Learn about Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and its diagnosis, treatment with R-CHOP, and management of relapsed disease.
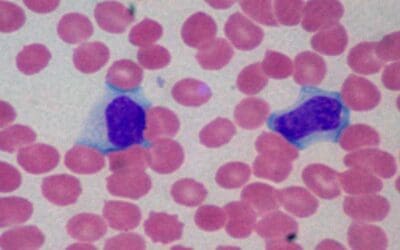
Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL Disease)
Explore the essentials of Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL). Learn about its unique genetic features, diagnosis, and current treatment strategies.
Eosinophilic Asthma
Eosinophilic asthma is a severe subtype of asthma, driven by high eosinophil levels. It often resists standard treatments and may not be allergy-related.
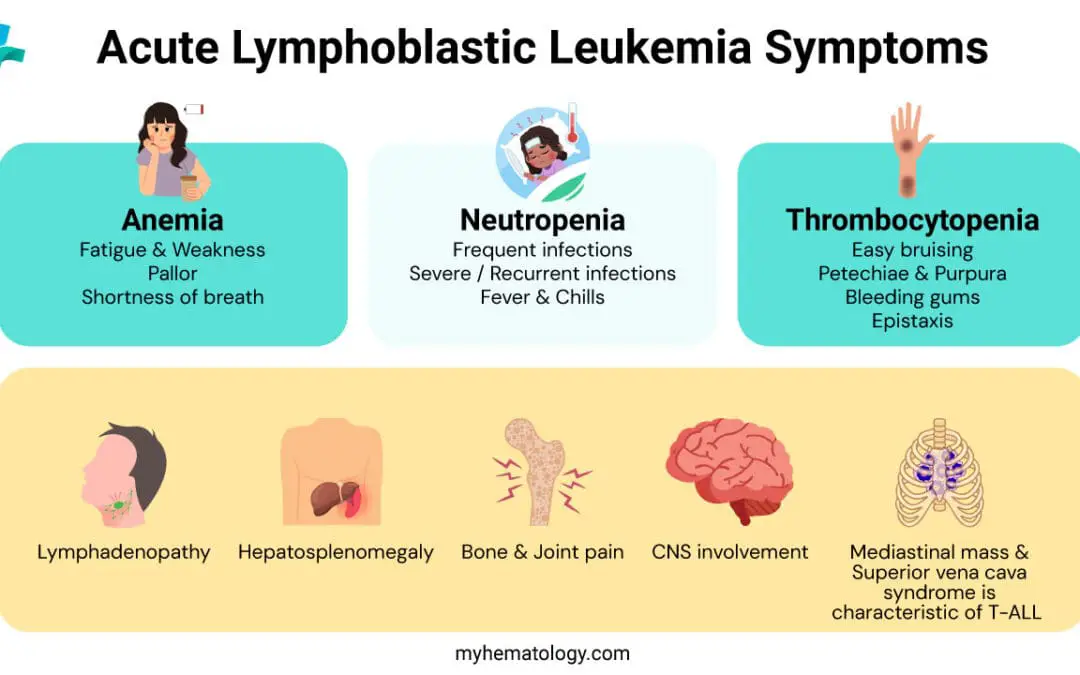
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia or ALL
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of immature white blood cells. Learn its cause, symptoms, and modern treatment, including CAR T-cell therapy.
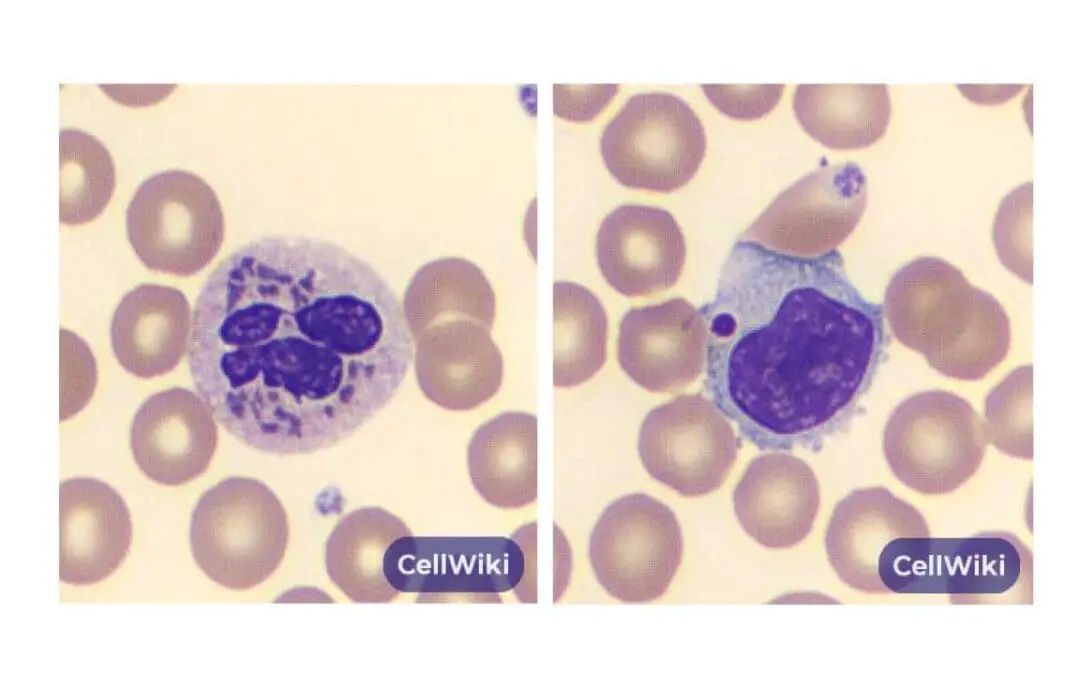
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Chediak-Higashi syndrome (CHS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by oculocutaneous albinism, immune deficiency, and neurological decline.

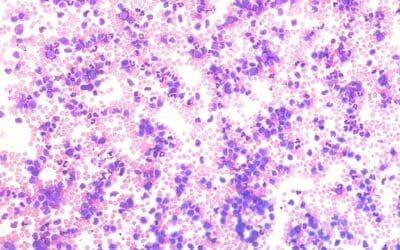
Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
Learn about Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and its diagnosis, treatment with R-CHOP, and management of relapsed disease.
Monocytosis (High Monocytes)
Monocytosis: Elevated monocytes signal underlying health issues. Learn causes (infections, cancers), symptoms, diagnosis, and management.
Lymphocytosis (High Lymphocytes)
Lymphocytosis: High lymphocyte count. It can be a harmless immune response or signal serious conditions like leukemia.
Leukopenia (Low White Cell Count)
Leukopenia: Low white blood cell count, weakening immunity. Learn about causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of this condition.
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy explained: Learn about swollen lymph nodes, their common causes (infections, inflammation, cancer), key symptoms, diagnostic tests (blood work, biopsy), and available treatment options. Understand when swollen glands are a cause for concern.
Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment Strategies
Hodgkin lymphoma explained: treatment, stages, and what to expect. Your guide based on the latest NCCN recommendations.
Causes of Polycythemia
Polycythemia has high red blood cell count. Learn causes, symptoms (headache, fatigue), diagnosis (CBC, EPO), and treatment options.