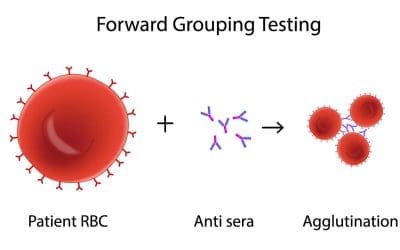
Cross-matching mimics transfusion by mixing recipient serum & donor cells. Clumping (agglutination) indicates incompatibility, preventing transfusion reactions.
Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping of Blood
Blood cells stained with fluorescent antibodies reveal hidden markers, like a cellular fingerprint. Flow cytometry analyzes millions of cells, painting a detailed picture of immune health, disease clues, and treatment insights.
Hematopoietic cell surface markers (CD34 and more)
Explore hematopoietic cell markers & CD34: identification, functions, flow cytometry, and clinical uses in hematology and leukemia.
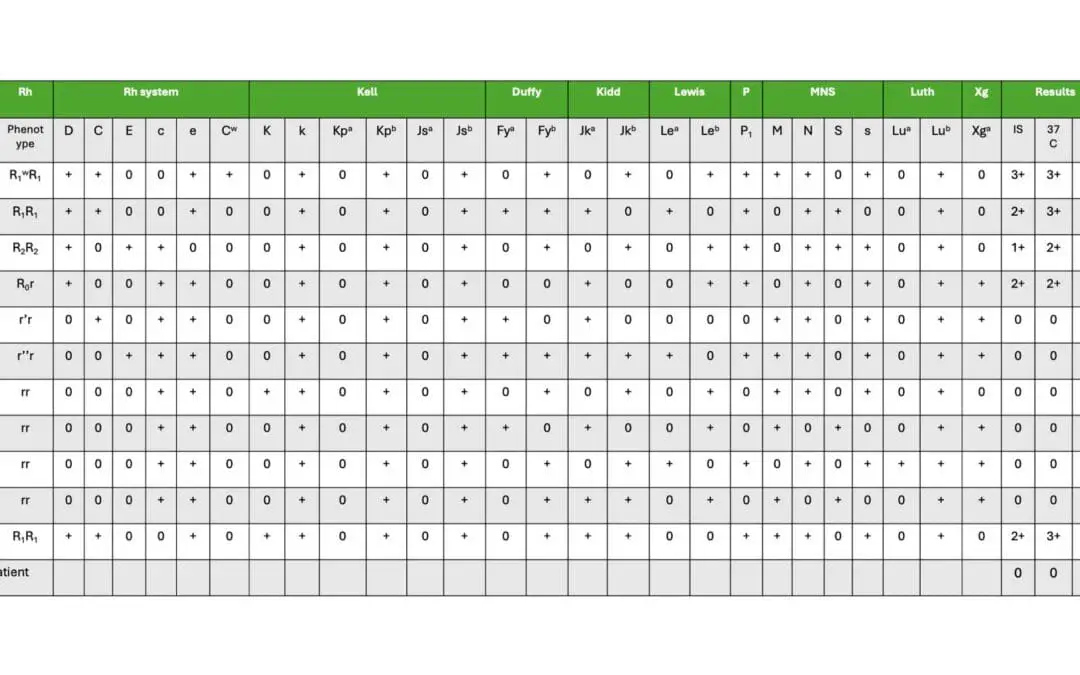
Antibody Identification
Incubate patient serum with panel RBCs, check for agglutination! Enzymes & antiglobulin tests may be used to reveal hidden antibody reactions.
