Hematuria: Blood in urine, gross (visible) or microscopic. Could signal infection, stones, or more serious issues.
Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH) is a rare autoimmune anemia. Cold exposure triggers red cell destruction, causing dark urine, back pain, and chills. Diagnosis relies on the Donath-Landsteiner test.
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH): An acquired blood disease where the immune system attacks red cells due to a mutation in the X chromosome.
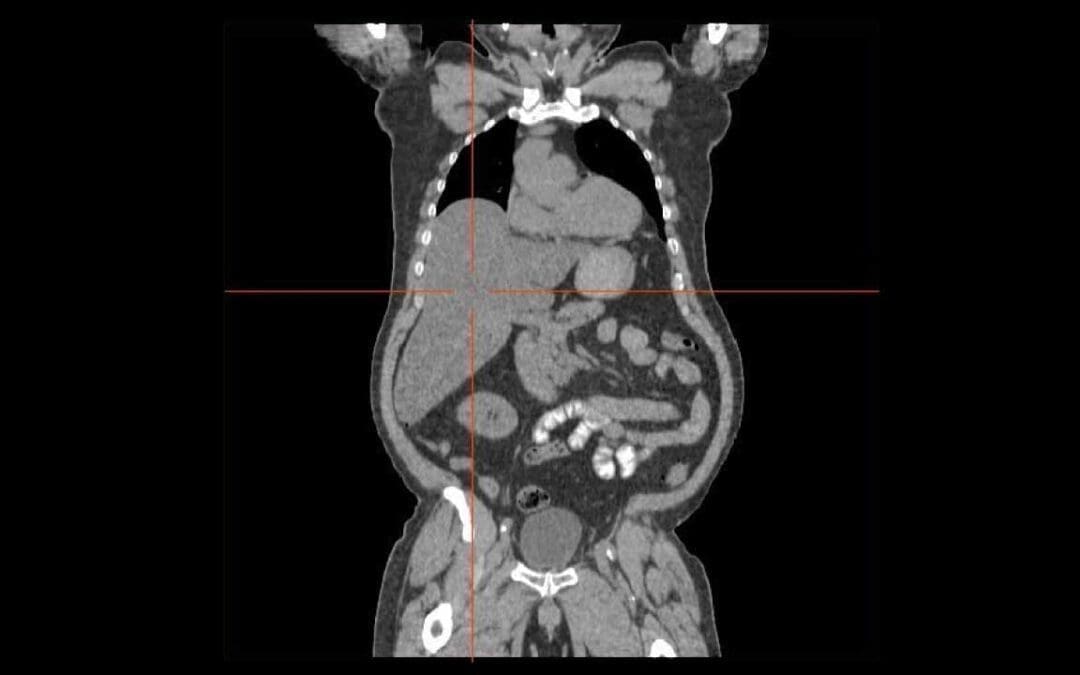
Liver and Causes of Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly means an enlarged liver, often a sign of underlying conditions like hepatitis, fatty liver, or heart failure. Diagnosis involves physical exams and imaging.
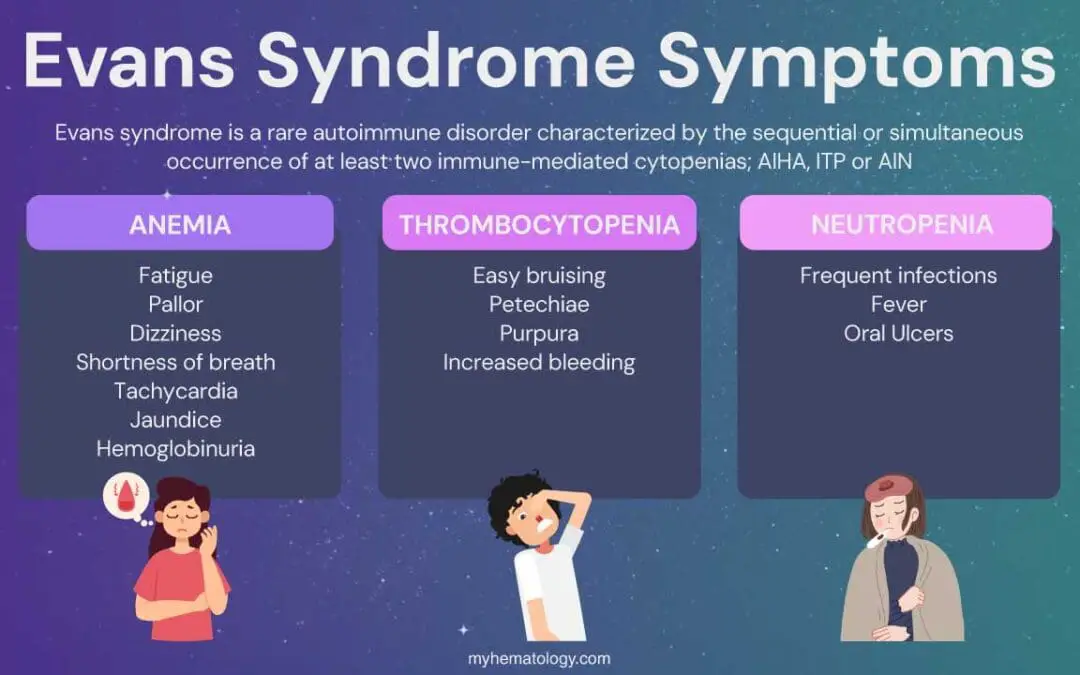
Evans Syndrome
Evans syndrome: Rare autoimmune disorder causing low red blood cells & platelets (AIHA & ITP). Can lead to fatigue, bruising, and bleeding.
