TL;DR
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies. In this condition, abnormal plasma cells multiply uncontrollably and accumulate in the bone marrow. It is slightly more common in males than females and most common between 50 – 80 years old.
Pathophysiology ▾
- Overproduction of monoclonal paraprotein
- Bone destruction: Myeloma cells produce substances that stimulate bone breakdown, leading to bone pain, fractures, and increased risk of infection.
- Suppression of normal hematopoiesis: The overgrowth of myeloma cells can crowd out healthy blood cells, resulting in anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia.
- Hypercalcemia: Bone destruction can release calcium into the bloodstream, causing hypercalcemia, which can lead to confusion, weakness, and kidney stones.
- Kidney damage: The abnormal proteins produced by myeloma cells can clog the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
Multiple myeloma symptoms ▾
- Bone pain or pathological fractures
- Bone marrow failure (marrow infiltration)
- Infections (immune paresis & neutropenia)
- Renal failure
- Hypercalcemia
- Amyloidosis
Laboratory investigations ▾
- Full blood count and Peripheral blood characteristics: Anemia, neutropenia & thrombocytopenia in advanced disease. Rouleaux formation and leucoerythroblastic picture may be present.
- Bone marrow characteristics: >15% plasma cells
- Serum paraproteinemia &/or Bence Jones protein in the urine
- ↑ ESR, CRP, serum light chain, β2M,
- Bone lytic lesions in CT scan, X-rays, MRI
- Hypercalcemia
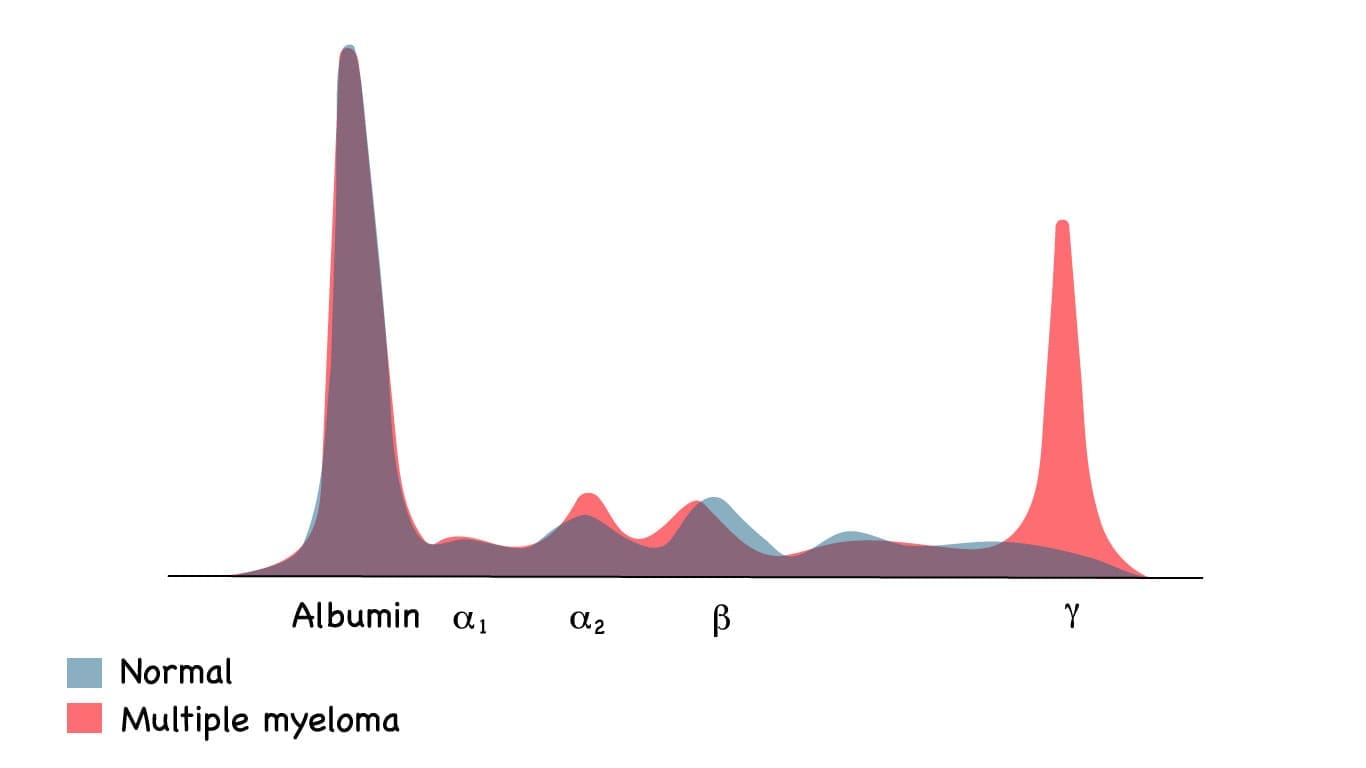
- M band in serum electrophoretic studies
- Renal function test: ↑ blood urea, serum creatinine and uric acid levels
Treatment and management ▾
- Chemotherapy
- Corticosteroid e.g. dexamethasone, prednisolone
- Thalidomide or Bortezomib
- Bone-modifying drugs
- Immunotherapy
- Stem cell transplantation
- Radiation therapy
*Click ▾ for more information
What is multiple myeloma (MM)?
Multiple myeloma is a neoplastic proliferation characterised by plasma cell accumulation in the bone marrow, presence of monoclonal immunoglobulins in the serum and/or urine and related tissue damage.
What are plasma cells?
Plasma cells are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that help the body fight infection. Plasma cells are produced in the bone marrow and then travel to the lymph nodes and spleen.
Plasma cells are formed from B cells, another type of white blood cell. When a B cell encounters an antigen, a foreign substance that the body does not recognize, it becomes activated and begins to divide. One of the daughter cells from this division becomes a plasma cell.
