You’re constantly tired, even after a good night’s sleep. You feel sluggish, forgetful, and your mood seems off. Could it be something more than just stress? Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an essential nutrient that the human body cannot produce on its own, making dietary intake crucial. This vital vitamin plays a multifaceted role in various bodily functions, including the breakdown of fatty acids, the formation of blood, the support of nerve function, and the promotion of cell division. Due to its critical involvement in these processes, a deficiency in vitamin B12 can have significant repercussions, potentially affecting various bodily systems, including the eyes, nerves, muscles, and hair. It is particularly important for women, especially those in their 30s and 40s, as hormonal changes and dietary restrictions can increase the risk of deficiency. A vitamin B12 blood test is essential for identifying potential deficiencies and addressing any underlying health issues that may be contributing to low levels. Early detection and treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve overall well-being.
Quick guide
Vitamin B12 Blood Test
- Tests for: Vitamin B12 level in your blood
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
- Cost: $54 – $67 (at the time of writing)
Vitamin B12 and Folate Test
- Tests for: Vitamin B12 and Folate levels in your blood
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
- Cost: $80 – $90 (at the time of writing)
Verisana Vitamin B12 Test (At-home test kit)
- Tests for: Vitamin B12 level
- How it works: Buy a kit from Amazon.com, collect your blood on a small card and mail it to a Verisana lab with a prepaid envelope
- Specimen required: Finger prick blood sample
- Results in: 7 – 10 business days
- Cost: $59 (at the time of writing)
Disclaimer: This information is based on research and is accurate to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication. Please note that the writer has not personally used or tested these products.
Why is Vitamin B12 Important?
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in several key physiological processes in the body.
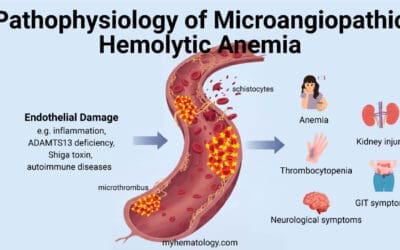
- Red Blood Cell Production: B12 is crucial for the formation of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. Deficiency can lead to anemia, causing fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
- DNA Synthesis: B12 is involved in the production of DNA, the genetic material found in every cell. This is essential for cell growth and repair.
- Nerve Function: B12 helps maintain healthy nerve cells. Deficiency can damage nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and problems with balance and coordination.
- Energy Production: B12 plays a role in converting food into energy, which is why deficiency can cause fatigue and weakness.
What are the Health Risks of Vitamin B12 Deficiency?
Vitamin B12 deficiency can have a range of health risks, some of which can be serious if left untreated.
Neurological Problems
- Nerve Damage: This can lead to numbness, tingling, and weakness, often starting in the hands and feet.
- Cognitive Decline: Difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and even dementia can occur in severe cases.
- Mental Health Issues: Depression and anxiety can be linked to B12 deficiency.
Anemia

- Fatigue: Feeling constantly tired and lacking energy.
- Weakness: Difficulty with everyday activities.
- Shortness of Breath: Due to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Other Potential Risks
- Increased risk of certain cancers: Some studies have suggested a possible link between B12 deficiency and an increased risk of stomach cancer.
- Birth defects: In pregnant women, severe B12 deficiency can increase the risk of neural tube defects in the developing fetus.
What are the Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency?
Vitamin B12 deficiency can arise from two primary sources.
Inadequate Intake
- Strict Vegetarian/Vegan Diets: Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy. Vegans and strict vegetarians may not consume enough B12 from their diets and may require supplementation.
Impaired Absorption
Even if you consume enough B12, your body might not absorb it properly due to various factors.
- Gastrointestinal Conditions: Diseases like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and pernicious anemia (an autoimmune condition) can interfere with B12 absorption in the intestines.
- Surgery: Certain gastrointestinal surgeries, such as gastric bypass, can reduce the amount of stomach acid and intrinsic factor (a protein needed to absorb B12), leading to malabsorption.
- Medications: Some medications, such as proton pump inhibitors (used to treat heartburn) and metformin (used to treat type 2 diabetes), can interfere with B12 absorption.
- Age-Related Changes: As we age, our ability to produce stomach acid and intrinsic factors may decline, making it harder to absorb B12.
- Alcoholism: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the lining of the stomach and intestines, hindering B12 absorption.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency?
