TL;DR
Arterial thrombosis forms when a clot blocks an artery, cutting off blood supply to vital organs.
- Risk factors ▾: Age, smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, and others.
- Symptoms ▾: Sudden pain, weakness, numbness, and discoloration can signal a clot.
- Related disorders ▾:CAD, stroke, peripheral artery disease, aortic dissection, acute limb ischemia etc.
- Early diagnosis ▾: Blood tests and imaging is crucial for prompt action.
- Treatment ▾: Reperfusion (clot removal), pain management, and supportive care.
- Secondary prevention ▾: Lifestyle changes, medications, and managing underlying conditions to prevent future clots.
*Click ▾ for more information
Introduction
Thrombosis, in its simplest form, is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) within the vascular system, specifically inside blood vessels. This clot acts as a physical barrier, partially or completely obstructing the flow of blood. Unlike extravascular clots that form outside the vessels, like a bruise, thrombi pose a significant threat by disrupting the vital delivery of oxygen and nutrients to organs and tissues. This blockage can lead to a variety of complications, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions, depending on the location and severity of the clot.
Definition of Arterial Thrombosis
While thrombosis can occur anywhere in the vascular network, arterial thrombosis poses a unique and particularly dangerous threat. Imagine the aorta, the grand artery that pumps blood from the heart like a mighty river, suddenly choked by a clot. This isn’t just a traffic jam; it’s a dam, cutting off vital supplies to vital organs like the brain, heart, and limbs.
The significance of arterial thrombosis lies in its potential to cause ischemia, a state where tissues are deprived of oxygen and nutrients due to the blocked blood flow. This can have devastating consequences, ranging from acute events like heart attack or stroke to chronic conditions like peripheral artery disease, leading to amputations.
The consequences of arterial thrombosis vary depending on the location of the clot. In the heart, it can trigger a myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, where a portion of the heart muscle dies due to oxygen deprivation. In the brain, a clot can lead to a stroke, disrupting blood flow to brain cells and causing potentially debilitating neurological damage. In the legs, chronic arterial thrombosis can lead to peripheral artery disease, characterized by pain, numbness, and even gangrene if left untreated.
The potential for these devastating consequences underscores the importance of understanding the risk factors and mechanisms behind arterial thrombosis. Unlike venous thrombosis that often form in the slower-moving blood of the legs, arterial clots typically arise from a combination of three factors: endothelial injury, blood flow stasis, and hypercoagulability. Damage to the inner lining of the arteries (endothelium) can act as a trigger, while sluggish blood flow (stasis) and an increased tendency for blood to clot (hypercoagulability) provide the perfect storm for clot formation.
Risk Factors of Arterial Thrombosis
Imagine your blood vessels as a highway network, bustling with traffic but flowing smoothly. Arterial thrombosis disrupts this flow, like a sudden roadblock that can have serious consequences. But while its consequences can be dramatic, understanding the risk factors that pave the way for this clot formation is key to prevention and early intervention.
The risk factors for arterial thrombosis are related to the development of artherosclerosis. The identification of patients at risk is largely based on clinical assessment. These profiles have allowed pre-symptomatic assessment of young and apparently fit subjects and are valuable in counselling a change in lifestyle of for recommending medical therapy in individuals at risk.
The Northwick Park Heart Study showed that elevated plasma levels of factor VII and fibrinogen are the strongest independent predictors of coronary events. Hyperhomocysteinemia has been recognized as a risk for peripheral and coronary arterial disease and stroke. Apart from these, there are many other types of risk factors for arterial thrombosis too.
Modifiable Risk Factors
- Age: As we age, our blood vessels naturally become less flexible and more prone to damage, increasing our susceptibility to thrombosis.
- Smoking: This notorious villain harms the endothelium, the inner lining of arteries, making it sticky and prone to clot formation.
- Diet: A diet high in saturated fat and cholesterol can contribute to the buildup of plaque in arteries, narrowing the passageway and slowing blood flow, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber promotes healthy blood vessel function.
- Hypertension: Uncontrolled high blood pressure puts constant strain on the artery walls, increasing the risk of damage and thrombosis.
- Dyslipidemia: High levels of LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) and low levels of HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol) can contribute to plaque formation and clot development.
- Diabetes: This chronic condition damages blood vessels and disrupts the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, making thrombosis more likely.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional strain on the cardiovascular system and increases inflammation, both of which contribute to thrombosis risk.
- Physical Inactivity: Regular exercise helps maintain healthy blood flow and reduces inflammation, both of which protect against thrombosis.
- Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure, inflammation, and unhealthy lifestyle choices, all of which increase thrombosis risk.
Non-modifiable Risk Factors
- Genetics: Some genetic variants can increase our susceptibility to thrombosis by affecting blood clotting factors or the structure of blood vessels.
- Family history: Having a family member with a history of arterial thrombosis increases your risk, suggesting a potential genetic component.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups are more prone to specific risk factors like high blood pressure or diabetes, which in turn can increase thrombosis risk.