Plasma cells are highly specialized for antibody production. They have a large cytoplasm, which contains a lot of ribosomes, the organelles that produce proteins. Plasma cells also have a well-developed Golgi apparatus, which is responsible for packaging and secreting proteins. Plasma cells can produce a large number of antibodies, each of which is specific to a particular antigen. When an antibody encounters the antigen that it is specific for, it binds to it and marks it for destruction by other immune cells.
Plasma cells play a vital role in the immune system. Antibodies help to protect the body from a wide range of infections, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Antibodies also play a role in other immune functions, such as allergy and autoimmunity. In addition to their role in the immune system, plasma cells also play a role in other bodily functions, such as bone remodeling and wound healing.
How do plasma cells produce antibodies?
Normally, the plasma cells, representing the final stage of B-cell maturation produce polyclonal immunoglobulins to fight infections. The maturation of B lymphocytes occurs in the bone marrow and afterwards migrates to secondary lymph nodes, where antigens are presented to B cells.
Immature plasma cells are characteristically short-lived cells and producers of IgM involved in the primary immune response. In some circumstances, plasma cells experience hypermutations of the Ig light and heavy chains variable genes, secreting other Ig isotypes such as IgG and IgA or infrequently IgE and IgD or paraproteins. Later, these cells migrate to the bone marrow to differentiate into long-lived plasma cells, lasting for days or months.
Here are some examples of diseases that can affect plasma cells:
- Multiple myeloma: A cancer of the plasma cells
- Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia: A cancer of the plasma cells that produce a type of antibody called IgM
- Amyloidosis: A disease in which abnormal proteins called amyloid fibrils accumulate in the tissues, including the plasma cells
- Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID): A disorder in which the body does not produce enough antibodies
How does multiple myeloma occur?
The characteristic immunophenotype of malignant plasma cells is CD38high, CD138high and CD45low. Paraproteinemia refers to the presence of a monoclonal immunoglobulin band (M-protein) in the serum. M-protein reflects the synthesis of immunoglobulin from only a single clone of plasma cells. Tumour cells have very complex genetic changes but dysregulated or increased expression of cyclin D is believed to be an early unifying event. Aberrations include hyperdiploidy, translocations of immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene and monoallelic loss of 13q. These myeloma cells produce pathogenic antibodies or antibody fragments.