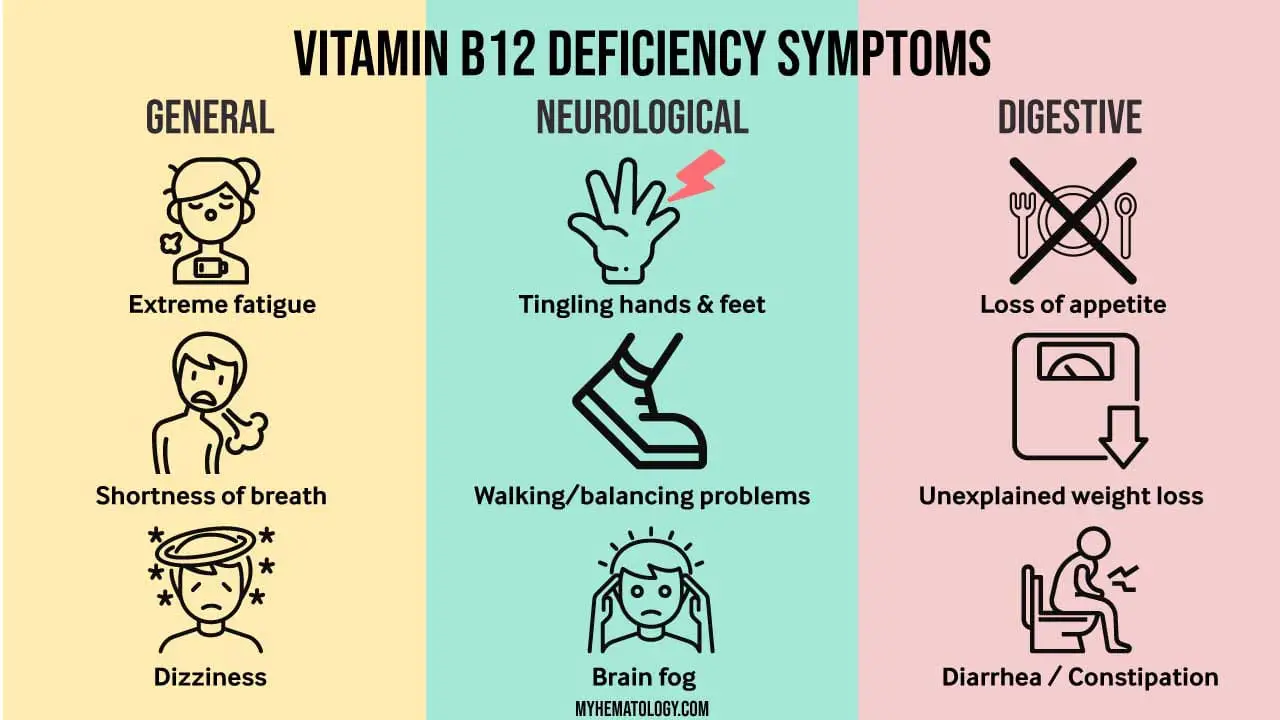
Vitamin B12 deficiency can present with a wide range of symptoms, some of which can be subtle and easily mistaken for other conditions.
General Symptoms
- Fatigue: Feeling constantly tired and lacking energy.
- Weakness: Difficulty with everyday activities.
- Shortness of Breath: Due to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Neurological Symptoms
- Numbness or Tingling: Often in the hands and feet.
- Muscle Weakness: Difficulty with coordination and balance.
- Problems with Walking or Speaking: Due to nerve damage.
- Cognitive Decline: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, confusion.
- Mental Health Issues: Depression, anxiety.
Other Symptoms
- Pale Skin: Due to anemia.
- Sore Tongue: The tongue may become smooth, red, and sore.
- Mouth Sores: Ulcers or sores inside the mouth.
- Vision Problems: Blurred vision or difficulty focusing.
- Constipation or Diarrhea: Digestive issues can occur.
Early detection and treatment of B12 deficiency are essential to prevent serious complications.
How Do We Test for Vitamin B12 Deficiency?
The most common method for testing vitamin B12 deficiency is through a simple vitamin B12 blood test that measures the level of vitamin B12 in your body.
The reference range for vitamin B12 can vary slightly between laboratories, but generally falls within:
- 160 to 950 picograms per milliliter (pg/mL)
- 118 to 701 picomoles per liter (pmol/L)
Other Potential Tests
In some cases, your doctor may order additional tests to help diagnose vitamin B12 deficiency or rule out other conditions.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test checks for anemia, which is a common complication of B12 deficiency.
- Methylmalonic Acid (MMA) Test: MMA is a substance that builds up in the body when B12 levels are low.
- Homocysteine Level Test: Elevated homocysteine levels can also indicate a B12 deficiency.
Why is a Vitamin B12 Test Important?
A vitamin B12 test is crucial for several reasons:
- Early Detection: It helps identify a deficiency early on, allowing for prompt treatment and preventing potential complications.
- Symptom Relief: Addressing B12 deficiency can significantly improve symptoms like fatigue, weakness, and neurological problems.
- Preventing Serious Complications: Untreated B12 deficiency can lead to irreversible nerve damage and other serious health issues.
- Personalized Treatment: Test results help determine the appropriate treatment plan, whether it’s supplements, dietary changes, or injections.
- Overall Well-being: Maintaining adequate B12 levels is essential for overall health and well-being, especially for women in their 30s and 40s.
Remember, early detection and treatment are key to preventing the long-term consequences of B12 deficiency.
Recommended Tests
Vitamin B12 Blood Test

- Tests for: Folate levels in your red blood cells
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
- Cost: $54 – $67 (at the time of writing)
- Special preparation: Quest: No special preparation is required. Labcorp: Fasting specimen preferred; must draw before Schilling test, transfusions or B12 therapy is started.This test may also produce inaccurate results if the patient is taking high doses of biotin supplements (also known as vitamin B7, B8, vitamin H, or coenzyme R). Individuals are advised to stop taking biotin supplements for at least 72 hours prior to the blood draw.
