TL;DR
What is ITP? ▾
- Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by a low platelet count.
- Platelets are essential blood cells that help form clots and prevent bleeding.
Causes ▾
- The immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy platelets.
- The exact trigger for this immune response is often unknown.
- ITP can be classified as acute (sudden onset, often resolves within 6 months) or chronic (long-lasting).
Risk Factors ▾
- Can occur at any age, but more common in children and adults between 50-60 years old.
- Slightly more common in females.
- Certain infections, medications, or underlying autoimmune diseases can increase the risk.
Symptoms ▾
- May be asymptomatic with mild ITP.
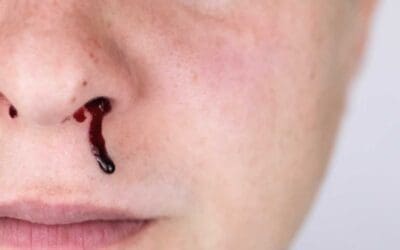
- Common symptoms include easy bruising, petechiae (tiny red spots on skin), prolonged bleeding from minor injuries.
- Severe cases can lead to bleeding from mucous membranes (mouth, nose, gastrointestinal tract).
Diagnosis ▾
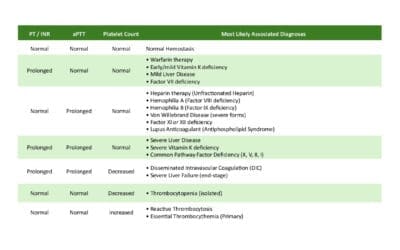
- Based on symptoms, physical examination findings, and blood tests (complete blood count).
- Additional tests might be needed to rule out other causes of low platelet count.
Treatment ▾
- Depends on the severity and type of ITP (acute or chronic).
- Corticosteroids are often the first-line treatment for acute ITP.
- Immunoglobulins (IVIG) can be used if corticosteroids are ineffective.
- Thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-RAs) stimulate platelet production and are used in chronic ITP or when other treatments fail.
- Splenectomy (spleen removal) might be considered in severe cases.
*Click ▾ for more information
Introduction
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) or previously known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is a condition in which the body’s immune system destroys platelets (autoimmune), the cells responsible for blood clotting. This can lead to a low platelet count, also known as thrombocytopenia and bleeding.
The incidence of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) varies depending on the age group
- Adults: The estimated annual incidence of immune thrombocytopenia in adults is between 1.6 and 3.9 cases per 100,000 people per year.
- Children: ITP is more common in children, with an estimated annual incidence of around 5 cases per 100,000 children.
Risk Factors for ITP
While the exact cause of immune thrombocytopenia is often unknown, certain factors may increase the risk.
Infections
- Viral infections: Particularly those caused by viruses like Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, hepatitis C, and influenza.
- Bacterial infections: Some bacterial infections can trigger ITP.
Autoimmune disorders
- Other autoimmune conditions: People with other autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, are at a higher risk.
Medications
- Certain drugs: Some medications, including antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and diuretics, can occasionally cause ITP as a side effect.
Pregnancy
- Postpartum ITP: ITP can sometimes develop after childbirth.
Age
- Children and adults: ITP can occur at any age, but it’s most common in children between 2-6 years old and adults between 50-60 years old.
Family history
- Genetic predisposition: Having a family history of ITP or other autoimmune diseases may increase the risk.
Clinical features of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) can manifest in various ways, depending on the severity of the platelet count decrease.
- May be asymptomatic: In some cases, particularly with mild ITP, there might not be any noticeable symptoms.
- Easy bruising (purpura): This is a common symptom, where even minor bumps or trauma can cause significant bruising due to the lack of sufficient platelets to form a proper clot.
- Petechiae: These are tiny, flat, reddish-purple spots under the skin caused by bleeding from small capillaries. They often appear on the lower legs, arms, or mucous membranes (mouth, gums).
- Prolonged bleeding from minor injuries: Cuts or injuries take longer than usual to stop bleeding due to the limited ability of platelets to form a clot.
- Bleeding from mucous membranes: In severe cases, bleeding can occur from the gums, nose, or gastrointestinal tract (manifesting as blood in vomit or stool). Menstrual periods may also become heavier and more prolonged.