Multiple myeloma cells most commonly secrete IgG or IgA antibodies. However, in addition to complete antibodies, they usually also secrete free, unpaired Ig light chains which are small in size and can pass from the blood through the filtration slits of the renal glomeruli and into the renal tubules. The Ig light chains are toxic to renal epithelial cells and tend to form precipitates and obstructive casts which contribute to renal dysfunction.
Free lambda light chains are also prone to form amyloids which are fibrillar deposits that may be found in the renal glomeruli and the perivascular spaces of many tissues including the liver, spleen and heart. Renal amyloidosis often causes nephrotic syndrome which is the spilling of albumin and other plasma proteins into the urine.
Bone resorption is caused by myeloma cells that stimulate the maturation and function of osteoclasts both directly, via release of factors such as macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1 alpha) and IL-3, and indirectly by stimulating marrow stromal cells to release osteoclastogenic factors such as receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL) and IL-6. At the same time, myeloma cells also release factors such as Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1) that suppress the activity of osteoblasts. The net effect of these alterations strongly favour bone resorption. The proliferation of malignant plasma cells also inhibits normal B-cell function and the production of normal antibodies resulting in an increased susceptibility to bacterial infections.
Pathophysiology
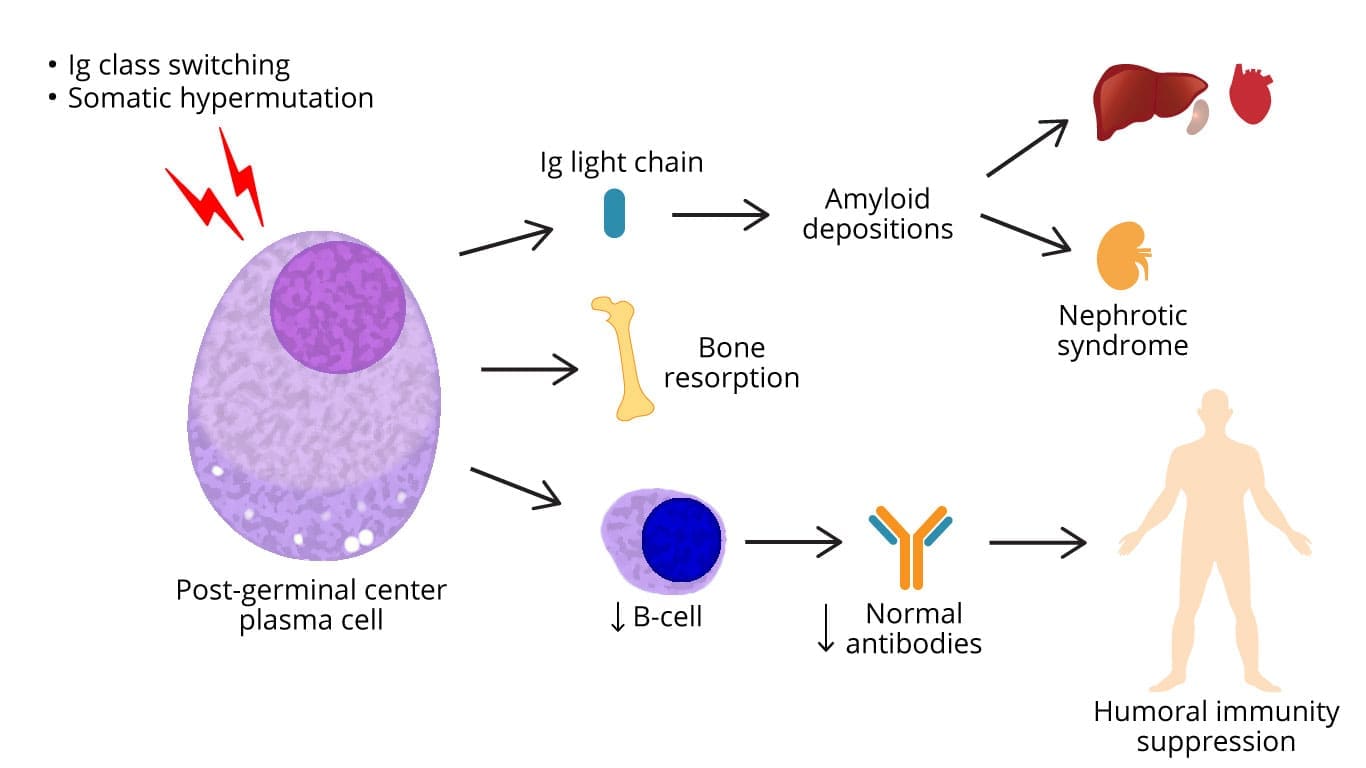
Multiple Myeloma (MM) Symptoms & Signs
98% of cases occur over the age of 40 years with a peak incidence at 70 years old.