- Gender: Men generally have a higher risk of arterial thrombosis than women, although the risk increases for women after menopause.
Acquired Risk Factors
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions like cancer, inflammatory diseases, and infections can increase inflammation and disrupt blood clotting, making thrombosis more likely.
- Medications: Some medications like oral contraceptives and hormone therapy can increase thrombosis risk, usually by affecting blood clotting factors.
- Trauma: Injuries to blood vessels can damage the endothelium and trigger clot formation.
- Surgery: Any surgical procedure, especially major surgeries, can increase the risk of thrombosis due to temporary changes in blood flow and inflammation.
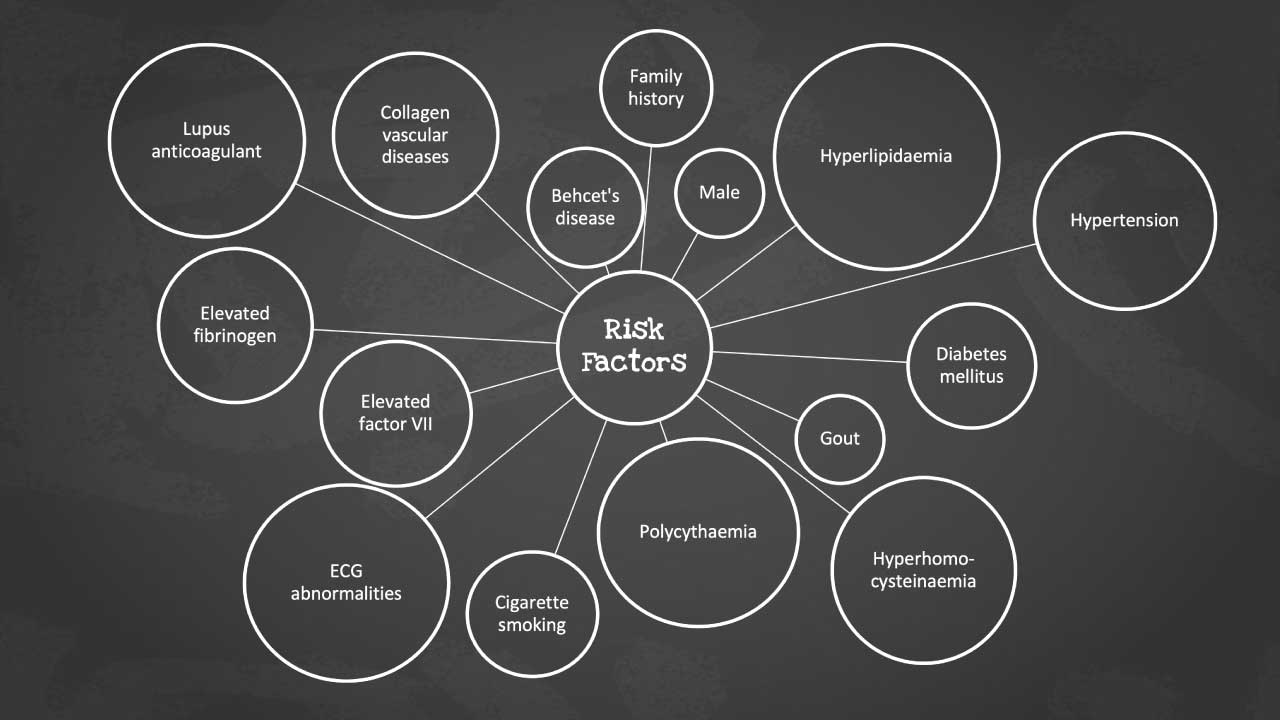
Signs and Symptoms Related to Arterial Thrombosis
While arterial thrombosis often lurks silently within our vascular system, its presence can manifest in a variety of ways, from subtle whispers to thunderous alarms. Recognizing these signs and symptoms, both acute and chronic, is crucial for early intervention and preventing disastrous consequences.
