Basophilia is when basophil count are elevated. It often signals underlying issues like MPNs, allergies, or inflammation.
Lymphopenia or Low Lymphocytes
Lymphopenia is a low lymphocyte count, weakening immunity. It increases infection risk and flags underlying issues like cancer or severe illness.
Monocytosis (High Monocytes)
Monocytosis: Elevated monocytes signal underlying health issues. Learn causes (infections, cancers), symptoms, diagnosis, and management.
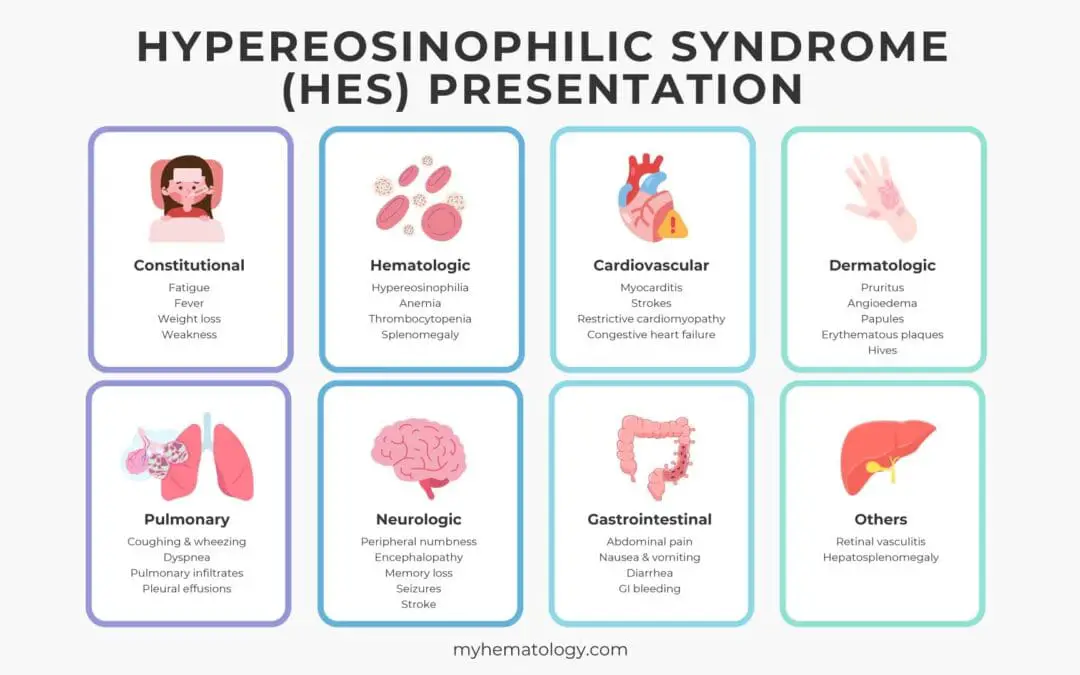
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES)
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES) is a rare disorder causing persistently high eosinophil levels, leading to organ damage and inflammation.
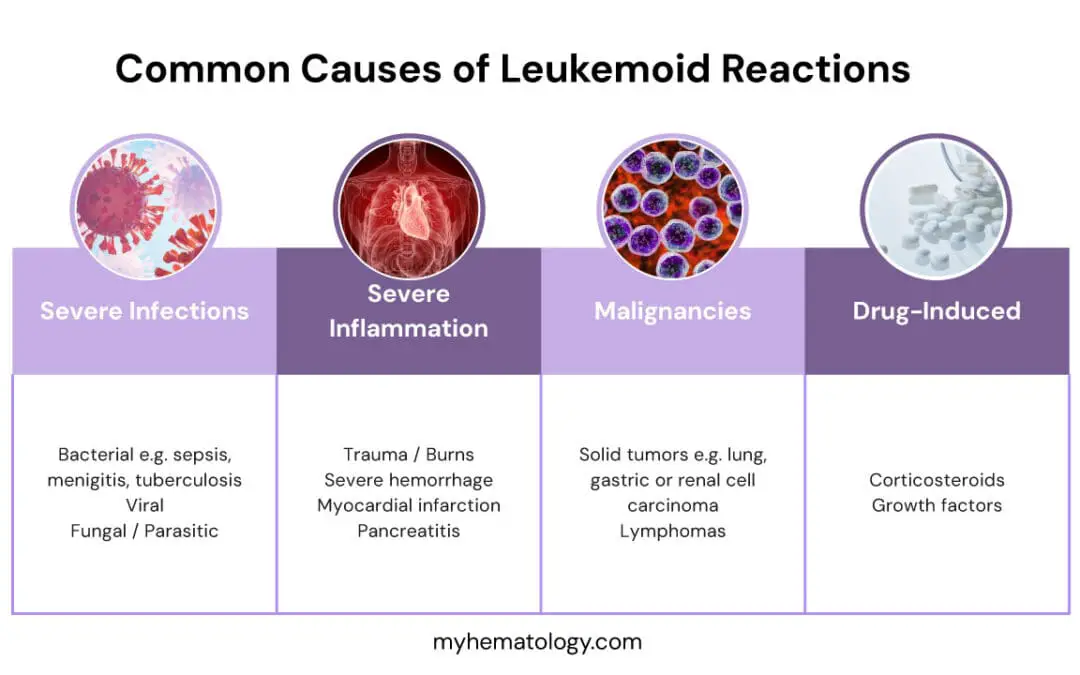
Leukemoid Reaction
Leukemoid reaction is a benign, reactive process with elevated LAP & no Philadelphia chromosome, unlike malignant CML.

Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES)
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES) is a rare disorder causing persistently high eosinophil levels, leading to organ damage and inflammation.
Sjögren’s Syndrome
Sjögren’s syndrome: An autoimmune disease causing dry eyes, mouth. Systemic effects is possible. Early diagnosis & management are key.
Waldenström Macroglobulinemia
Waldenström Macroglobulinemia (WM): Rare lymphoma, excess IgM. Causes fatigue, neuropathy, & hyperviscosity. Early diagnosis & tailored treatment are key.
Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) process antigens & present them to T cells, triggering immune responses.
Natural Killer Cells
Natural Killer (NK) cells are vital immune cells that provide rapid defense against infections and cancer. They recognize and eliminate stressed or infected cells without prior sensitization, playing a key role in immunosurveillance.
Burkitt Lymphoma
Burkitt Lymphoma is a rare cancer affecting children and adults. Key symptoms include rapidly growing tumors, often in the jaw or abdomen.
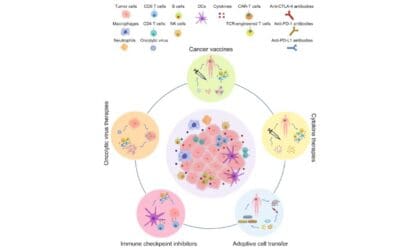
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It offers a targeted approach with fewer side effects compared to traditional treatments, providing hope for many cancer patients