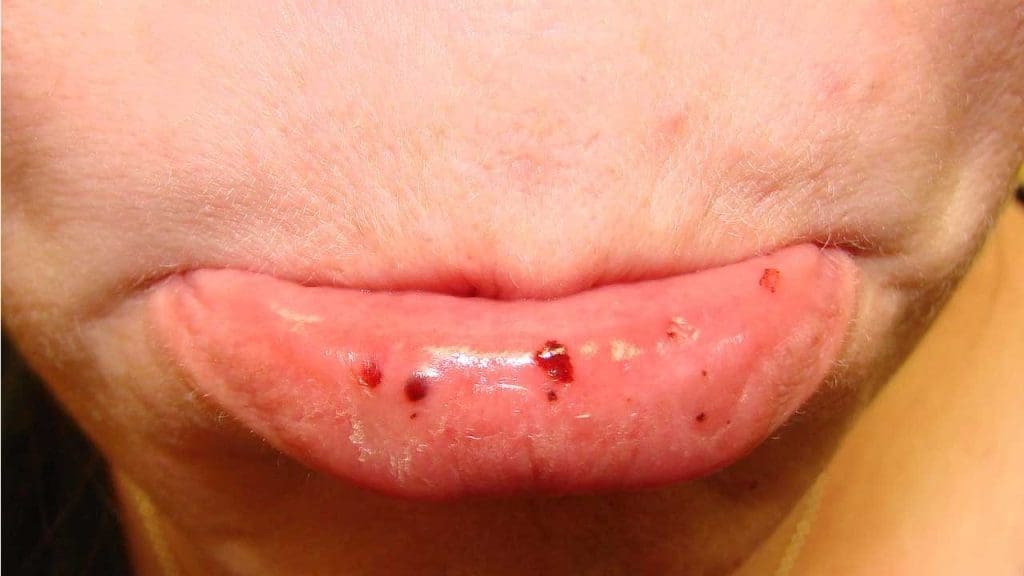
Other symptoms of ITP may include:
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Pale skin
- Dizziness
- Headache
Chronic ITP can also cause complications, such as:
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Splenomegaly (enlarged spleen)
- Infection
- Autoimmune disorders
How is immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) an autoimmune disorder?
The mechanism of how ITP occurs is not well understood. However, it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder.
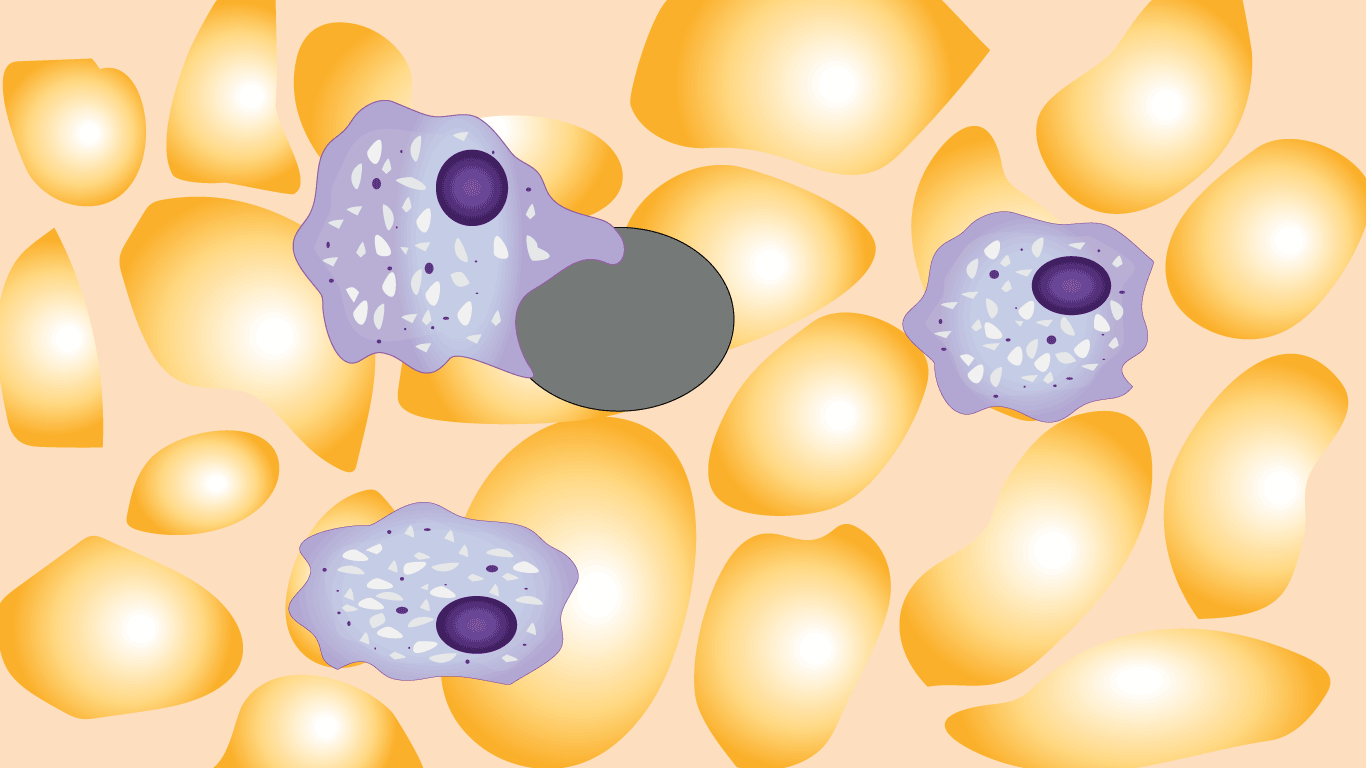
The thrombocytopenia is due to premature removal of platelets that are coated by allo/autoantibodies. These are detected by macrophage as foreign material. Hence there is removal of the platelet-Ab complex in the spleen.
