What is von Willebrand disease (VWD)?
Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is the most common inherited bleeding disorder, caused by a deficiency or abnormality of von Willebrand factor (VWF) resulting from a point mutation or major deletion.

What is the von Willebrand factor (VWF)?
Von Willebrand factor (VWF) is a large glycoprotein that plays a vital role in hemostasis, the process by which blood clots to stop bleeding. It is encoded by the VWF gene, which is located on chromosome 12. The VWF gene is approximately 178 kilobase pairs long and contains 52 exons. VWF is synthesized as a large 300 kDa protein which then forms mutimers up to 106 in weight.
VWF is produced by endothelial cells (the cells that line the inside of blood vessels) and megakaryocytes (the cells in the bone marrow that give rise to platelets). VWF is secreted into the blood plasma, where it circulates as a multimeric protein of varying sizes. The largest VWF multimers are the most active and have the greatest ability to bind to platelets.
VWF has two main functions in hemostasis:
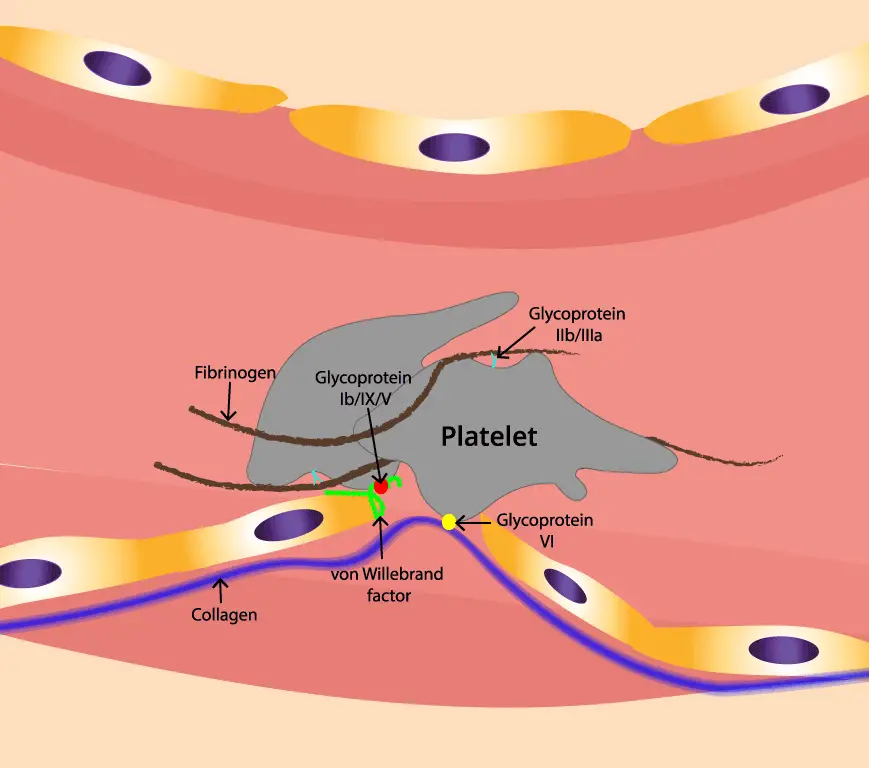
- Platelet adhesion: VWF helps platelets to adhere to each other and to the damaged blood vessel wall. This is the first step in the formation of a blood clot.
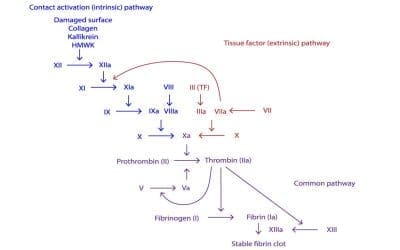
- Factor VIII stabilization: VWF binds to factor VIII, another important clotting factor, and protects it from degradation. Factor VIII is essential for the formation of thrombin, the enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin, the main component of a blood clot.
Mutations in the VWF gene can cause von Willebrand disease (VWD), a bleeding disorder that is characterized by easy bruising, nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual periods. The severity of VWD varies depending on the type and severity of the mutation.
