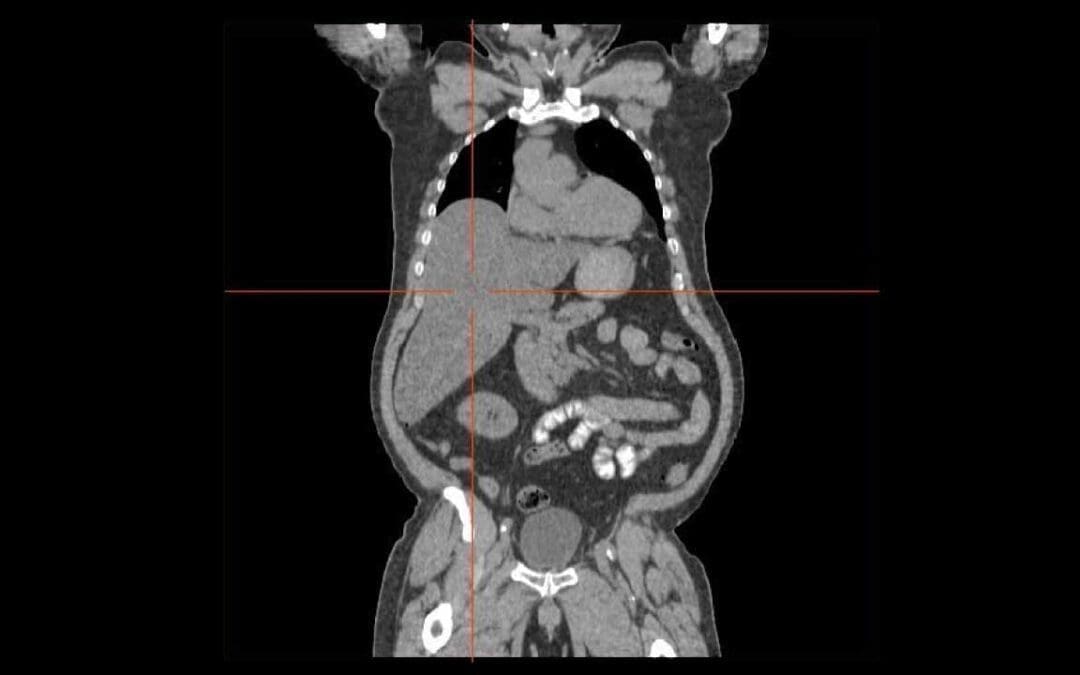
Liver and Causes of Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly means an enlarged liver, often a sign of underlying conditions like hepatitis, fatty liver, or heart failure. Diagnosis involves physical exams and imaging.
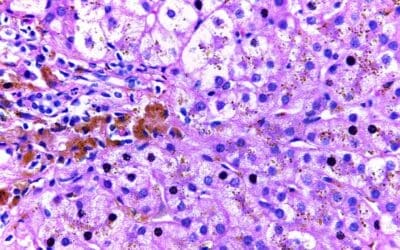
Hereditary Hemochromatosis
Hereditary hemochromatosis, an inherited disorder, disrupts iron absorption leading to excessive iron buildup in organs like the liver, heart, and pancreas. Early diagnosis through blood tests is crucial to prevent potential complications like cirrhosis, heart failure, and diabetes. Treatment focuses on iron reduction through phlebotomy and may prevent severe health consequences.
Sideroblastic Anemia
Sideroblastic anemia disrupts iron use in red blood cells. Caused by genetic mutations or factors like alcohol abuse, it’s diagnosed by analyzing bone marrow for ring sideroblasts, iron-laden structures.
Differential Diagnosis of Macrocytic Anemias
Macrocytosis, larger-than-normal red blood cells, can be a sign of vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, liver disease, or bone marrow issues. Early diagnosis is key for targeted treatment.
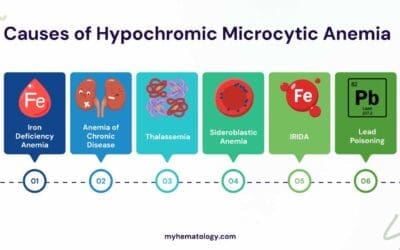
Causes of Hypochromic Microcytic Anemia
Hypochromic microcytic anemia, marked by pale, small red blood cells, has various causes beyond iron deficiency. A proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Ruling out conditions like thalassemia or lead poisoning ensures targeted therapy.
Anemia of Chronic Disease (ACD)
ACD (anemia of chronic disease) occurs when inflammation disrupts iron use for red blood cells, causing anemia despite iron stores.
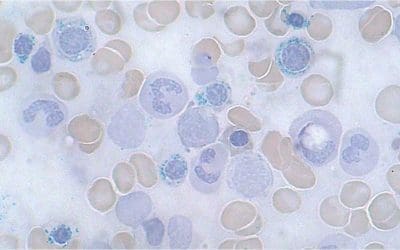
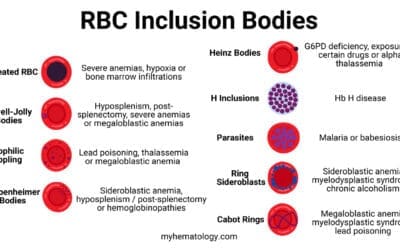
Red Blood Cell Inclusion Bodies
Red blood cell inclusions are hidden clues! These structures in RBCs signal underlying issues. Learn how they help diagnose anemia & other blood disorders.