Multiple myeloma symptoms are commonly related to hypercalcemia (C), renal failure (R), anemia (A), bone resorption (B).
- Bone pain: Bone pain is the most common multiple myeloma symptom, occurring in about 70% of patients at diagnosis. The pain is often located in the back, ribs, or pelvis. Occasionally patients experience bone pain especially backache due to vertebral collapse and pathological fractures.
- Anemia: Anemia is present in about 50% of patients at diagnosis. There may be abnormal bleeding tendency as myeloma protein may interfere with platelet function and coagulation factors.
- Hypercalcemia: Hypercalcemia is present in about 20% of patients at diagnosis.
- Immunosuppression: Immunosuppression is present in about 50% of patients at diagnosis. Recurrent infections are related to deficient antibody production, abnormal cell-mediated immunity and neutropenia.
- Amyloidosis and hyperviscosity syndrome may occur too.
Other multiple myeloma symptoms may include:
- Fatigue: Fatigue is a common multiple myeloma symptom, occurring in about 80% of patients.
- Shortness of breath: Shortness of breath is a common symptom of anemia, which is a common complication of multiple myeloma.
- Dizziness: Dizziness is a common symptom of anemia, which is a common complication of multiple myeloma.
- Nausea and vomiting: Nausea and vomiting can be symptoms of hypercalcemia, which is a common complication of multiple myeloma.
- Constipation: Constipation can be a symptom of hypercalcemia, which is a common complication of multiple myeloma.
- Frequent infections: Frequent infections can be a sign of immunosuppression, which is a common complication of multiple myeloma.
Laboratory Investigation
The diagnostic indicators of multiple myeloma are hypercalcemia, renal disease, anemia and bone lesions which give the abbreviation (CRAB).
- Characteristic “punched out” lytic skeletal lesions are produced by expanding masses of plasma cells.
- Rouleaux formation is marked in peripheral blood film.
- Bone marrow examination shows more than 10% plasma cells.
- Serum protein electrophoresis shows IgG in 60% of cases. Free light chains or Bence Jones proteins can be detected using the same methods.
- Raised serum beta-2 microglobulin is a useful indicator of prognosis.
- Cytogenetics are becoming more and more important in staging and prognostic purposes.
What are the different stages of multiple myeloma (MM)?
Multiple myeloma (MM) is staged for treatment purposes to help doctors determine the best treatment plan for each patient.
For myeloma, staging-wise it is important to begin with whether the patient is experiencing symptoms. It is common to classify people with newly diagnosed myeloma as either:
- Asymptomatic. This means the person does not have any multiple myeloma symptoms and signs. This is called smoldering myeloma.
- Symptomatic. This means the person has multiple myeloma symptoms and signs. Patients with multiple myeloma symptoms, or who are about to develop symptoms, need treatment. Multiple myeloma symptoms are described with the mnemonic acronym “CRAB.”
The Revised International Staging System (R-ISS) is now used more commonly to classify multiple myeloma. It defines the factors that affect a person’s survival of the disease. The system has 3 stages based on:
- Serum albumin level: Albumin is a protein that is produced by the liver. It helps to regulate the fluid balance in the blood and tissues. A low albumin level is a sign of advanced multiple myeloma.
- Beta-2 microglobulin (β2-M) level: β2-M is a protein that is produced by all cells in the body. It is removed from the blood by the kidneys. A high β2-M level is a sign of advanced multiple myeloma.