Acute Signs of Arterial Thrombosis
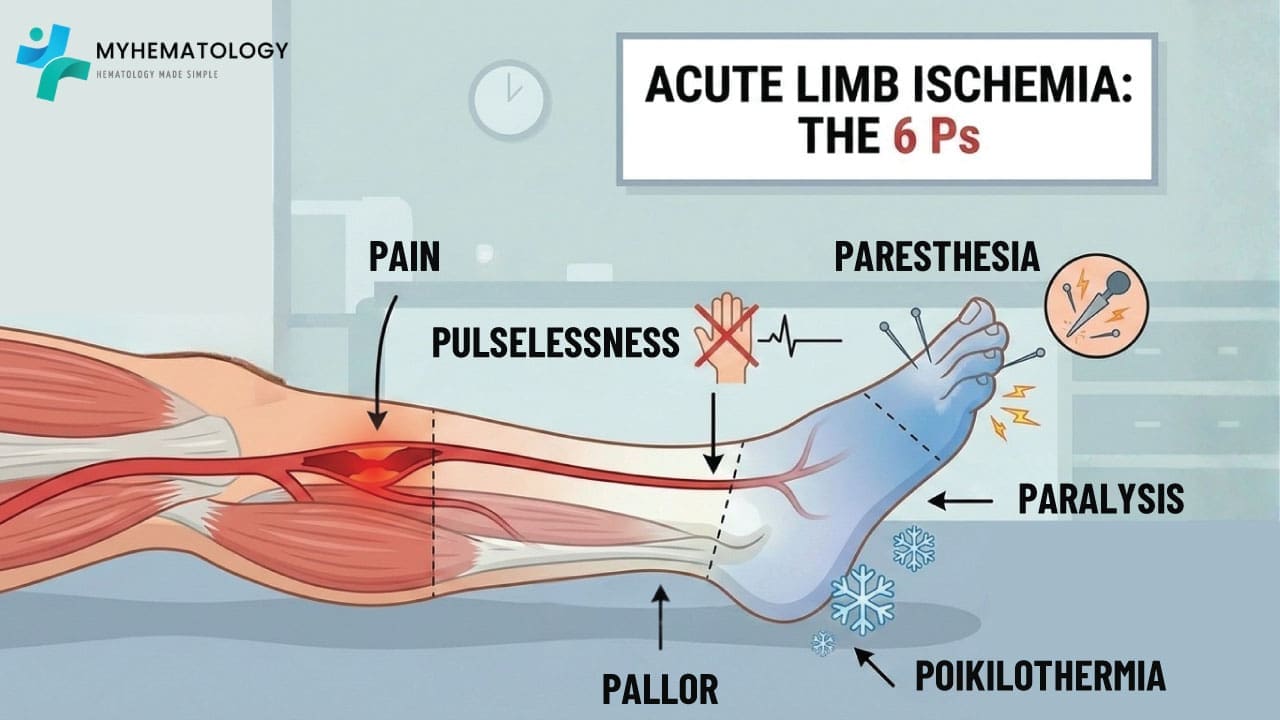
The blood flow in an artery blocked by a clot can trigger an acute event, a sudden disruption with alarming symptoms.
- Pain: A sharp, intense pain is often the first sign, This can be severe and localized, depending on the affected artery. Chest pain in a heart attack, leg pain in peripheral artery disease, or excruciating headache in a stroke are all potential clues.
- Ischemia: The tissues downstream of the clot experience oxygen deprivation, leading to weakness, numbness, and even paralysis in the affected area.
- Discoloration: Pallor (paleness) or cyanosis (bluish discoloration) can occur in the affected area due to the reduced blood flow.
- Paresthesia: Pins and needles, numbness, or tingling sensations signal nerve damage from the lack of blood supply.
- Weakness: Muscles deprived of oxygen lose their strength, leading to difficulty moving or even complete paralysis.
- Loss of Function: Depending on the affected artery, the consequences can be dramatic, from slurred speech in a stroke to paralysis in a limb.
These acute signs are like flashing red lights, demanding immediate medical attention. Ignoring them can mean the difference between recovery and irreversible damage.
Chronic Symptoms of Arterial Thrombosis
Not all arterial thrombi announce themselves with such fanfare. Sometimes, the clot acts like a slow leak, gradually eroding health with chronic symptoms.
- Gradual Onset: The symptoms creep in insidiously, often mistaken for aging or overexertion until they become undeniable.
- Recurrent Pain: This could be a nagging ache or a sharp twinge, occurring in the affected area, especially with exertion.
- Claudication: This refers to leg pain that occurs on exertion and disappears with rest.
- Coldness: The affected area may feel cold to the touch due to reduced blood flow.
- Ulceration: In severe cases, chronic ischemia can lead to skin breakdown and ulcer formation.
Virchow’s Triad
Imagine a three-legged stool, each leg representing a crucial element of a stable structure. In the world of blood flow, that stool is Virchow’s Triad, a concept that explains the formation of blood clots (thrombi) within arteries. Each leg of this triad represents a factor that, when present in excess or imbalance, can tilt the balance towards thrombosis.
Endothelial Injury
The endothelium, the smooth inner lining of arteries, ensures smooth flow and preventing unwanted blood clot formation. When this lining gets damaged, it becomes rough and sticky, like Velcro attracting platelets and other clotting factors. This damage can be caused by:
- High blood pressure: This constant pressure wears down the endothelium, making it more susceptible to damage.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoke contains toxins that directly harm the endothelium, increasing inflammation and clot formation.
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in arteries can irritate and damage the endothelium.
- Dyslipidemia: High levels of LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) can damage the endothelium and promote plaque buildup.
- Diabetes: This chronic condition disrupts blood flow and weakens the endothelium, making it more prone to injury.