Types of von Willebrand disease (VWD)
Three types of VWD have been described. Types 1 and 3 are caused by vWF protein deficiency, as measured by vWF antigen levels. Type 1 is by far the most common form, accounting for over 70% of affected individuals. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner with varying expressions of 15% – 60%. The severity of the bleeding is variable. Typically, there is mucous membrane bleeding, excessive blood loss from superficial cuts and abrasions and operative and post-traumatic hemorrhage.
In contrast to type 1 disease, levels of vWF antigen are less than 5% of normal in type 3 VWD and the inheritance pattern is autosomal recessive. Due to the fact that levels of vWF protein are so low in type 3 patients, they have much more severe bleeding and may develop hemarthrosis and other deep tissue bleeding similar to hemophilia A patients.
Type 2 disease is inherited in the same autosomal dominant manner as type 1. It accounts for about 25% of VWD. In these patients, the vWF antigen and factor VIII levels are generally normal but the vWF protein is qualitatively abnormal, leading to low ristocetin cofactor activity. Type 2 disease includes several subtypes.
Most individuals with type 2A disease have defective multimerization of vWF protein thus they bleed because of failure to form large multimers which greatly impairs the ability of vWF to tether platelets to injured endothelium. In type 2B, there is also reduction in the very large multimers but due to structural mutations that increase the binding of vWF to platelet GPIb/IX. This results in clearance of large multimers from the plasma and sometimes causes mild thrombocytopenia. Type 2M is characterised by reduced binding of von Willebrand factor to GPIb while in type 2N, patients inherit 2 defective copies of vWF with mutations within the N-terminal domain that abolish vWF binding to factor VIII. As a result, the vWF factor antigen and ristocetin cofactor levels are normal but the factor VIII are very low, and the patient has a clinical phenotype very similar to that of hemophilia A.
In summary,
- Type 1 VWD is the most common type, and it is caused by a quantitative deficiency of VWF.
- Type 2 VWD is caused by a qualitative abnormality of VWF. There are four subtypes of type 2 VWD, each with its own characteristic defect in VWF function.
- Type 3 VWD is the rarest and most severe type of VWD, and it is caused by a complete absence of VWF.
How does von Willebrand disease (VWD) cause bleeding?
The pathophysiology of VWD varies depending on the type and severity of the disorder. However, all types of VWD can lead to bleeding problems because of the deficiency or dysfunction of VWF.
In type 1 VWD, the low levels of VWF impair platelet adhesion and factor VIII stabilization. This can lead to bleeding from cuts, injuries, surgery, dental work, and childbirth.
In type 2 VWD, the qualitative defects in VWF can impair platelet adhesion and factor VIII stabilization in different ways. Some people with type 2 VWD may have bleeding problems similar to those with type 1 VWD, while others may have more severe bleeding problems.
In type 3 VWD, the complete or nearly complete deficiency of VWF leads to severe bleeding problems from even minor cuts and injuries. People with type 3 VWD may also experience spontaneous bleeding, such as bleeding into the joints or internal organs.
The severity of bleeding problems in VWD also depends on the level of factor VIII. People with VWD often have low levels of factor VIII because VWF helps to stabilize factor VIII in the blood. Low levels of factor VIII can make the bleeding problems in VWD worse.
In addition to the bleeding problems, VWD can also lead to other complications, such as:
- Iron deficiency anemia: This can occur from chronic blood loss.
- Arthritis: This can occur from repeated bleeding into the joints.
- Pregnancy complications: Women with VWD may have an increased risk of heavy bleeding during childbirth and miscarriage.
Clinical signs and symptoms of VWD
The clinical manifestations of von Willebrand disease (VWD) vary depending on the type and severity of the disorder. Some people with VWD have mild or no symptoms, while others have heavy and prolonged bleeding. However, all types of VWD can lead to bleeding problems.
The most common clinical manifestations of VWD include:
- Easy bruising: People with VWD may bruise easily, even from minor bumps or knocks.