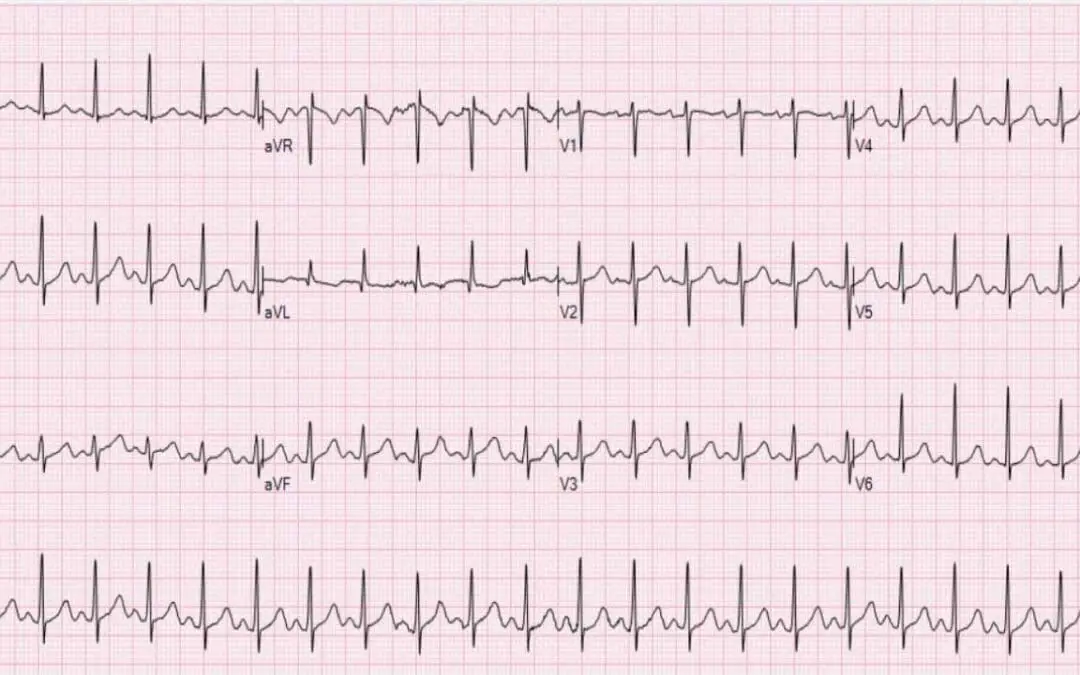
Tachycardia in Hematological Patients
Tachycardia in hematology is critical. Often signals anemia, infection, or treatment issues. Early recognition improves patient outcomes.
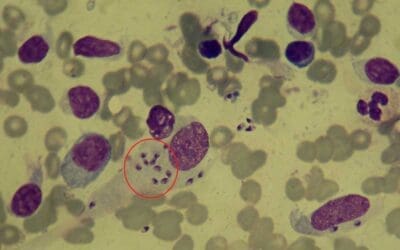
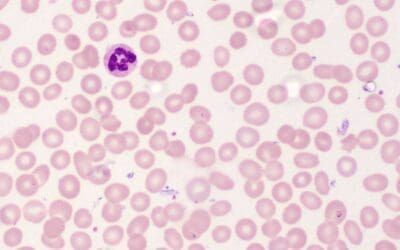
Preparation of Thick Blood Films for Parasites
Unveiling hidden threats! Learn the quick & easy technique for preparing thick blood smears to identify malaria, leishmaniasis & other blood parasites.
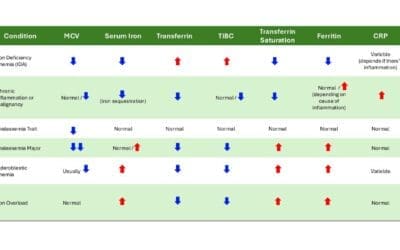
Iron Studies Interpretation: The Highs and Lows
Iron studies reveal iron deficiency, overload, and other conditions. Learn how MCV, ferritin, and other markers help decipher iron status and guide treatment.
Folate Deficiency
Folate deficiency, a lack of vitamin B9, can lead to fatigue, weakness, and even birth defects.
Pernicious Anemia
Pernicious anemia, an autoimmune condition, disrupts vitamin B12 absorption. This leads to fatigue, nerve problems, and a special type of anemia. Early diagnosis and B12 replacement therapy are key for good health.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia
Vitamin B12 keeps the red cells & nerves healthy, but deficiency can lead to fatigue, numbness, and weakness. Early diagnosis is key to prevent complications.
Systemic Approach to Anemia
Systematic anemia diagnosis starts with a detailed history, exam & blood tests. Iron studies, B12/folate levels & other tests pinpoint the cause (iron deficiency, vitamin deficiency, etc.) leading to targeted treatment & improved outcomes.