- Infections: Certain infections can damage the endothelium, especially in smaller arteries.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like lupus can attack the endothelium, increasing its vulnerability.
- Physical trauma: Injuries to blood vessels can directly damage the endothelium, triggering clot formation.
Blood Flow Stasis
Imagine a slow-moving river; debris is more likely to accumulate in stagnant areas. This sluggishness, known as stasis, allows blood cells to linger longer in one place, increasing the chance of them clumping together and forming a clot. Factors contributing to stasis include:
- Atherosclerosis: Plaque buildup in arteries narrows the passageway, slowing blood flow.
- Varicose veins: These enlarged, twisted veins have sluggish blood flow, increasing the risk of thrombosis.
- Prolonged bed rest or immobilization: Lack of movement can lead to blood pooling and stasis in the legs.
- Heart failure: This condition weakens the heart’s pumping ability, leading to reduced blood flow and stasis.
- Certain medications: Some medications, like diuretics, can thicken the blood and slow its flow.
Hypercoagulability
Think of blood as a delicate balance between clotting and flowing. Hypercoagulability, or an increased tendency for blood to clot, tips this balance towards the formation of unwanted thrombi. Factors promoting hypercoagulability include:
- Genetic factors: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of excessive clotting.
- Medical conditions: Cancer, inflammatory diseases, and hormonal imbalances can all disrupt the normal balance of clotting factors.
- Pregnancy and childbirth: These physiological changes increase the risk of blood clots.
- Smoking: As mentioned earlier, smoking promotes inflammation and clot formation.
- Certain medications: Hormone therapy and some birth control pills can increase the risk of clotting.
Remember, Virchow’s Triad isn’t a simple checklist; it’s a complex interplay of these three factors. Often, a combination of two or even all three elements contributes to the formation of arterial thrombi.
Alternative and evolving theories of thrombosis
While Virchow’s Triad has stood as the cornerstone of understanding thrombosis for centuries, emerging research and clinical observations have led to alternative and evolving theories that paint a more nuanced picture of clot formation.
The Response to Injury Hypothesis
This theory expands on Virchow’s Triad by emphasizing the dynamic interplay between endothelial injury and the body’s inflammatory response. It suggests that endothelial damage triggers an inflammatory cascade, attracting immune cells like neutrophils and platelets. These immune cells, along with the damaged endothelium, release inflammatory mediators that further promote clot formation. This broader perspective highlights the role of inflammation in thrombosis, potentially opening doors for new therapeutic strategies targeting inflammatory pathways.
The Shear Stress Hypothesis
This theory focuses on the impact of blood flow dynamics on clot formation. It suggests that areas of low shear stress (slow or turbulent flow) within the vasculature promote platelet aggregation and activation, leading to thrombus formation. This can occur in areas of plaque buildup or vessel bifurcations where blood flow patterns are disrupted. Understanding how shear stress influences clot formation could lead to the development of devices or medications that modify blood flow patterns and prevent thrombosis.
The Virchow Plus Hypothesis
This theory acknowledges the limitations of Virchow’s Triad by adding additional factors that contribute to thrombosis. These include genetic predisposition, specific protein and enzyme abnormalities, and environmental factors like air pollution and stress. By considering these additional elements, this hypothesis provides a more comprehensive framework for understanding the complex web of factors that contribute to clot formation.
The Role of Microcirculation
Recent research suggests that thrombus formation might not be limited to large arteries but could also occur in the intricate network of microscopic vessels. This “microthrombosis” is increasingly recognized as a potential contributor to various diseases, including organ failure and chronic inflammatory conditions. Understanding the mechanisms of microthrombosis could lead to the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic tools for these complex diseases.
Pathophysiology of Arterial Thrombosis
Imagine a peaceful river of blood flowing through the intricate network of your arteries. Suddenly, a disturbance ripples through the current – endothelial injury, sluggish flow, or a hyperactive clotting system. This disturbance triggers a cascade of events, culminating in the formation of a fibrin clot, a potentially life-threatening dam in the arterial highway.