- Lactodehydrogenase (LDH) level: LDH is an enzyme that is found in all cells in the body. It is responsible for converting lactate to pyruvate, which is a source of energy for the cells. Elevated serum LDH levels are associated with a more aggressive form of multiple myeloma and a worse prognosis. Patients with elevated serum LDH levels are more likely to have bone marrow involvement, and they are more likely to develop complications from multiple myeloma, such as hypercalcemia and renal failure.
- Cytogenetic risk: Certain chromosomal abnormalities are associated with a worse prognosis in multiple myeloma. Recent efforts have been made to further classify myeloma based on patterns of gene expression in myeloma cells. Detection of specific chromosomal abnormalities are through fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) technique. High-risk cytogenetic abnormalities include:
- del(17p) (deletion of chromosome 17p)
- t(4;14) (translocation between chromosomes 4 and 14)
- t(14;16) (translocation between chromosomes 14 and 16)
Based on these three factors, patients are assigned to one of three stages:
Certainly. The Revised International Staging System (R-ISS) is a crucial tool for assessing the prognosis of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. It builds upon the original International Staging System (ISS) by incorporating cytogenetic abnormalities and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels.
Revised International Staging System (R-ISS)
| Stage | Criteria |
|---|---|
| R-ISS I | β2-microglobulin < 3.5 mg/L Albumin ≥ 3.5 g/dL Standard-risk cytogenetics (absence of high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities) Normal LDH |
| R-ISS II | Not R-ISS stage I or III |
| R-ISS III | β2-microglobulin > 5.5 mg/L And either: High-risk cytogenetics (presence of del(17p) and/or t(4;14) and/or t(14;16)) or elevated LDH |
- Recurrent or relapsed myeloma is myeloma that returns after a period of being in control after treatment is called recurrent myeloma or relapsed myeloma. If there is a recurrence, the cancer may need to be staged again (called re-staging) using one of the systems above.
Patients with stage I multiple myeloma have the best prognosis, while patients with stage III have the worst prognosis.
The ISS staging system is used to guide treatment decisions in multiple myeloma. Patients with stage I are typically treated with less aggressive regimens, while patients with stage III are typically treated with more aggressive regimens.
In addition to the ISS staging system, there are a number of other staging systems that are used in multiple myeloma. These staging systems are more complex, but they may be more accurate in predicting prognosis.
Treatment and Management
The current treatment depends on a number of factors, including the stage of the disease, the patient’s age and health, and the patient’s preferences.
The main goal of multiple myeloma treatment is to achieve remission, which is a state in which there is no evidence of the disease. Remission can be achieved with a variety of treatments, including:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy is often used in combination with other treatments, such as stem cell transplantation and immunotherapy. Currently, newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients are treated with induction therapy that usually includes triple combinations such as bortezomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone. Other preferred regimens may be selected depending on the eligibility of the candidates for transplants.
This first phase of multiple myeloma treatment has the objective of reducing tumour burden and improving the hematopoietic stem cell collection. After achieving response, this primary therapy is followed by high dose melphalan and autologous stem cell transplantation, consolidation and or maintenance using bortezomib or lenalidomide.
For relapse multiple myeloma patients, the situation has also improved with new multiple myeloma treatment options being recently approved, new strategies for therapy sequence and novel double or triple combinations. To date, no treatment has been proven to be curative in myeloma, but these new multiple myeloma treatments have roughly doubled the median survival, providing reason for optimism.
Stem cell transplantation
Stem cell transplantation is a procedure in which healthy stem cells are transplanted into the patient’s body. Stem cells are the immature cells that develop into different types of blood cells. Stem cell transplantation can help to restore the patient’s immune system and to kill cancer cells.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy uses the patient’s own immune system to fight cancer. Immunotherapy drugs can help to activate the immune system to kill cancer cells. It uses materials made either by the body or in a laboratory to improve, target, or restore immune system function.
In CAR T-cell therapy, some T cells are removed from a patient’s blood. Then, the cells are changed in a laboratory so they have specific proteins called receptors. The receptors allow the changed T cells to recognize the cancer cells.
