Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES) is a rare disorder causing persistently high eosinophil levels, leading to organ damage and inflammation.
Leukemoid Reaction
Leukemoid reaction is a benign, reactive process with elevated LAP & no Philadelphia chromosome, unlike malignant CML.
Causes of Atypical Lymphocytes (Reactive Lymphocytes)
Atypical lymphocytes are activated immune cells, often seen in infections. Their unique look aids diagnosis, but distinguishing it from cancer is important.

Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
Learn about Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and its diagnosis, treatment with R-CHOP, and management of relapsed disease.

Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL Disease)
Explore the essentials of Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL). Learn about its unique genetic features, diagnosis, and current treatment strategies.

Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL Disease)
Explore the essentials of Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL). Learn about its unique genetic features, diagnosis, and current treatment strategies.
Neutropenia
Neutropenia is a condition with a low count of neutrophils, key infection-fighting white blood cells. This increases susceptibility to various infections.
Infectious Mononucleosis (Mono)
Infectious mononucleosis (Mono), the “kissing disease,” is a common viral illness (EBV). Symptoms include sore throat, fever, fatigue, and swollen glands. Usually resolves on its own.
Causes of Eosinophilia (High Eosinophils)
High eosinophil count in blood. May indicate allergies, infections, or other conditions. Symptoms vary. Diagnosis via blood test.
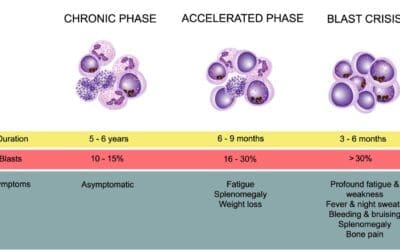
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treatment Strategies
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treatment: TKIs are the main therapy, targeting the BCR::ABL1 gene. Chemotherapy & stem cell transplant are also used.
Neutrophilia (High Neutrophils) & Absolute Neutrophilia
Discover causes & implications of high neutrophils, from general neutrophilia to absolute neutrophilia, a key blood cell elevation.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
EoE: Chronic esophageal inflammation. Dysphagia, food impaction. Diagnosis: endoscopy, biopsies. Treatment: diet, meds, dilation.