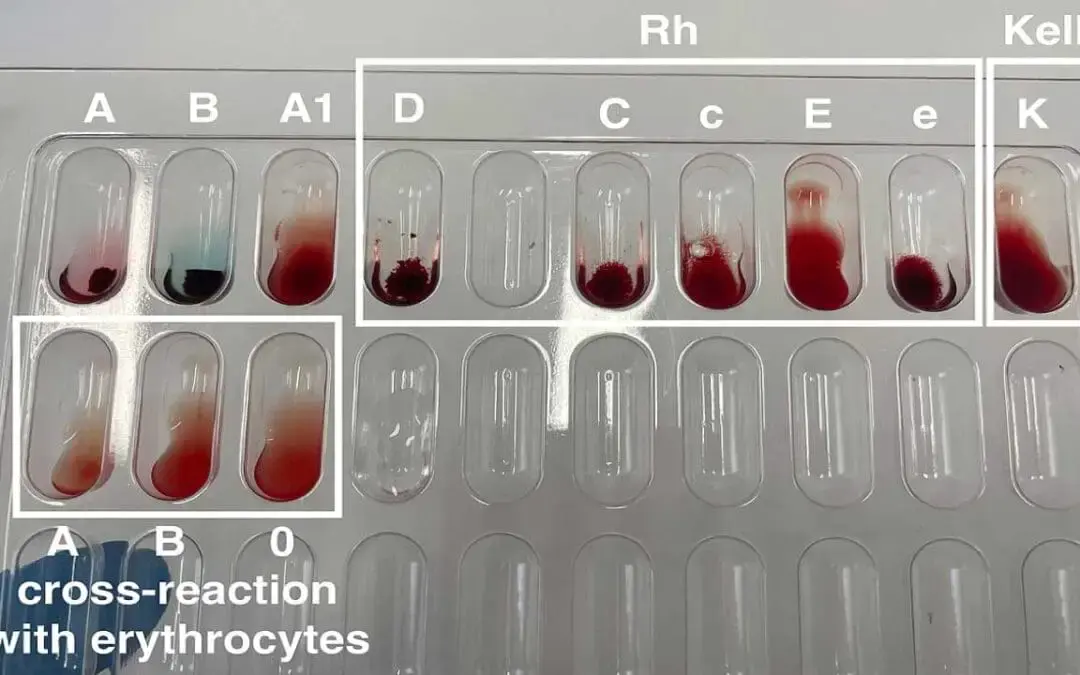
Antigen identification antigrams decode antibody reactions in blood transfusions, ensuring safe blood selection by identifying compatible red blood cells that lack the antigen targeted by the recipient’s antibody.
Antibody Identification
Incubate patient serum with panel RBCs, check for agglutination! Enzymes & antiglobulin tests may be used to reveal hidden antibody reactions.
Antibody Screening
Antibody screening mixes patient plasma with red blood cells to detect unexpected antibodies. Agglutination indicates possible antibodies, requiring further identification for safe blood transfusions
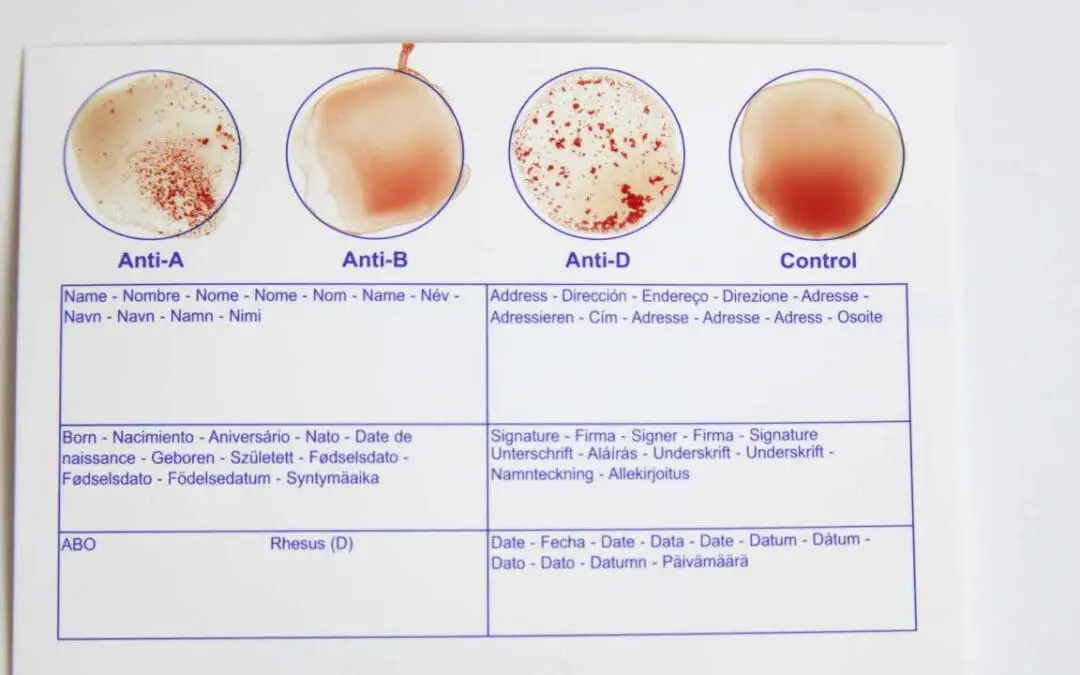
Blood Typing: Exploring Blood Type Tests and Beyond
Unlock your blood type! Simple tests reveal vital health info. Discover ABO & Rh factors with at-home kits or lab visits. Know your type today.