- Nosebleeds: People with VWD may have frequent or long-lasting nosebleeds.
- Heavy menstrual periods: Women with VWD may have heavy menstrual periods, with bleeding that lasts longer than 7 days or requires more than one pad or tampon per hour.
- Bleeding after surgery or dental work: People with VWD may experience excessive bleeding after surgery or dental work.
- Bleeding into the joints or internal organs: People with severe VWD may experience spontaneous bleeding, such as bleeding into the joints or internal organs.
- Heavy bleeding during labor and delivery
- Blood in the urine or stool
How is VWD diagnosed?
VWD can be difficult to diagnose because the bleeding problems can vary in severity and can be similar to other bleeding disorders. However, there are a number of tests that can be used to diagnose VWD.
The first step in diagnosing VWD is to take a medical history and perform a physical examination. The doctor will ask about the patient’s bleeding symptoms, including when they started, how often they occur, and how severe they are. The doctor will also ask about the patient’s family history of bleeding disorders.
The doctor will also perform a physical examination to look for signs of bleeding, such as bruises, nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual periods.
If the doctor suspects VWD, they may order a number of blood tests, including:
- Complete blood count (CBC): This test measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood. Platelet count is normal in this disease except for type 2B where it is low.
- Prothrombin time (PT): This test measures how long it takes for the blood to clot. PT is normal in vWD.
- Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT): This test measures how long it takes for the blood to clot in the presence of certain clotting factors. A prolonged APTT may be a sign of a bleeding disorder, such as VWD.
- Von Willebrand factor antigen (VWF:Ag): This test measures the amount of VWF in the blood. A low VWF:Ag level may be a sign of VWD.
- Von Willebrand factor activity (VWF:RCo): A functional assay of plasma VWF based upon the degree of platelet agglutination induced after the addition of Ristocetin. This test measures how well VWF is working. A low VWF:RCo level may be a sign of VWD.
If the results of the blood tests are abnormal, the doctor may order additional tests, such as:
- VWF multimer analysis: This test measures the size and distribution of VWF multimers in the blood. People with VWD may have abnormal VWF multimers.
- Factor VIII activity: This test measures the amount of factor VIII in the blood. Factor VIII is another important clotting factor that is stabilized by VWF. People with VWD may have low levels of factor VIII.
In some cases, the doctor may also recommend genetic testing to identify the specific mutation in the VWF gene that is causing the disorder.
How is von Willebrand disease (VWD) treated?
The goal of treatment for VWD is to prevent or control bleeding episodes. Treatment depends on the type and severity of VWD, as well as the individual patient’s needs.
Treatment options for VWD include:
- Desmopressin: Desmopressin is a medication that stimulates the release of VWF from the body’s stores like endothelial cells by acting on the V2 receptor. It is available as a nasal spray or an injection. Desmopressin is often used to treat mild to moderate VWD and to prevent bleeding before surgery or dental work. However, desmopressin is contraindicated in type 2B von Willebrand disease because it induces severe thrombocytopenia.
- Von Willebrand factor concentrate: Von Willebrand factor concentrate is a blood product that contains VWF. It is administered intravenously (into a vein). Von Willebrand factor concentrate is used to treat severe VWD and to prevent or control bleeding episodes in people with mild to moderate VWD who do not respond to desmopressin.
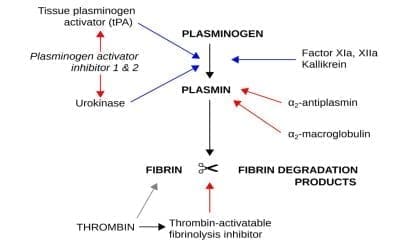
- Clot-stabilizing medications (fibrinolytic inhibitors): Clot-stabilizing medications, such as aminocaproic acid and tranexamic acid, can help to prevent blood clots from breaking down. These medications are often used to prevent bleeding in people with VWD who are undergoing surgery or dental work.
- Birth control pills: Birth control pills can help to control heavy menstrual periods in women with VWD as it can increase the amount of VWF and factor VIII in the blood and decrease menstrual blood loss.
