Discover causes & implications of high neutrophils, from general neutrophilia to absolute neutrophilia, a key blood cell elevation.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
EoE: Chronic esophageal inflammation. Dysphagia, food impaction. Diagnosis: endoscopy, biopsies. Treatment: diet, meds, dilation.
AL Amyloidosis (Primary Amyloidosis)
AL amyloidosis occurs when misfolded light-chain proteins deposit in organs. Prompt treatment improves outcomes.
Leukopenia (Low White Cell Count)
Leukopenia: Low white blood cell count, weakening immunity. Learn about causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of this condition.
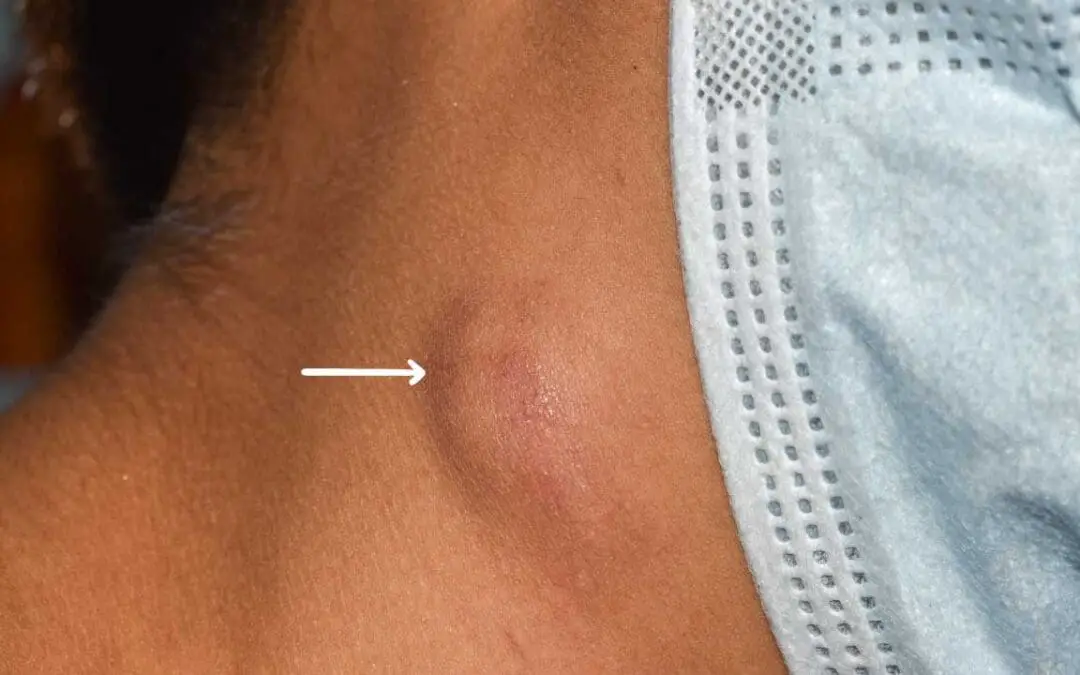
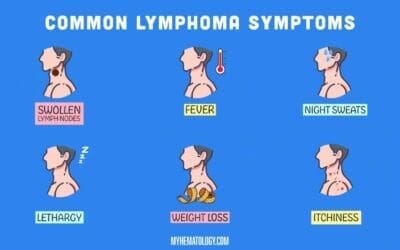
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy explained: Learn about swollen lymph nodes, their common causes (infections, inflammation, cancer), key symptoms, diagnostic tests (blood work, biopsy), and available treatment options. Understand when swollen glands are a cause for concern.