About the test
This test measures the vitamin B12 levels in your serum.
Pros
✔ No doctor visit required
✔ Excellent service
Cons
❌ Quest: Tests cannot be conducted at lab locations in Arizona, New Jersey, New York, or Rhode Island.
Vitamin B12 and Folate Test

- Tests for: Vitamin B12 and Folate levels in your blood
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
- Cost: $80 – $90 (at the time of writing)
- Special preparation: Dietary supplements containing biotin may interfere with this panel, causing results to be either falsely high or falsely low. We recommend pausing biotin-containing supplements 72 hours prior to being tested.
About the test
This test measures the vitamin B12 and folate level in your serum.
Pros
✔ No doctor visit required
✔ Excellent service
✔ HSA/FSA accepted
Cons
❌ Quest: Tests cannot be conducted at lab locations in Arizona, New Jersey, New York, or Rhode Island.
Verisana Vitamin B12 Test (At-home test kit)

- Tests for: Vitamin B12 level
- How it works: Buy a kit from Amazon.com, collect your blood on a small card and mail it to a Verisana lab with a prepaid envelope
- Specimen required: Finger prick blood sample
- Results in: 7 – 10 business days
- Cost: $59 (at the time of writing)
About the test
The Verisana B12 test kit is a home test that measures the levels of vitamin B12 in your blood. Order your kit, collect a sample at your convenience, and return it to the lab. The laboratory will analyze the blood sample and determine the levels of vitamin B12. Your results will be available online and emailed to you. The test kit encompasses all necessary components, including sampling instructions, supplies, and a return shipping envelope. No additional fees are incurred – scientific analysis and a comprehensive laboratory report are included.
Pros
✔ Easy-to-use
✔ Can be done at your convenience in the privacy of your own home
✔ CLIA-certified lab
Cons
❌ Needs blood sample to dry for one hour and then needs to ship within 24 hours
❌ Due to regulatory reasons, this test is currently not available in NY/NJ/RI/MD
❌ Must be at least 18 & over to take the test
Who Can/Should Get Tested?
Individuals who should consider getting tested for vitamin B12 deficiency include:
- People with symptoms: Those experiencing fatigue, weakness, numbness, tingling, memory problems, or other symptoms suggestive of B12 deficiency.
- Vegans and strict vegetarians: As B12 is primarily found in animal products, these individuals may be at increased risk.
- Older adults: B12 absorption can decline with age.
- People with certain medical conditions:
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, pernicious anemia
- Autoimmune diseases
- Diabetes: People on metformin medication.
- Individuals who have undergone certain surgeries: Gastric bypass or other surgeries that affect digestion.
- People taking medications: Several medications can interfere with vitamin B12 absorption, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2-receptor antagonists, metformin, colchicine, aminosalicylates, and some antibiotics. These medications can reduce stomach acid production or interfere with B12 absorption in the intestines. It’s crucial to consult with your doctor or pharmacist about any potential drug interactions and discuss any concerns you may have about vitamin B12 deficiency.
How is Vitamin B12 Deficiency Treated?
There are several treatment options for vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Vitamin B12 Supplements: These are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and oral sprays. In some cases, higher doses or injections may be necessary.
- Dietary Changes: Include vitamin B12-rich foods in the diet.
- Addressing Underlying Causes: If the deficiency is caused by an underlying condition, such as pernicious anemia or a gastrointestinal disorder, treating the underlying condition is essential.
Treatment Approach
The specific treatment approach will depend on the severity of the deficiency and the underlying cause. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate treatment plan for you.
What Foods are High in Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods.
- Meat: Liver, beef, pork, lamb
- Poultry: Chicken, turkey
- Fish and Seafood: Salmon, tuna, cod, clams, mussels, oysters, sardines
- Eggs
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, yogurt
Fortified Foods
- Some fortified breakfast cereals
- Fortified plant-based milk alternatives
- Fortified nutritional yeast
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health.
References
- Anemia: Diagnosis and Treatment (Willis, 2016).
- Management of Anemia: A Comprehensive Guide for Clinicians (Provenzano et al., 2018)
- Goldberg S, Hoffman J. Clinical Hematology Made Ridiculously Simple, 1st Edition: An Incredibly Easy Way to Learn for Medical, Nursing, PA Students, and General Practitioners (MedMaster Medical Books). 2021.
- Wang H, Li L, Qin LL, Song Y, Vidal-Alaball J, Liu TH. Oral vitamin B12 versus intramuscular vitamin B12 for vitamin B12 deficiency. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 15;3(3):CD004655. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004655.pub3. PMID: 29543316; PMCID: PMC6494183.
- Health Quality Ontario. Vitamin B12 and cognitive function: an evidence-based analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2013 Nov 1;13(23):1-45. PMID: 24379897; PMCID: PMC3874776.