Clot Formation
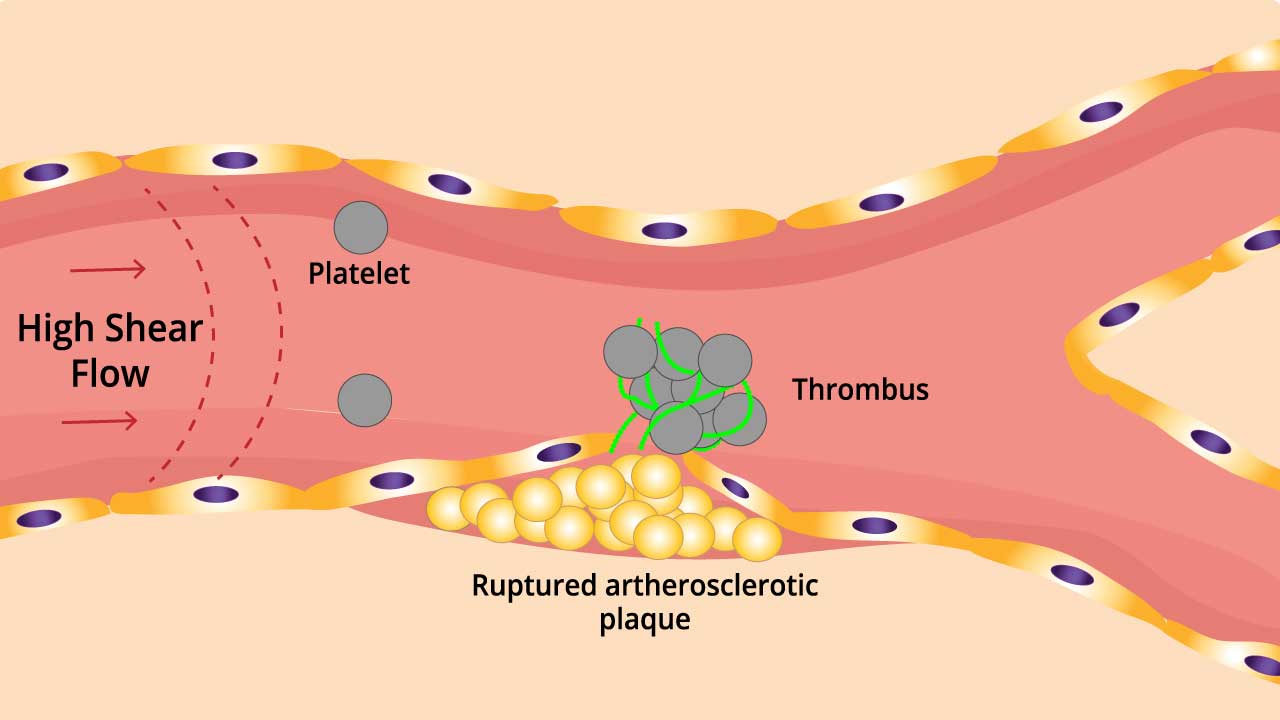
- Initiation: Clot formation begins with endothelial injury, often due to atherosclerosis, inflammation, or trauma. This injury exposes underlying collagen, a potent platelet activator.
- Platelet Adhesion and Activation: Sticky platelets, the first responders, adhere to the exposed collagen. Activated platelets release a plethora of signals, attracting more platelets and initiating the coagulation cascade.
- Coagulation Cascade: A cascade of protein activations ensues, culminating in the formation of thrombin, the enzyme responsible for converting fibrinogen into fibrin, the mesh-like structure of a clot.
- Fibrin Clot Formation: Thrombin cleaves fibrinogen into fibrin monomers, which then polymerize into a stable fibrin network, trapping platelets and red blood cells, forming a clot that blocks the artery.
The Key Players
- Platelets: These sticky cells act as the initial bridge, forming the first layer of the clot. Their activation and aggregation are crucial for the process.
- Coagulation Factors: These proteins, like actors in a play, work in a specific order to convert fibrinogen into fibrin, the main building block of the clot.
- Complement System: This immune system component adds another layer of reinforcement, stabilizing the fibrin clot and preventing its breakdown.
Arterial vs. Venous Thrombosis
While the basic principles of clot formation are similar in arteries and veins, key differences exist:
- Flow dynamics: Arterial flow is faster and more turbulent, favoring rapid platelet aggregation and clot formation. Venous flow is slower, allowing for a slower, more pro-coagulant environment.
- Clot composition: Arterial clots are typically platelet-rich and fibrin-rich, making them more stable and resistant to breakdown. Venous clots are often looser, containing more red blood cells and fibrin, making them more prone to dislodging and traveling as emboli.
- Triggering factors: Arterial thrombosis often arises from endothelial injury or hypercoagulability, while venous thrombosis is more commonly associated with stasis and hyperviscosity of blood.
| Feature | Arterial Thrombosis | Venous Thrombosis (VTE/DVT) |
| Primary Cause | Atherosclerosis (plaque rupture) & Platelet activation | Stasis (slow blood flow) & Coagulation factor activation |
| Clot Composition | “White Clot” (Rich in platelets) | “Red Clot” (Rich in fibrin and red blood cells) |
| Common Symptoms | The 5 P’s: Pain, Pallor, Pulselessness, Paresthesia, Paralysis | Swelling, redness, warmth, dull ache |
| Primary Treatment | Antiplatelets (e.g., Aspirin, Clopidogrel) | Anticoagulants (e.g., Heparin, Warfarin) |
| Major Risks | Heart Attack (MI), Stroke, Limb Ischemia | Pulmonary Embolism (PE), Post-thrombotic syndrome |
Understanding the clot formation in arteries, the unique roles of platelets, coagulation factors, and the complement system, and the key differences between arterial and venous thrombosis is crucial for developing effective strategies for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of these potentially devastating events.
