The plasma cell is the terminal B-lymphocyte, the immune system’s antibody factory for mass Ig secretion, recognized by its eccentric nucleus.
Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS)
MGUS is an asymptomatic clonal disorder. It is the precursor to Multiple Myeloma, requiring only active surveillance and risk monitoring.
Smoldering Multiple Myeloma (SMM)
Smoldering Multiple Myeloma (SMM) is an asymptomatic precursor to MM, defined by high clonal plasma cell burden and M-protein without MDEs. Risk stratification is key.
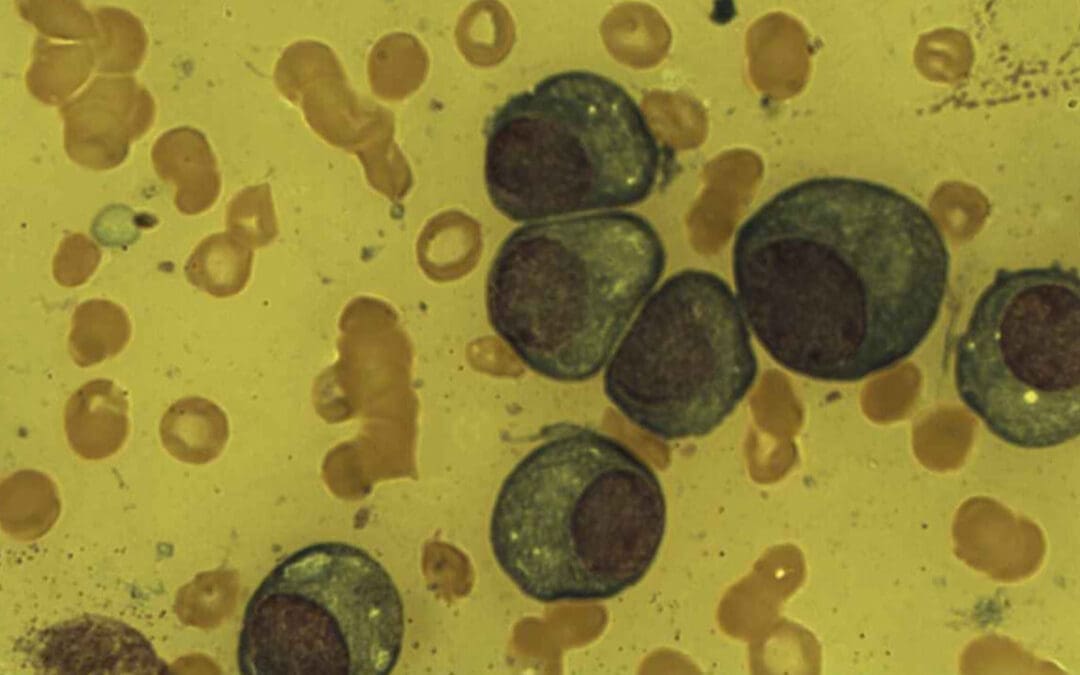
Plasma Cell
The plasma cell is the terminal B-lymphocyte, the immune system’s antibody factory for mass Ig secretion, recognized by its eccentric nucleus.

Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS)
MGUS is an asymptomatic clonal disorder. It is the precursor to Multiple Myeloma, requiring only active surveillance and risk monitoring.