The primary public antigen targeted for immune attack in immune thrombocytopenia is GPIIb/IIIa which undergoes a conformational change during platelet activation and is the site of fibrogen cross-linking. This cross-linking event is the crucial step in platelet aggregation and the propagation of the primary platelet plug. Once the antibody-coated platelet is recognized and engulfed by the macrophage, GPIIb/IIIa as well as other platelet membrane proteins are degraded.
These peptide antigens are then coupled with HLA class 2 molecules and displayed on the macrophage cell surface. This antigen-presenting complex interacts with the T-cell receptor on CD4 helper lymphocytes, inducing proliferation and recruitment of antigen-specific B-cell clones which also proliferate and produce high levels of antibody against not only GPIIb/IIIa, but also GPIb/IX and other platelet antigens.
The rapid destruction of platelets by resident macrophages results in Tpo-mediated stimulation of megakaryocyte production in the bone marrow. Thus the marrow can have normal or increased megakaryocyte numbers. The normal lifespan of a platelet is 7 -10 days but in ITP this is reduced to a few hours.
Pathophysiology
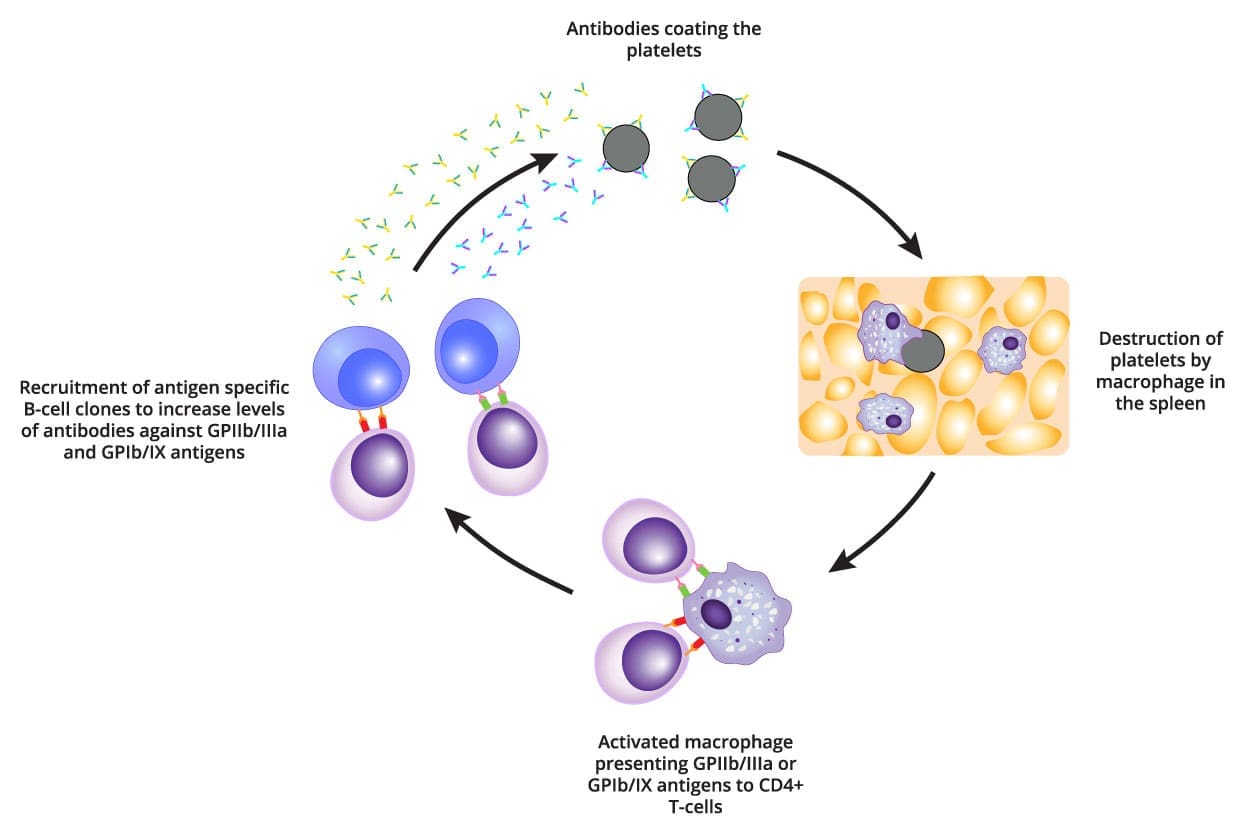
At the heart of ITP lies an autoimmune attack, where the body’s immune system mistakenly targets its own platelets. Antibodies, the body’s defense against foreign invaders, are produced and attach to the surface of platelets, marking them for destruction.