Disorders Related to Arterial Thrombosis
Arterial thrombosis isn’t just a singular event; it can lead to a cascade of disorders depending on the affected artery and the extent of the blockage. Here’s a quick look of some of the most common culprits:
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): CAD narrows the heart’s own supply arteries, often via atherosclerosis. When a clot forms here, it can trigger a myocardial infarction (heart attack), robbing the heart of vital oxygen, leading to tissue damage and potentially fatal consequences.
2. Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke): When a clot blocks arteries supplying the brain, the result is a stroke. Sudden loss of blood flow can deprive brain cells of oxygen and nutrients, leading to paralysis, speech difficulties, or cognitive impairment, depending on the affected area.
3. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): PAD targets arteries in the legs, causing them to narrow and weaken. Clots here can lead to claudication (pain on walking), leg ulcers, and even gangrene, requiring amputation in severe cases.
4. Aortic Dissection: This dramatic event sees the inner layer of the aorta, our body’s largest artery, tear, allowing blood to dissect its way between layers. Clots can form within this dissection, further disrupting blood flow and potentially leading to life-threatening complications.
5. Acute Limb Ischemia: This rapid loss of blood flow to an arm or leg often stems from a sudden arterial clot. Severe pain, coldness, and limb discoloration are warning signs, demanding immediate medical attention to prevent irreversible tissue damage and amputation.
6. Others.
- Renal Artery Stenosis: Narrowed arteries supplying the kidneys can lead to high blood pressure and kidney damage.
- Intestinal Ischemia: Clots in mesenteric arteries can deprive the intestines of blood, causing severe abdominal pain and tissue death.
- Vision Loss: Clots in retinal arteries can block blood flow to the eye, leading to vision loss or blindness.
Arterial Thrombosis Investigations
Arterial thrombosis is a medical emergency that requires a systematic approach, moving from rapid diagnosis to a deep dive into etiology. Investigations are often categorized into confirmatory (is there a clot?), impact assessment (what is the organ damage?), and etiological (why did it happen?).
Clinical & Bedside Assessment
Before laboratory results return, clinical signs guide the urgency:
- The 6 P’s: Pain, Pallor, Pulselessness, Paresthesia, Paralysis, and Poikilothermia (coldness) indicate acute limb ischemia.
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): A bedside physiological test to assess the severity of peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Crucial to rule out atrial fibrillation, a leading cause of cardioembolic arterial events.
Diagnostic Imaging (The Gold Standard)
Imaging is required to confirm the location, extent, and nature of the thrombus.
- Duplex Ultrasonography: The first-line, non-invasive tool. It combines B-mode imaging (structure) with Doppler (blood flow velocity) to detect occlusions.
- CT Angiography (CTA): The most common rapid imaging modality. It provides high-resolution 3D maps of the arterial tree and can identify atherosclerotic plaques or “soft” thrombi.
- MR Angiography (MRA): Useful for patients who cannot tolerate CT contrast or for detailed imaging of the carotid and intracranial arteries.
- Catheter-based Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): Still considered the gold standard. It allows for both definitive diagnosis and immediate intervention (e.g., thrombectomy or stenting).
Core Laboratory Investigations
These assess the patient’s general state and the immediate biochemical impact of the clot.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) with Differential: Look for thrombocytosis, polycythemia, or leukocytosis. The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) is an emerging marker of systemic inflammation and a predictor of adverse outcomes in arterial events.+1
- Coagulation Profile: PT, aPTT, and Fibrinogen. While often normal in arterial thrombosis, they provide a baseline before starting anticoagulation.
- Markers of Organ Damage:
- Creatine Kinase (CK) & Myoglobin: To assess for skeletal muscle necrosis in limb ischemia.
- LDH & AST: Elevated in renal or splenic infarctions.
- Troponin: To rule out concurrent or causative myocardial infarction.
- Metabolic Panel: HbA1c and lipid profile (LDL-C, HDL-C, Lp(a)) to assess traditional atherosclerotic risk.
Hematological & Etiological Workup
When an arterial event is “unexplained” (non-atherosclerotic and non-cardioembolic), hematologists look for specialized triggers.
Thrombophilia Screening
Arterial thrombosis is more strongly linked to acquired rather than hereditary thrombophilia.
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Workup: This is the most critical “hematological” investigation for arterial events. Test for:
- Lupus Anticoagulant (LA)
- Anti-cardiolipin (aCL) antibodies (IgG/IgM)
- Anti-β2-glycoprotein I (aβ2GPI) antibodies
- Hereditary Thrombophilias: Testing for Factor V Leiden or Prothrombin G20210A is generally lower yield for arterial events compared to venous ones, but may be considered in young patients without other risk factors.
- Homocysteine Levels: Hyperhomocysteinemia is a recognized independent risk factor for arterial premature atherosclerosis and thrombosis.