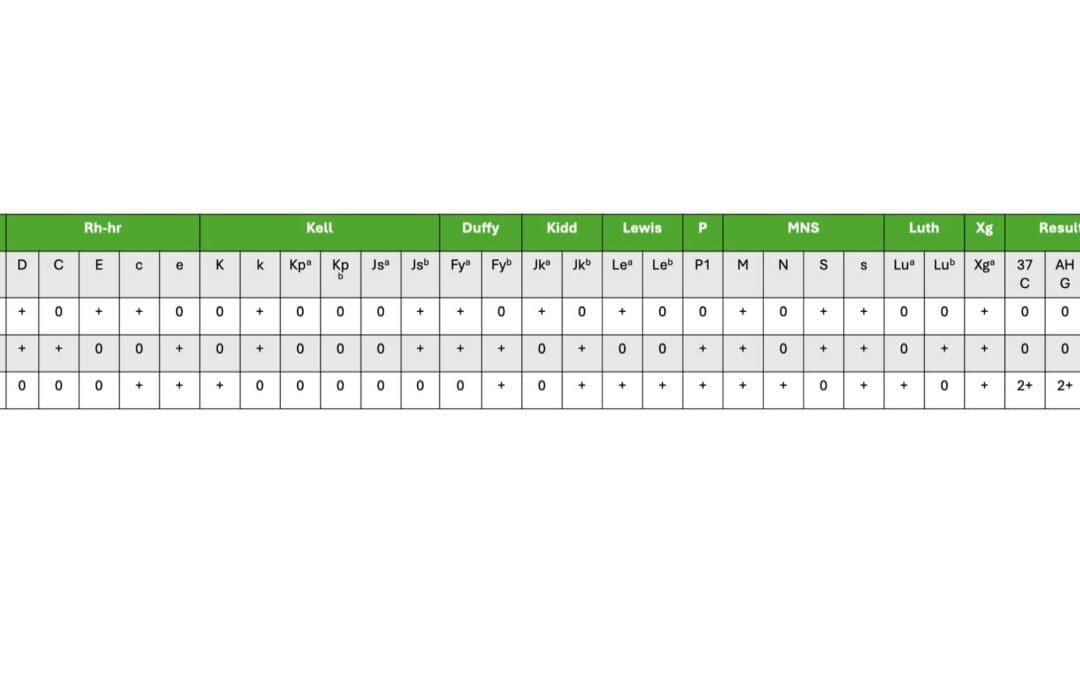
Antibody Screening
Antibody screening mixes patient plasma with red blood cells to detect unexpected antibodies. Agglutination indicates possible antibodies, requiring further identification for safe blood transfusions

Antibody Screening
Antibody screening mixes patient plasma with red blood cells to detect unexpected antibodies. Agglutination indicates possible antibodies, requiring further identification for safe blood transfusions
ABO RhD Test (Blood Group Typing) Tube Method
The ABO RhD Blood Grouping Tube Method is a serological technique used to determine an individual’s blood type by mixing blood serum and red blood cells with antisera and observing for agglutination.
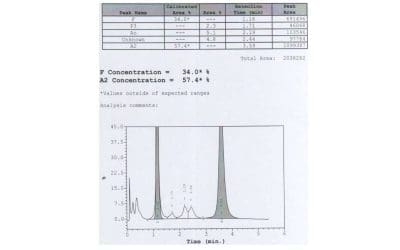
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) for Hemoglobinopathies Screening
HPLC for hemoglobin subtype identification separates and quantifies different hemoglobin variants based on their unique chromatographic properties.
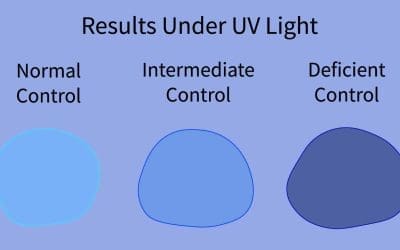
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) Fluorescent Spot Test (G6PD Test)
The G6PD fluorescent spot test is a rapid and simple screening method for G6PD deficiency that utilizes the enzyme’s ability to reduce NADP+ to NADPH.
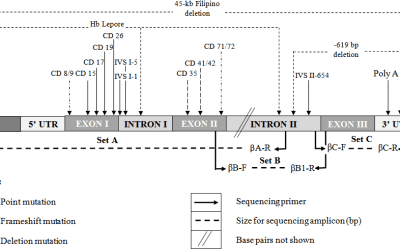
Conventional PCR Protocol for Beta Thalassemia Downstream Sequencing
The beta globin gene PCR protocol for sequencing involves amplifying the beta globin gene using specific primers, followed by Sanger sequencing to determine the DNA sequence.
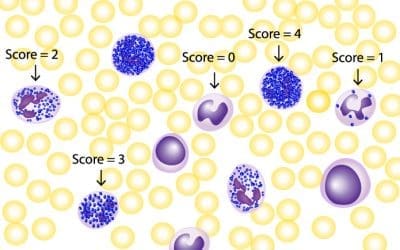
Leukocyte/Neutrophil Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP/NAP) Stain
The NAP stain is used to differentiate between granulocytes and agranulocytes based on their naphthol AS-D chloroacetate esterase (NASD-CE) enzyme activity.
Periodic Acid Schiff Stain (PAS Staining)
PAS stain is a histochemical technique that utilizes periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) reagent to detect and visualize carbohydrate-rich structures in cells and tissues, such as glycogen, glycoproteins, and mucins.