Rh Blood Group System
TL;DR The Rh blood group system is a classification of blood types based on the presence or absence of certain proteins (antigens) on the surface of red blood cells. Rh incompatibility can lead to serious complications. Antigen System: Rh antigens on red blood cells...
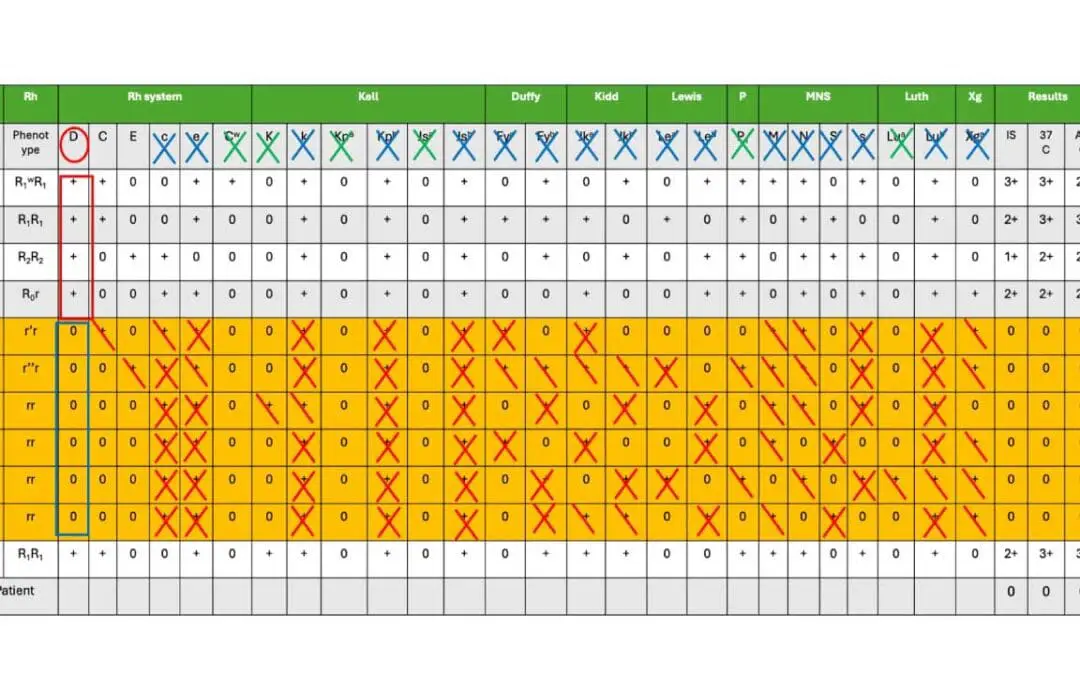
Interpretation of Antibody Identification Antigram
Antigen identification antigrams decode antibody reactions in blood transfusions, ensuring safe blood selection by identifying compatible red blood cells that lack the antigen targeted by the recipient’s antibody.
Components of Donated Blood Products
Many different blood components can be derived from donated blood. These components have different functions for different indications. This article gives an overview of the function of the different blood components available.
Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
Acute hemolytic transfusion reaction (AHTR) is a rare but life-threatening complication of blood transfusion that occurs when the recipient’s immune system attacks the transfused blood cells and destroyed them.
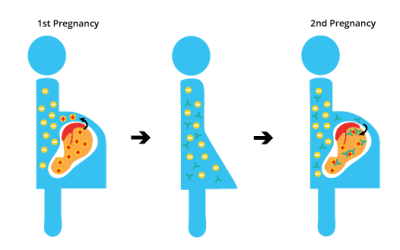
Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (Erythroblastosis Fetalis)
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) is a condition in which a newborn baby’s red blood cells are destroyed. It is caused by incompatibility between the baby’s and mother’s blood types. HDN is preventable and treatable.