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN)
Arterial thrombosis can be the first sign of an “occult” MPN.
- JAK2 V617F Mutation: Essential if the CBC shows even borderline high hemoglobin or platelets.
- CALR and MPL Mutations: To be screened if JAK2 is negative but clinical suspicion of MPN remains.
Specialized and Global Assays
- Platelet Function Testing: (e.g., PFA-100, Light Transmission Aggregometry) Used to assess “aspirin resistance” or hyper-reactivity.
- Viscoelastic Assays (TEG/ROTEM): While primarily used in bleeding management, they can identify a “hypercoagulable” profile (short R-time, high Maximum Amplitude) in acute settings.
- Thrombin Generation Assays (TGA): A research-grade tool that measures the “thrombin potential” of a patient’s plasma, providing a more global view than traditional PT/aPTT.
Searching for the Source (Embolic Workup)
If the thrombus is embolic, the source must be found:
- Transthoracic/Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TTE/TEE): To look for left atrial thrombi, vegetations (endocarditis), or a Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) which could allow a “paradoxical” embolus from the venous side.
- Holter Monitoring: For detecting paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
Summary Investigation Checklist
| Category | Key Investigations |
| Immediate Diagnosis | CTA, Doppler, ABI, ECG |
| Basic Hematology | CBC (NLR), PT/aPTT, Fibrinogen, D-dimer |
| Atherosclerotic Risk | Lipids, HbA1c, hs-CRP, Lp(a) |
| Primary Hematology Workup | APS Screen, JAK2 Mutation, Homocysteine |
| Embolic Source | Echocardiogram (TEE), Holter Monitor |
| Advanced Tools | TEG/ROTEM, Thrombin Generation, Platelet Aggregometry |
General Treatment and Management of Arterial Thrombosis
The management of arterial thrombosis is a medical race against the clock. Because arteries deliver oxygenated blood to vital organs, any delay in treatment can lead to irreversible tissue death (infarction).
Acute Reperfusion: Restoring the Flow
The primary goal in an acute arterial event (like a heart attack, stroke, or acute limb ischemia) is to physically or chemically open the vessel.
- Thrombolysis (“Clot-Busting”): Medications like Alteplase (tPA) or Tenecteplase are administered to dissolve the fibrin mesh of the clot. These carry a high risk of bleeding and are time-sensitive (e.g., usually within 4.5 hours for a stroke).
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: A catheter is inserted into the artery to physically pull or suck the clot out. This is now the gold standard for many large-vessel strokes and limb-threatening clots.
- Angioplasty and Stenting: A balloon is inflated to crush the underlying plaque, and a mesh stent is placed to keep the artery propped open.
- Surgical Bypass: If the blockage is too long or complex, surgeons “reroute” the blood using a graft (either a vein from the patient or a synthetic tube) to bypass the obstruction.
Pharmacological Management
Since arterial clots are “white clots” (primarily composed of platelets), the medication strategy differs significantly from venous clots.
- Antiplatelet Therapy: These are the frontline defense for arterial issues.
- Aspirin: Irreversibly inhibits COX-1, preventing platelet activation.
- P2Y12 Inhibitors: (e.g., Clopidogrel, Ticagrelor, Prasugrel) Often used alongside aspirin in Dual Antiplatelet Therapy (DAPT), especially after a stent is placed.
- Anticoagulation: While arterial clots are platelet-heavy, the coagulation cascade still plays a role in stabilizing the clot.
- Heparin (UFH or LMWH): Used in the acute phase to prevent the clot from propagating.
- Warfarin or DOACs: Typically reserved for cases where the clot came from the heart (e.g., Atrial Fibrillation) or in specific conditions like Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS).
Secondary Prevention
Treatment doesn’t end when the clot is gone; the focus shifts to preventing the next “Silent Killer.”
| Category | Goal/Medication |
| Lipid Management | High-intensity Statins (e.g., Atorvastatin) to stabilize plaques and lower LDL. |
| Blood Pressure | Goal typically <130/80 mmHg using ACE inhibitors or Beta-blockers. |
| Diabetes Control | Tight glucose control to prevent further endothelial “caramelization” (damage). |
| Lifestyle Changes | Smoking cessation is non-negotiable; smoking is a massive trigger for arterial stickiness. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can you tell the difference between DVT and arterial thrombosis?
DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) and arterial thrombosis differ in location and symptoms. DVT occurs in veins, often the legs, causing swelling, pain, and redness. Arterial thrombosis happens in arteries, often leading to sudden, severe pain, numbness, or coldness in the affected limb. It’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention for both conditions.
What are the common sites of arterial thrombosis?
Common sites of arterial thrombosis include:
- Heart: Coronary arteries leading to a heart attack
- Brain: Carotid arteries leading to a stroke
- Legs: Arteries in the legs and feet
- Other organs: Less common sites include kidneys, intestines, and eyes.
What are the 5 P’s of arterial thrombosis?
