Wilson’s disease: A rare genetic disorder causing toxic copper buildup in the liver and brain. Early diagnosis and lifelong treatment are crucial.
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS): A rare but serious condition causing red blood cell damage, low platelets, and kidney failure. Early diagnosis is key.
Hemoglobinuria: Overview and Causes
Hemoglobinuria: Red urine from free hemoglobin, not whole RBCs. Signals serious issues like hemolysis. Prompt diagnosis is vital.

Causes of Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia is excessive period bleeding. Explore the causes, symptoms and the approach to diagnose it.
Tachycardia in Hematological Patients
Tachycardia in hematology is critical. Often signals anemia, infection, or treatment issues. Early recognition improves patient outcomes.

Causes of Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia is excessive period bleeding. Explore the causes, symptoms and the approach to diagnose it.
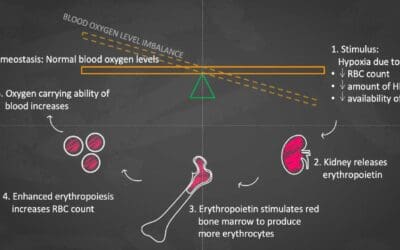
Erythropoietin
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production. It plays a crucial role in oxygen transport and is used to treat anemia in various conditions like kidney disease and cancer.
Fanconi Anemia
Fanconi anemia, a rare genetic disorder, causes bone marrow failure and increases cancer risk. Learn about symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
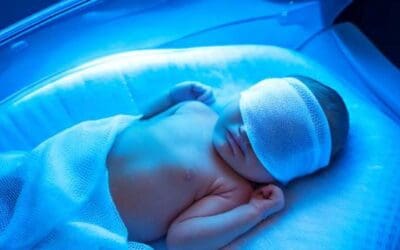
Neonatal Jaundice (High Bilirubin Levels in Newborns)
Neonatal jaundice is a common condition in newborns causing yellowing of the skin and eyes due to excess bilirubin in the blood. It can be caused by various factors, including immature liver function and certain medical conditions. While often harmless, severe cases can lead to complications.
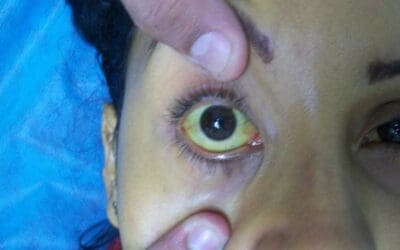
Jaundice (Hyperbilirubinemia)
Jaundice, a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, is caused by hyperbilirubinemia, an abnormally high level of bilirubin in the blood. It can be a symptom of various liver or biliary tract diseases.
Thalassemia
Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder causing reduced hemoglobin production. Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and jaundice. Treatment involves blood transfusions, iron chelation, and bone marrow transplants.
Severe Malarial Anemia
Malaria, a mosquito-borne illness, can cause severe anemia (low red blood cells) leading to weakness & fatigue. While most malaria cases are mild, severe anemia requires prompt medical attention.