Methemoglobinemia: a blood disorder where hemoglobin can’t carry oxygen. Learn its causes, diagnosis, and treatment in this overview.
Hydrops Fetalis
Explore hydrops fetalis: a severe fetal condition marked by excessive fluid accumulation. Learn its diverse causes, from genetic to infectious.
Causes of Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia is excessive period bleeding. Explore the causes, symptoms and the approach to diagnose it.
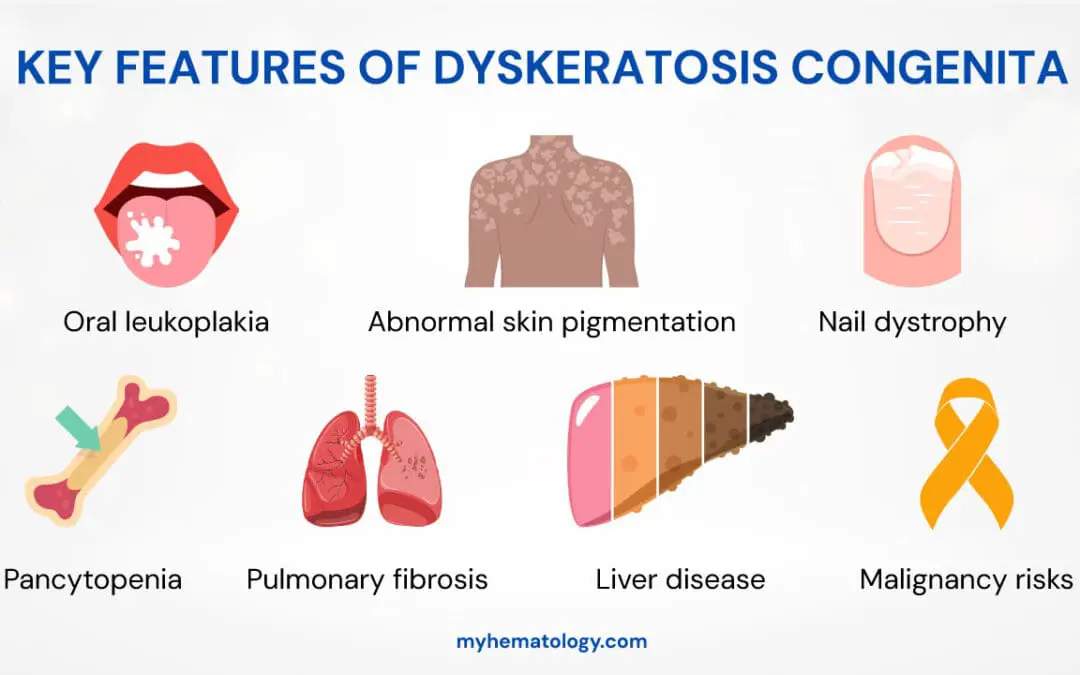
Dyskeratosis Congenita
Dyskeratosis congenita (DC) is a genetic disorder causing bone marrow failure and premature aging due to short telomeres.
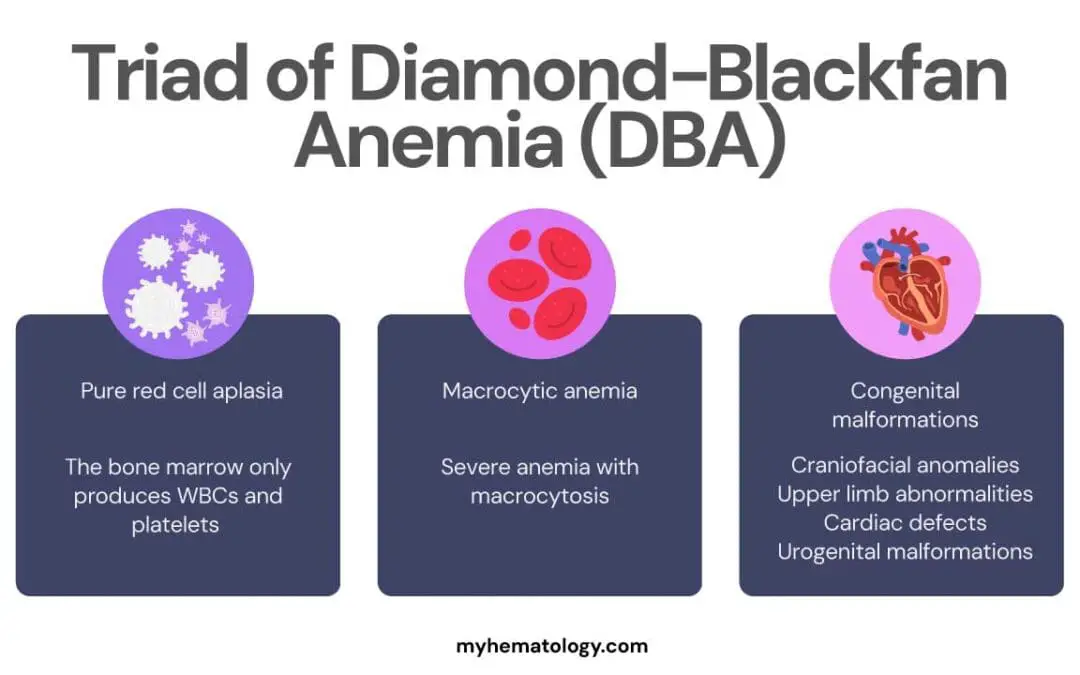
Diamond-Blackfan Anemia (DBA)
A rare genetic disorder, Diamond-Blackfan anemia stops the bone marrow from making enough red blood cells.

Methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia: a blood disorder where hemoglobin can’t carry oxygen. Learn its causes, diagnosis, and treatment in this overview.
Hematuria (Blood in Urine): Overview & Causes
Hematuria: Blood in urine, gross (visible) or microscopic. Could signal infection, stones, or more serious issues.
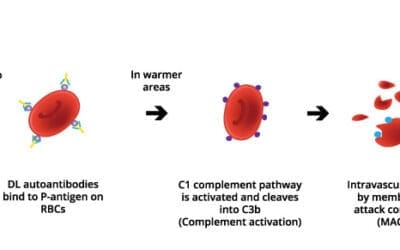
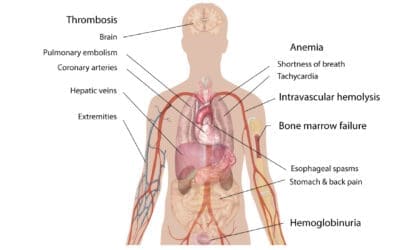
Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH) is a rare autoimmune anemia. Cold exposure triggers red cell destruction, causing dark urine, back pain, and chills. Diagnosis relies on the Donath-Landsteiner test.
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH): An acquired blood disease where the immune system attacks red cells due to a mutation in the X chromosome.
Warm Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (warm AIHA)
Warm AIHA: Immune system attacks red blood cells, causing anemia. Symptoms include fatigue, pallor, and jaundice. Treatment targets immune suppression.
Cold Agglutinin Disease
Cold Agglutinin Disease (CAD) is a rare autoimmune anemia. Cold-reactive antibodies destroy red blood cells, causing fatigue, cold sensitivity, and anemia.
Homocysteine Test
A homocysteine blood test measures the level of homocysteine in your blood. Elevated levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. This simple test can help identify potential vitamin deficiencies and guide personalized treatment plans