In the case of idecabtagene vicleucel, the cells recognize BCMA on the myeloma cells. The changed T cells are grown in large numbers in the laboratory and returned to the patient’s body. Once there, they seek out and destroy cancer cells.
Immunomodulatory drugs
Thalidomide, lenalidomide , and pomalidomide are classified as immunomodulatory drugs, which stimulate the immune system. These drugs also keep new blood vessels from forming and feeding myeloma cells.
- Thalidomide and lenalidomide are approved to treat newly diagnosed patients.
- Lenalidomide and pomalidomide are also effective for treating recurrent myeloma.
- Steroids, such as prednisone and dexamethasone, are very effective at reducing the burden of plasma cells, but this effect is only temporary.
In addition to these main multiple myeloma treatments, there are a number of other treatments that may be used, including:
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy drugs target specific proteins or molecules that are involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. Targeted therapy is a treatment that targets the cancer’s specific genes, proteins, or the tissue environment that contributes to cancer growth and survival. This type of treatment blocks the growth and spread of cancer cells and limits damage to healthy cells. Targeted therapy for multiple myeloma includes proteasome inhibitors, histone deacetylase inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, nuclear export inhibitors and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) targeting agent.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is often used to treat specific areas of bone pain or to treat tumors that are blocking the flow of urine.
- Bisphosphonates: Bisphosphonates are drugs that help to strengthen bones and reduce the risk of bone fractures.
- Bone marrow stimulants: Bone marrow stimulants are drugs that help to stimulate the production of blood cells. Bone marrow stimulants may be used to treat patients with anemia caused by MM.
The best mutliple myeloma treatment plan for each patient will vary depending on the individual factors listed above. It is important to work with a doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
In recent years, there have been a number of advances in the multiple myeloma treatment. New drugs and treatment regimens have been developed that have improved the outcomes for multiple myeloma patients.
Current research on multiple myeloma treatment is focused on developing new and more effective treatments, as well as on finding ways to improve the quality of life for multiple myeloma patients.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is life expectancy with multiple myeloma?
The life expectancy with multiple myeloma can vary greatly depending on several factors, including:
- Stage of diagnosis: Earlier stages generally have a better prognosis.
- Age and overall health: Younger individuals and those with good overall health tend to have a better prognosis.
- Specific genetic features: Certain genetic mutations can influence the course of the disease.
- Response to treatment: Patients who respond well to treatment typically have a better prognosis.
Here’s a breakdown of some general statistics:
- Overall 5-year survival rate: Around 50-60% of people with multiple myeloma will survive for at least 5 years after diagnosis.
- Early-stage diagnosis: For the 5% of people diagnosed at an early stage, the 5-year survival rate is significantly higher, around 71%.
- Later-stage diagnosis: If the cancer has spread to a distant part of the body, the 5-year survival rate is lower, around 48%.
Can you fully recover from multiple myeloma?
There is currently no cure for multiple myeloma. However, with advancements in treatment, it can be managed effectively, potentially leading to long-term remission.
What is smoldering myeloma?
Smoldering myeloma, also known as asymptomatic myeloma, is a precursor stage to the blood cancer multiple myeloma. In smoldering myeloma, abnormal plasma cells are present in higher numbers than usual, but not high enough to cause symptoms or organ damage. Unlike active multiple myeloma, smoldering myeloma typically doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms. This is why it’s called “asymptomatic.” Identifying smoldering myeloma early allows doctors to monitor your condition closely and potentially intervene before it progresses to active myeloma. Some individuals may have this stage for a decade or even longer before transitioning to active myeloma.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between smoldering myeloma and active multiple myeloma:
| Feature | Smoldering Myeloma | Active Multiple Myeloma |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Usually none | Fatigue, bone pain, weakness, frequent infections, anemia |
| Plasma Cells | Elevated in bone marrow, may be detectable in blood/urine | High levels in bone marrow, blood, and urine |
| Bone Damage | No significant damage | May cause bone weakening and fractures |
| Organ Damage | No | May affect kidneys and other organs |
| Treatment | Usually no immediate treatment, only monitoring | Requires treatment to control the disease |
Why is Early Detection Important?