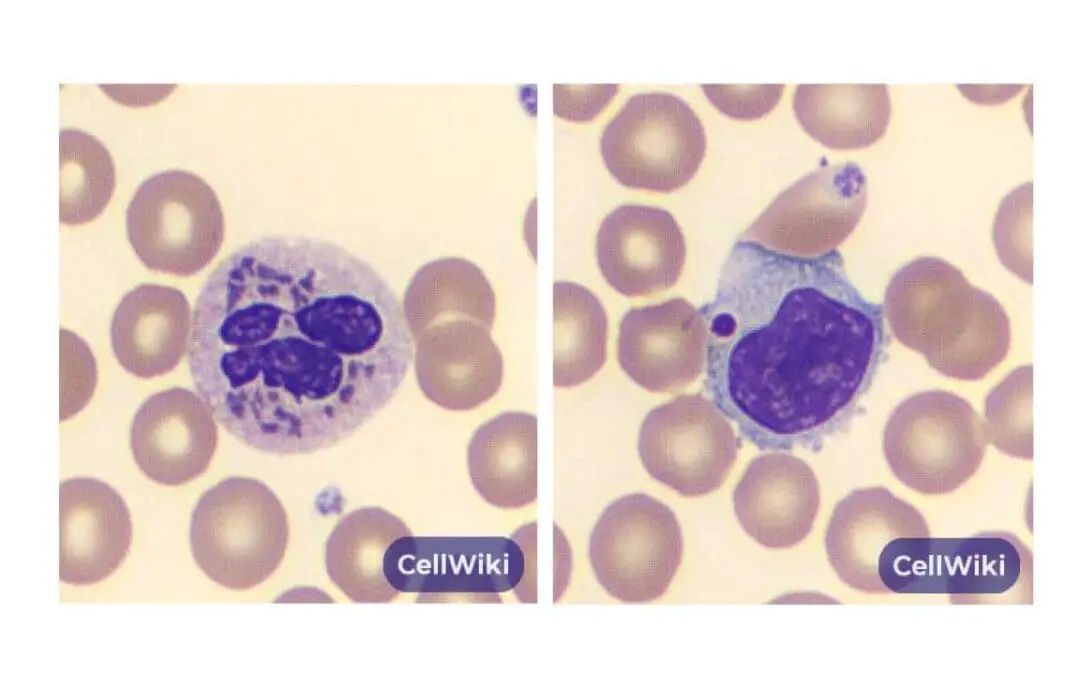
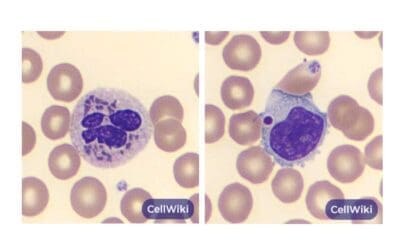
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Chediak-Higashi syndrome (CHS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by oculocutaneous albinism, immune deficiency, and neurological decline.
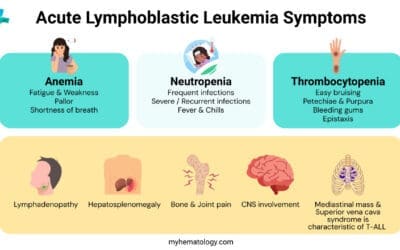
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia or ALL
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of immature white blood cells. Learn its cause, symptoms, and modern treatment, including CAR T-cell therapy.
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Chediak-Higashi syndrome (CHS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by oculocutaneous albinism, immune deficiency, and neurological decline.
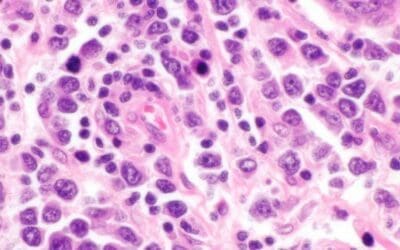
Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
Learn about Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and its diagnosis, treatment with R-CHOP, and management of relapsed disease.
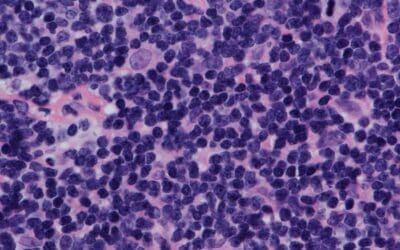
Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL Disease)
Explore the essentials of Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL). Learn about its unique genetic features, diagnosis, and current treatment strategies.
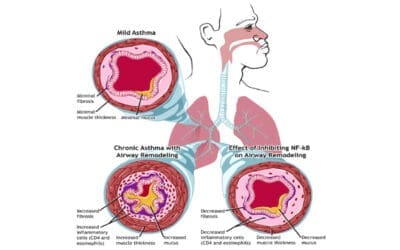
Eosinophilic Asthma
Eosinophilic asthma is a severe subtype of asthma, driven by high eosinophil levels. It often resists standard treatments and may not be allergy-related.
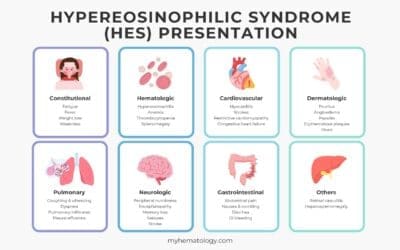
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES)
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES) is a rare disorder causing persistently high eosinophil levels, leading to organ damage and inflammation.