In addition to medication, there are a number of lifestyle changes that can help people with VWD manage their condition. These lifestyle changes include:
- Avoiding activities that could lead to bleeding: People with VWD should avoid contact sports and other activities that could lead to bleeding.
- Taking care of their teeth and gums: People with VWD should brush and floss their teeth regularly and see a dentist for regular checkups and cleanings.
- Getting regular exercise: Exercise can help to improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of bleeding.
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet can help to maintain a healthy weight and improve overall health.
- Avoid taking blood thinners like aspirin.
People with VWD should work with their doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for them. With proper treatment, most people with VWD can live full and active lives.
Here are some additional tips for managing von Willebrand disease:
- Wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace: This will let medical professionals know that you have VWD in case of an emergency.
- Carry a copy of your medical records with you: This should include your diagnosis, treatment plan, and contact information for your doctor.
- Educate yourself and your loved ones about VWD: This will help you to understand your condition and how to manage it.
- Join a support group: There are a number of support groups available for people with VWD and their families. These groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
With proper management, most people with VWD can live long and healthy lives.
Key points of VWD
Definition
An inherited coagulation disorder caused by mutations in the von Willebrand factor (vWF). vWF is a factor VIII carrier protein and mediates platelet adhesion to endothelium
Pathogenesis
- Quantitative deficiency
- Type 1: partial deficiency. Autosomal dominant, mild disorder, most common.
- Type 3: complete deficiency. Autosomal recessive, severe disorder.
- Qualitative defects
- Type 2: functional abnormalities.
- Subtypes: 2A, 2B, 2M, 2N
Signs and symptoms
- Excessive bleeding from cuts, injuries, surgery, dental procedures, and menstruation
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Heavy or long menstrual periods
- Heavy bleeding during labor and delivery
- Blood in the urine or stool
- Easy bruising
- Lumpy bruises
Laboratory diagnosis
- Increased: APTT, bleeding time
- Normal: PT, platelet count
- Decrease: vWF assay, platelet function test, aggregation with ristocetin
Treatment and management
- DDAVP in mild bleeding
- Intermediary purity factor VIII concentrates
- Fibrinolytic inhibitors
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the life expectancy of someone with von Willebrand disease?
People with von Willebrand disease (VWD) generally have a normal life expectancy, especially those with the most common and mild form, type 1 VWD. This is because VWD is a manageable bleeding disorder, and with proper treatment, people with VWD can live long and healthy lives.
However, it’s important to note that there are different types of VWD, and the severity of symptoms can vary. In rare cases, people with severe VWD may experience life-threatening bleeding episodes.
Is von Willebrand disease painful?
Von Willebrand disease (VWD) itself doesn’t directly cause pain, but it can lead to symptoms that can be painful, such as:
- Bleeding into joints and muscles: This is a less common symptom but can occur in some people with VWD, especially those with the more severe type 3. This bleeding can cause swelling, stiffness, and pain in the affected joint or muscle.
- Heavy menstrual periods: This can be a significant issue for some women with VWD and can cause pain and discomfort.
Is von Willebrand disease life threatening?
In most cases, von Willebrand disease (VWD) is not life-threatening. The most common type, type 1 VWD, is usually mild and doesn’t cause life-threatening bleeding. Even with other types, proper management through treatment significantly reduces the risk.
However, it’s important to understand that:
- Uncontrolled bleeding can be life-threatening: While rare, severe bleeding episodes in any person, regardless of VWD, can become life-threatening if not addressed promptly.
- Severity of VWD matters: People with severe forms of VWD (types 2 and 3) are more prone to experiencing heavy, prolonged, or internal bleeding that can be life-threatening if left untreated.
- Certain situations increase risk: Situations like surgery, childbirth, or major injuries can increase the risk of life-threatening bleeding in individuals with VWD, even those with mild forms.
Can people with von Willebrand have babies?