The 5 P’s of arterial thrombosis are:
- Pain: Severe pain in the affected limb.
- Pallor: Unusually pale skin in the affected limb.
- Pulselessness: Absence or weak pulse in the affected limb.
- Paresthesia: Numbness or tingling in the affected limb.
- Paralysis: Loss of movement in the affected limb.
Why is aspirin used in arterial thrombosis?
Aspirin is used in arterial thrombosis prevention because it helps prevent blood platelets from sticking together and forming clots. By inhibiting platelet aggregation, aspirin reduces the risk of blood clots blocking arteries, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes. It’s important to note that aspirin should be used under medical guidance as it can increase the risk of bleeding.
How long do you use anticoagulant for arterial thrombosis?
The duration of anticoagulant use for arterial thrombosis varies depending on the specific case. Generally, it’s recommended for at least 3 to 6 months, but can be longer based on the patient’s risk factors, severity of the thrombosis, and the underlying cause. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan are often necessary.
Is arterial thrombosis curable?
Arterial thrombosis itself isn’t curable, but its effects can be managed and prevented. While medications can dissolve existing clots and procedures like angioplasty or surgery can restore blood flow, the underlying conditions that led to the clot, such as atherosclerosis, often require ongoing management. The focus is on preventing future clots and minimizing damage to affected organs.
What is the difference between a thrombus and an embolus?
A thrombus is a blood clot that forms and stays in one place (e.g., inside a coronary artery). An embolus is a clot that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream until it gets stuck in a smaller vessel (e.g., traveling from the heart to the brain to cause a stroke).
Can COVID-19 cause arterial thrombosis?
Yes. COVID-19 can cause severe inflammation and damage to the lining of blood vessels (endothelium), leading to a higher risk of both venous and arterial clots, including strokes and heart attacks, even in younger patients.
Is arterial thrombosis hereditary?
While the thrombosis itself is not directly inherited, the risk factors often are. Genetic conditions like high cholesterol (Familial Hypercholesterolemia), high blood pressure, or specific clotting disorders (like Antiphospholipid Syndrome or elevated Homocysteine) can run in families and increase your risk.
Can stress cause arterial thrombosis?
Indirectly, yes. Chronic stress increases blood pressure and inflammation, and can lead to “stress cardiomyopathy.” Acute physical or emotional stress can also trigger plaque rupture, leading to a sudden heart attack or stroke.
What is the “Golden Hour” in treating arterial thrombosis?
This refers to the critical window of time immediately after a blockage occurs (like a stroke or heart attack). Receiving treatment (such as thrombolytics or surgery) within the first 60 minutes significantly increases the chances of survival and minimizes permanent tissue damage.
Glossary of Related Medical Terms
- Atherosclerosis: A condition where plaque (fat, cholesterol, and other substances) builds up in the artery walls, narrowing them and restricting blood flow.
- Claudication: Pain caused by too little blood flow, usually occurring in the legs during exercise and relieved by rest.
- Embolus: A blood clot (or other foreign matter) that breaks loose from its site of origin and travels through the bloodstream to block a smaller vessel elsewhere.
- Endothelium: The thin membrane that lines the inside of the heart and blood vessels; injury to this layer is a primary trigger for arterial thrombosis.
- Ischemia: An inadequate blood supply to an organ or part of the body, especially the heart muscles.
- Infarction: Tissue death (necrosis) caused by a lack of oxygen due to an obstruction of the tissue’s blood supply.
- Platelet Aggregation: The process where platelets clump together to form a clot; this is the primary mechanism in arterial thrombosis.
- Reperfusion: The restoration of blood flow to an organ or tissue after a blockage has been removed.
- Stenosis: The abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel.
- Thrombolysis: The breakdown (lysis) of blood clots by pharmacological means, commonly called “clot-busting.”
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and is specifically targeted towards medical students. It is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. While the information presented here is derived from credible medical sources and is believed to be accurate and up-to-date, it is not guaranteed to be complete or error-free. See additional information.
References
- Saba HI, Roberts HR. Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Practical Guidelines in Clinical Management (Wiley Blackwell). 2014.
- DeLoughery TG. Hemostasis and Thrombosis 4th Edition (Springer). 2019.
- Keohane EM, Otto CN, Walenga JM. Rodak’s Hematology 6th Edition (Saunders). 2019.
- Kaushansky K, Levi M. Williams Hematology Hemostasis and Thrombosis (McGraw-Hill). 2017.
- Ten Cate H, Meade T. The Northwick Park Heart Study: evidence from the laboratory. J Thromb Haemost. 2014 May;12(5):587-92. doi: 10.1111/jth.12545. PMID: 24593861.
- Ashorobi D, Ameer MA, Fernandez R. Thrombosis. [Updated 2024 Feb 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538430/
- May, J. E., & Moll, S. (2020). How I treat unexplained arterial thrombosis. Blood, 136(13), 1487–1498. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2019000820