Laboratory tests of ITP
The laboratory investigations of immune thrombocytopenia are aimed at assessing the platelet count and other factors that may be contributing to the condition.
The most important laboratory investigation for immune thrombocytopenia is a complete blood count (CBC). A CBC measures the number of platelets and other types of blood cells in the blood. A low platelet count is the hallmark of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) (10 – 50 x 109/L).
Other laboratory investigations that may be ordered for immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) include:
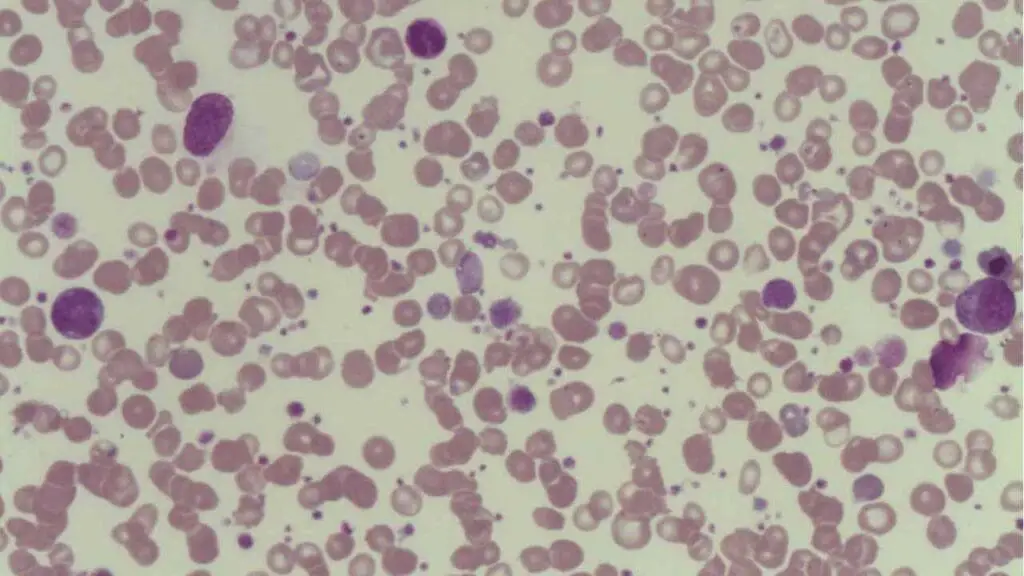
- Peripheral blood smear: A peripheral blood smear is a microscopic examination of blood cells. There will be thrombocytopenia with large platelets.
- Bone marrow biopsy: A bone marrow biopsy is a procedure in which a small sample of bone marrow is removed and examined under a microscope. This test can be used to assess the production of platelets and other blood cells.
- Direct antiglobulin test (DAT): The DAT is a test that is used to detect antibodies on the surface of red blood cells. A positive DAT may be seen in immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) if the autoantibodies are also targeting red blood cells.