Yes, women with von Willebrand disease (VWD) can have healthy pregnancies and births. However, due to the potential for bleeding complications, pre-conceptional counseling and close monitoring throughout pregnancy are essential. Here’s a breakdown of key points to remember:
- VWD Types and Pregnancy Risk
- Type 1 VWD: Most common and mildest form. VWF levels often increase during pregnancy, minimizing bleeding risk.
- Type 2 VWD: More severe bleeding symptoms. VWF levels may not rise significantly, requiring closer monitoring and potential treatment adjustments.
- Type 3 VWD: Rarest and most severe. VWF levels remain low, and factor replacement therapy is likely necessary throughout pregnancy.
- Increased Bleeding Risks During Pregnancy
- Vaginal bleeding: More common in the third trimester, especially with type 3 VWD.
- Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH): Increased risk for all VWD types due to physiological changes after delivery.
- Management Strategies
- Pre-pregnancy counseling: Discussing VWD severity, potential risks, and individualized management plans with a hematologist familiar with VWD and obstetrics.
- VWF level monitoring: Regular monitoring of VWF activity throughout pregnancy to assess potential need for factor replacement therapy.
- Delivery planning: Minimizing invasive procedures (forceps, vacuum) and considering prophylactic factor replacement therapy around delivery, especially for types 2 & 3.
- Multidisciplinary team approach: Collaboration between hematologist, obstetrician, and potentially anesthesiologist for optimal care.
- Fetal Considerations
- Risk of inheriting VWD: Offspring have a 50% chance of inheriting the condition, but genetic counseling can provide further information.
Can Von Willebrand disease affect the baby?
Yes, von Willebrand disease (VWD) can potentially affect a baby in a few ways, but the risk depends on the severity of the mother’s VWD and the specific type.
Risk of inheriting VWD
- Babies born to a parent with VWD have a 50% chance of inheriting the condition. However, the severity of the inherited VWD can vary.
Bleeding complications during pregnancy
- Mothers with VWD, particularly those with severe types (2 & 3), have a higher risk of excessive bleeding during pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum. This can potentially lead to complications like:
- Anemia: If blood loss is significant, the mother might develop iron deficiency anemia, which can affect the baby’s growth and development.
- Premature birth or low birth weight: In severe cases, excessive blood loss can compromise blood flow to the baby, potentially leading to these complications.
What not to do with von Willebrand disease?
Medications
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and aspirin: These medications can further inhibit platelet function and worsen bleeding tendencies in VWD patients. Consider alternative pain relievers like acetaminophen.
- Antiplatelet medications: Drugs like clopidogrel (Plavix) and ticagrelor (Brilinta) are typically contraindicated due to their additional inhibition of platelet function, which can exacerbate bleeding in VWD.
Procedures
- Unnecessary invasive procedures: Practices like unnecessary biopsies, venipunctures, or intramuscular injections can increase bleeding risk. Explore alternative non-invasive options whenever possible.
- Uncontrolled blood pressure: Elevated blood pressure can put additional stress on already weakened blood vessels in VWD patients, potentially increasing bleeding risk. Ensure proper blood pressure management.
Activities
- High-contact sports and activities: Activities with a high risk of falls or injuries, like contact sports (rugby, football), should be approached with caution and discussed individually with the patient. Alternative lower-risk activities might be encouraged.
Other
- Smoking and alcohol: These habits can negatively impact overall health and potentially worsen bleeding tendencies. Encourage smoking cessation and moderate alcohol consumption.
- Ignoring warning signs: Educate patients to recognize and report any unusual bleeding symptoms promptly, such as prolonged nosebleeds, excessive menstrual bleeding, or bleeding into joints or muscles.
Can I donate blood if I have von Willebrand’s disease?
Generally, people with von Willebrand disease (VWD) are not recommended to donate blood. This is due to a few key reasons:
- Risk of bleeding complications: Individuals with VWD already have a tendency to bleed due to a deficiency or malfunction of the von Willebrand factor, a protein crucial for blood clot formation. Donating blood further reduces their blood volume and potentially exacerbates this bleeding risk.
