Lp(a): genetic risk for clots & heart disease. Not lowered by diet. Tests measure levels. Manage other risk factors.
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a life-threatening blockage in lung arteries, often from a leg clot. Urgent diagnosis and treatment are vital.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
PAD: Narrowed leg arteries causing pain, slow healing. Risk factors include smoking & diabetes. Early detection is key to prevent complications.

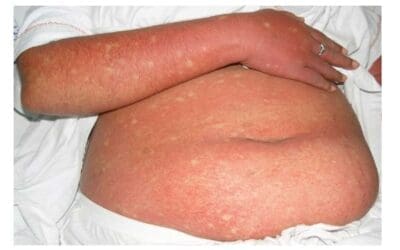
Ecchymoses
Ecchymoses, or bruises, are skin discolorations from blood leakage. Causes range from minor injury to underlying medical issues. Understanding them is key.
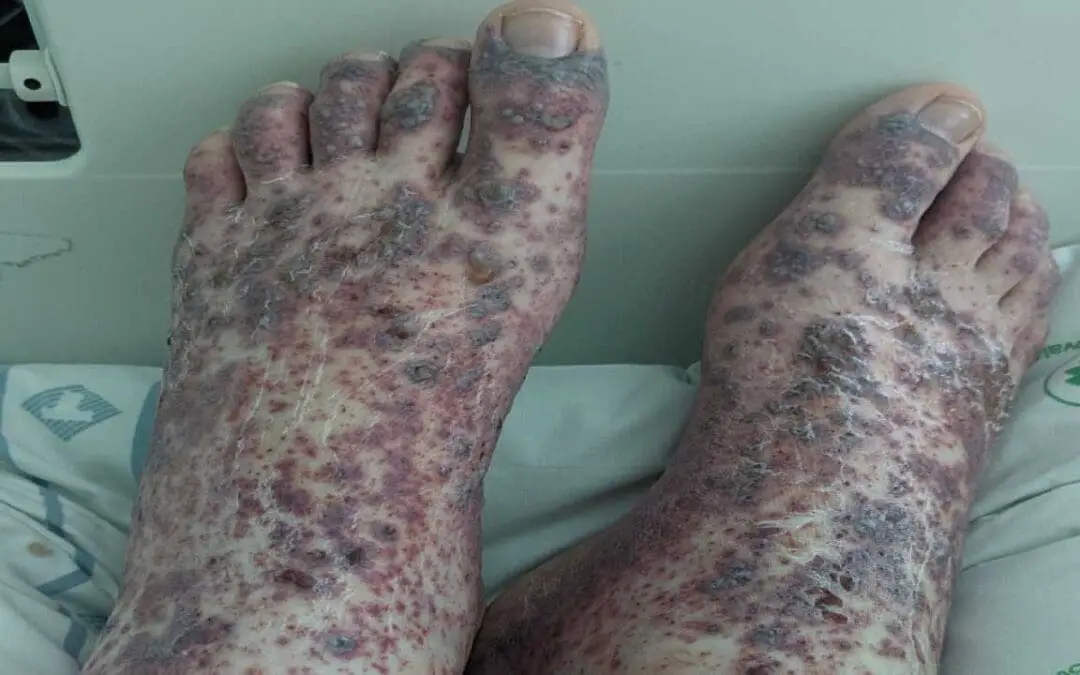
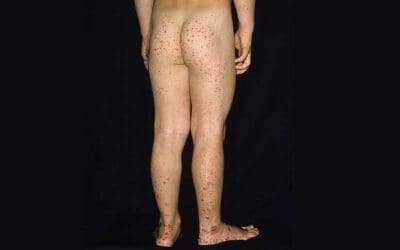
Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP)
Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP): Palpable rash, joint & belly pain, often in kids. Usually resolves in weeks, but need to monitor kidneys.

Ecchymoses
Ecchymoses, or bruises, are skin discolorations from blood leakage. Causes range from minor injury to underlying medical issues. Understanding them is key.
Vascular Bleeding Disorders
Vascular bleeding disorders come in two forms: inherited (passed down in families) and acquired (developed throughout life due to factors like vitamin deficiencies or medications). Both cause easy bruising & abnormal bleeding.
Dengue & Thrombocytopenia
Dengue isn’t just a fever and rash. This mosquito-borne illness can cause severe complications like bleeding and shock. Early diagnosis is key to preventing these and ensuring a smooth recovery for patients.
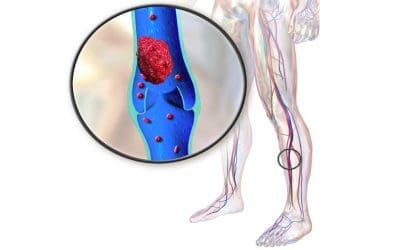
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Blood clot in leg vein, triggered by slow flow & damage. Can travel to lungs (PE), causing breathing problems & even death.
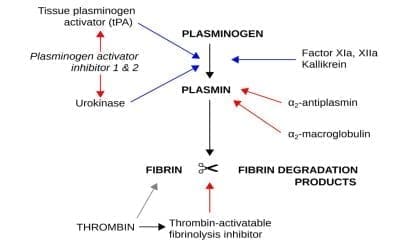
Fibrinolysis
The process of fibrinolysis dissolves fibrin clots after wound healing, restoring blood flow and preventing unwanted thrombus formation.
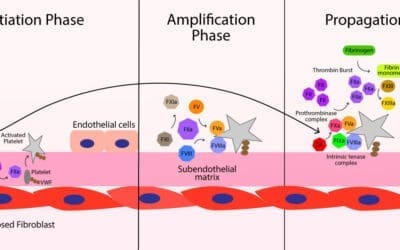
Secondary Hemostasis: Coagulation Cascade
Coagulation cascade creates a fibrin mesh that strengthens and stabilizes the platelet plug into a permanent clot.
Primary Hemostasis: The Platelet Plug
A formation of an quick but unstable plug as a first response to stop bleeding. Our very own platelet patch.