- Other autoimmune tests: Other autoimmune tests, such as an antinuclear antibody (ANA) test or a rheumatoid factor (RF) test, may be ordered to rule out other autoimmune disorders that may be associated with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
- Specific antiglycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa or GPIb antibodies on the platelet surface or in the serum of most chronic patients.
How are immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) treated and managed?
The treatment and management of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) are aimed at preventing bleeding and improving the quality of life. The specific treatment approach will vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s needs.
Observation
In some cases, immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) may improve on its own without treatment. If platelet count is over 30 x 109/L no treatment is necessary unless the bleeding is severe, which involves regular monitoring of platelet count and symptoms. If the platelet count is stable and there are no bleeding symptoms, patient will be monitored and observed. The treatment of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) aims to maintain a platelet count above 50 x 109/L to prevent spontaneous bruising or bleeding.
Medications
If the platelet count is low or experiencing bleeding symptoms, there are a number of medications that can be used to treat immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), including:
1. Corticosteroids
- These are often the first-line treatment for acute ITP, especially in adults and children with a low platelet count and significant bleeding symptoms.
- Corticosteroids like prednisone suppress the immune system’s activity, thereby reducing platelet destruction.
- They are typically used for a short course (weeks to months) due to potential side effects with long-term use.
2. Immunoglobulins (IVIG)
- Intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) is another option for acute ITP, particularly when corticosteroids are ineffective or contraindicated.
- IVIG provides a concentrated dose of antibodies from healthy blood donations, which can block the immune system from attacking platelets.
- Its effect is temporary, and it may be used in combination with other treatments.
3. Thrombopoietin Receptor Agonists (TPO-RAs)
- These medications stimulate the bone marrow to produce more platelets.
- They are often used in chronic ITP or when corticosteroids and IVIG are not effective or well-tolerated.
- Examples of TPO-RAs include eltrombopag (Promacta), romiplostim (Nplate), and avatrombopag (Doptelet).
4. Other Medications
- Rituximab: This medication targets B cells in the immune system and can be used in specific cases of ITP, particularly those unresponsive to other treatments.
- Antiplatelet medications (like aspirin) are generally avoided in ITP as they can further increase bleeding risk.
Platelet transfusions
If the platelet count is very low or there is severe bleeding, the patient may need platelet transfusions. Platelet transfusions can help to increase the platelet count and reduce the risk of bleeding although their benefit will only last a few hours.
Splenectomy
The spleen is an organ that plays a role in the destruction of platelets. In some severe or chronic cases that don’t respond well to other treatments, surgical removal of the spleen (splenectomy) might be considered. Splenectomy is often considered a last resort, as it is associated with some risks, such as an increased risk of infection.
Complications
Increased risk of bleeding, which can be life-threatening in severe cases.
Prognosis
Acute ITP often resolves on its own within 6 months. Chronic ITP can be managed with medications, and some individuals may experience spontaneous remission.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and is specifically targeted towards medical students. It is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. While the information presented here is derived from credible medical sources and is believed to be accurate and up-to-date, it is not guaranteed to be complete or error-free. See additional information.
References
- Neunert C, Terrell DR, Arnold DM, et al. American Society of Hematology 2019 guidelines for immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2019;3(23):3829-3866.
- Kim DS. Recent advances in treatments of adult immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Res. 2022 Apr 30;57(S1):112-119. doi: 10.5045/br.2022.2022038. PMID: 35483935; PMCID: PMC9057657.
- Gernsheimer T. Chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: mechanisms of pathogenesis. Oncologist. 2009 Jan;14(1):12-21. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0132. Epub 2009 Jan 14. PMID: 19144680.
- Rank A, Weigert O, Ostermann H. Management of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura: targeting insufficient megakaryopoiesis as a novel therapeutic principle. Biologics. 2010 May 25;4:139-45. doi: 10.2147/btt.s3436. PMID: 20531970; PMCID: PMC2880346.
- Liebman HA, Pullarkat V. Diagnosis and management of immune thrombocytopenia in the era of thrombopoietin mimetics. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011;2011:384-90. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2011.1.384. PMID: 22160062.
- Goldberg S, Hoffman J. Clinical Hematology Made Ridiculously Simple, 1st Edition: An Incredibly Easy Way to Learn for Medical, Nursing, PA Students, and General Practitioners (MedMaster Medical Books). 2021.