- Donor safety: The blood donation process itself involves needle punctures, which can increase the risk of bleeding at the puncture site for individuals with VWD.
- Blood product quality: Because of the potential presence of low levels of von Willebrand factor in the donated blood, it might not be suitable for all transfusion recipients, especially those who also have bleeding disorders.
Does von Willebrand worsen with age?
VWD itself doesn’t necessarily worsen with age. VWF levels may increase with age in some, particularly those with type 1 VWD, but this doesn’t always translate to reduced bleeding risk. Individuals with severe forms (types 2 & 3) are unlikely to experience significant improvement in symptoms with age.
Does von Willebrand disease make you tired?
Von Willebrand disease (VWD) itself doesn’t directly cause fatigue. However, it can lead to situations that can contribute to fatigue in some individuals, such as:
- Iron deficiency anemia: This is a common complication of heavy menstrual bleeding, especially in women with VWD. Iron deficiency can lead to symptoms like fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and pale skin.
- Frequent bleeding episodes: Even if not severe, repeated bleeding episodes can lead to iron loss and contribute to fatigue, especially if iron stores are not adequately replenished.
- Pain: VWD can sometimes cause painful symptoms like bleeding into joints and muscles, which can disrupt sleep and contribute to fatigue.
- Psychological stress: The burden of managing a chronic condition like VWD, including potential anxieties about bleeding episodes or limitations in activities, can contribute to psychological stress and potentially lead to fatigue.
At what age is von Willebrand disease diagnosed?
Here’s a general breakdown of diagnosis age based on available data:
- Men: Studies suggest an average diagnosis age of around 30-40 years for men with VWD.
- Women: Due to menstrual bleeding being a common symptom, women are diagnosed earlier, on average between 12 and 50 years old.
- Children: While less common, VWD can be diagnosed in children as well, especially if they experience frequent nosebleeds, prolonged bleeding from cuts, or excessive bleeding after procedures like tooth extraction.
Overall, there’s no single definitive age for VWD diagnosis.
Is it harder to get pregnant with von Willebrand disease?
No, von Willebrand disease (VWD) itself doesn’t necessarily make it harder to get pregnant. In fact, many women with VWD have successful pregnancies. However, there are some factors to consider:
- VWD Type:
- Type 1 VWD (most common): Fertility is usually not affected. VWF levels may even increase during pregnancy, further reducing bleeding risk.
- Type 2 & 3 VWD (more severe): While conception is possible, there might be a higher risk of miscarriage or bleeding complications due to lower VWF levels.
- Hormonal therapy: Medications used to regulate heavy menstrual bleeding, a common symptom in some women with VWD, can interfere with ovulation and make conception more challenging.
Can you have von Willebrand’s if your parents don’t?
While von Willebrand disease (VWD) is typically inherited from parents, it’s possible to have VWD even if your parents don’t, due to a phenomenon called sporadic mutations. In rare cases, VWD can occur due to a spontaneous genetic mutation in the egg or sperm cell, not inherited from either parent. This is known as a de novo mutation. These mutations can happen during cell division and are not present in the parents’ genes. Such sporadic mutations account for approximately 10-30% of VWD cases.
Is Von Willebrand’s disease curable?
No, there is currently no cure for von Willebrand disease (VWD). However, it is a treatable and manageable condition.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and is specifically targeted towards medical students. It is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. While the information presented here is derived from credible medical sources and is believed to be accurate and up-to-date, it is not guaranteed to be complete or error-free. See additional information.
References
- Saba HI, Roberts HR. Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Practical Guidelines in Clinical Management (Wiley Blackwell). 2014.
- DeLoughery TG. Hemostasis and Thrombosis 4th Edition (Springer). 2019.
- Keohane EM, Otto CN, Walenga JM. Rodak’s Hematology 6th Edition (Saunders). 2019.
- Kaushansky K, Levi M. Williams Hematology Hemostasis and Thrombosis (McGraw-Hill). 2017.
- Yawn BP, Nichols WL, Rick ME. Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease: Guidelines for Primary Care. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80(11):1261-1268.