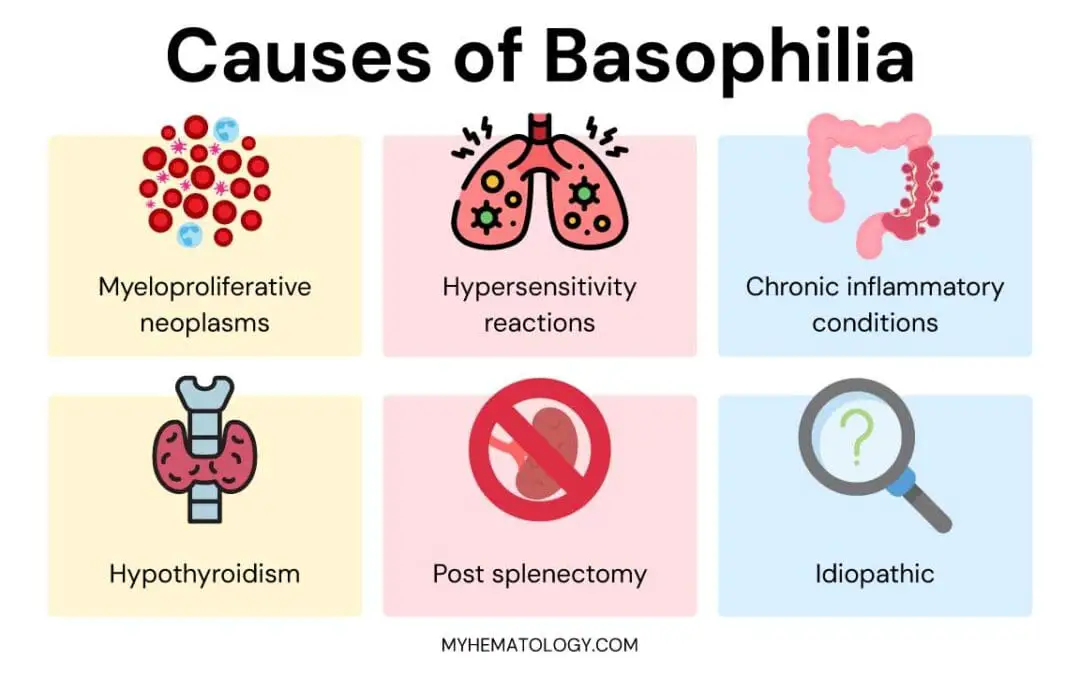
Basophilia (High Basophils)
Basophilia is when basophil count are elevated. It often signals underlying issues like MPNs, allergies, or inflammation.
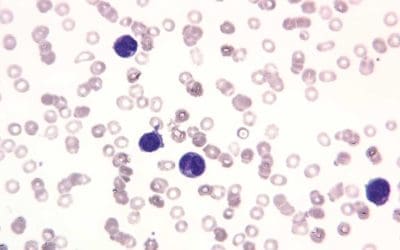
Leukemia: An Overview
Leukemia: Hematopoietic malignancy affecting blood cell production, presenting with cytopenias, blasts in peripheral blood, and requiring prompt diagnosis & treatment.
Lymphoma
Lymphoma: Diverse malignancies of lymphocytes. Hodgkin’s & Non-Hodgkin’s subtypes present with swollen nodes, fever, night sweats, fatigue.
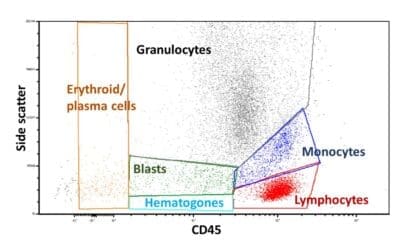
Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping of Blood
Blood cells stained with fluorescent antibodies reveal hidden markers, like a cellular fingerprint. Flow cytometry analyzes millions of cells, painting a detailed picture of immune health, disease clues, and treatment insights.
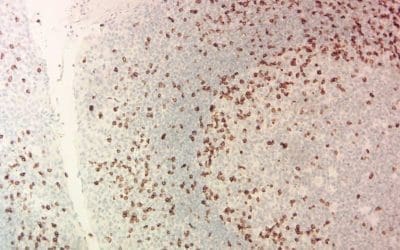
IHC – Immunohistochemistry Staining
This immunohistochemistry protocol guides you step-by-step through visualizing specific proteins in tissue sections, aiding in accurate diagnosis of various diseases.
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS): An Overview
MDS is a blood disorder where bone marrow malfunctions, causing abnormal blood cell production. Symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and infections may occur.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia or AML
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a rapidly progressing and aggressive blood cancer that arises from the uncontrolled growth of myeloid cells in the bone marrow.