Catching smoldering myeloma early allows for:
- Close monitoring: Doctors can track the progression of the disease and intervene if needed.
- Potential to delay or prevent active myeloma: Early intervention with medications or other therapies may help delay or even prevent the development of symptomatic multiple myeloma.
- Improved long-term outcomes: Early detection and management can significantly improve your overall prognosis and quality of life.
What causes death in multiple myeloma?
Multiple myeloma itself, through complications like bone damage, kidney failure, or severe infections, is the most frequent cause of death in patients. However, some individuals may succumb to infections due to weakened immunity, cardiovascular disease which can be more prevalent in myeloma patients, or even other unrelated cancers that can develop during the course of the disease.
What are the first symptoms of myeloma?
While multiple myeloma often has no symptoms in the early stages (smoldering myeloma), initial signs when they do occur can be subtle. Look out for persistent fatigue, unexplained bone pain, especially in the back or ribs, increased susceptibility to infections, or easy bruising. These can be indicative of underlying problems with blood cell production and bone health, and warrant consultation with a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Are multiple myeloma and lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukemia related?
Multiple myeloma, lymphoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are all blood cancers, but they target different cell types. Myeloma affects plasma cells (antibody producers), while lymphomas originate in lymphocytes (infection fighters) in the lymph nodes or other organs. CLL is a specific type of lymphoma that affects a particular subtype of lymphocyte. While they share some features like abnormal blood cell production, the specific cells involved and their locations within the body distinguish these blood cancers.
Can multiple myeloma spread to other organs or metastasize?
Yes, multiple myeloma can spread beyond the bone marrow, which is where it originates. This spread, sometimes called metastasis, involves abnormal plasma cells traveling through the bloodstream and potentially forming tumors in other organs. While less common than bone involvement, these tumors can occur in places like the skin, lymph nodes, or even the liver. This spread can worsen the disease and requires additional treatment strategies.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and is specifically targeted towards medical students. It is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. While the information presented here is derived from credible medical sources and is believed to be accurate and up-to-date, it is not guaranteed to be complete or error-free. See additional information.
References
- Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV. Multiple myeloma. Blood. 2008 Mar 15;111(6):2962-72. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-078022. PMID: 18332230; PMCID: PMC2265446.
- Wallington-Beddoe, C.T., Mynott, R.L. Prognostic and predictive biomarker developments in multiple myeloma. J Hematol Oncol 14, 151 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01162-7
- Minnie SA, Hill GR. Immunotherapy of multiple myeloma. J Clin Invest. 2020 Apr 1;130(4):1565-1575. doi: 10.1172/JCI129205. PMID: 32149732; PMCID: PMC7108923.
- Rendo MJ, Joseph JJ, Phan LM, DeStefano CB. CAR T-Cell Therapy for Patients with Multiple Myeloma: Current Evidence and Challenges. Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2022 Aug 29;12:119-136. doi: 10.2147/BLCTT.S327016. PMID: 36060553; PMCID: PMC9439649.
- Avet-Loiseau H, Ludwig H, Landgren O, Paiva B, Morris C, Yang H, Zhou K, Ro S, Mateos MV. Minimal Residual Disease Status as a Surrogate Endpoint for Progression-free Survival in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma Studies: A Meta-analysis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Jan;20(1):e30-e37. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.09.622. Epub 2019 Oct 9. PMID: 31780415; PMCID: PMC7444731.
- Solimando AG, Krebs M, Desantis V, Marziliano D, Caradonna IC, Morizio A, Argentiero A, Shahini E, Bittrich M. Breaking through Multiple Myeloma: A Paradigm for a Comprehensive Tumor Ecosystem Targeting. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11072087
- Hussain M, Yellapragada S, Al Hadidi S. Differential Diagnosis and Therapeutic Advances in Multiple Myeloma: A Review Article. Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2023 Sep 15;13:33-57. doi: 10.2147/BLCTT.S272703. PMID: 37731771; PMCID: PMC10508231.