Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is an essential water-soluble B vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It is involved in the production of DNA and RNA, the genetic material in every cell, and is essential for cell growth and development. Folate is particularly important during pregnancy as it helps prevent neural tube defects in the developing fetus. Adequate folate intake is also crucial for brain development and cognitive function in young children. Folate deficiency is easily detectable through a folate blood test.
Quick guide
Folate, RBC Blood Test
- Tests for: Folate levels in your red blood cells
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
Vitamin B12 and Folate Test
- Tests for: Vitamin B12 and Folate levels in your blood
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
Verisana B Vitamins Test (At-home test kit)
- Tests for: Folate and Vitamin B12 level
- How it works: Buy a kit from Amazon.com, collect your blood on a small card and mail it to a Verisana lab with a prepaid envelope
- Specimen required: Finger prick blood sample
- Results in: 7 – 10 business days
Disclaimer: This information is based on research and is accurate to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication. Please note that the writer has not personally used or tested these products.
Why is Folate Important?
Folate is a type of vitamin B that is crucial for many bodily functions. The role of folate in the body includes:
- Cell Growth and Development: Folate is essential for the production of new cells, including red blood cells.
- DNA Synthesis and Methylation: It is one of the building blocks of DNA, the genetic material in every cell. Folate also provides the necessary methyl groups for the methylation of DNA. Methylation is a chemical process that modifies DNA and influences gene expression.
- Neural Tube Development: During pregnancy, folate is crucial for the proper development of the neural tube, which forms the baby’s brain and spinal cord.
- Brain Development: Folate is important for brain development in both fetuses and young children.
What are the Health Risks of Folate Deficiency?
For Women Trying to Conceive or During Pregnancy
- Neural Tube Defects: Insufficient folate during the first few weeks of pregnancy significantly increases the risk of neural tube defects, such as spina bifida (where the spinal cord doesn’t form properly).
- Premature Birth: Low folate levels have been linked to an increased risk of premature birth.
- Low Birth Weight: Babies born to mothers with folate deficiency are more likely to have low birth weight.
- Miscarriage: In some cases, folate deficiency may increase the risk of miscarriage.
- Preeclampsia: A condition characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage during pregnancy.
For Developing Fetuses
- Growth Restriction: Folate deficiency can hinder the proper growth and development of the fetus.
- Developmental Delays: It may contribute to developmental delays in areas like cognitive and motor skills.
For Young Children
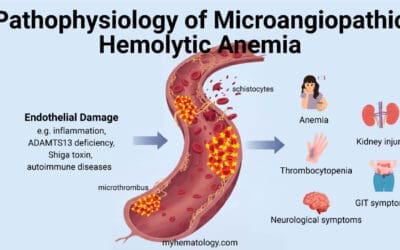
- Anemia: Folate deficiency can lead to anemia, a condition where the body doesn’t produce enough healthy red blood cells.
- Brain Development: Folate is crucial for proper brain development in young children.
- Cognitive Function: Adequate folate intake is essential for cognitive development, including learning and memory.
- Developmental Delays: As mentioned earlier, it can impact cognitive and motor development.
What are the Causes of Folate Deficiency?
- Inadequate Dietary Intake: Not consuming enough foods rich in folate, such as leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, and legumes.
- Malabsorption: Conditions like celiac disease or Crohn’s disease can interfere with the absorption of folate from the intestines.
- Alcoholism: Excessive alcohol consumption can impair folate absorption and increase its excretion.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as anticonvulsants and methotrexate, can interfere with folate metabolism or increase its excretion.
- Pregnancy: Increased folate requirements during pregnancy can lead to deficiency if intake is not adequate.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Folate Deficiency?
General signs and symptoms of folate deficiency include:
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak
- Shortness of breath
- Pale skin
- Diarrhea
- Sore tongue
- Irritability
- Headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
In young children, folate deficiency can present with some unique signs and symptoms:
- Developmental Delays: This is a major concern. Folate is crucial for brain development, so a deficiency can lead to delays in:
- Cognitive development: Learning, memory, and problem-solving skills
- Motor development: Crawling, walking, and fine motor skills (like grasping and manipulating objects)
- Speech and language development
- Irritability and Behavioral Changes: Children with folate deficiency may become more irritable, fussy, and have difficulty concentrating.
If a child shows any of these signs, testing for folate deficiency through a folate blood test and addressing it through diet or supplements can significantly improve their development and overall well-being.
Important Note: These signs can be subtle and may overlap with other conditions. If you suspect your child might have a folate deficiency, it’s crucial to consult with their pediatrician for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
How Do We Test for Folate Deficiency?
Folate deficiency is diagnosed through a simple folate blood test. A small sample of blood is drawn from a vein in your arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory where it is analyzed to determine the level of folate in your blood.
The reference range for folate can vary slightly between laboratories, but generally falls within:
Serum Folate:
- 2.7 to 17.0 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL)
- Or 6.12 to 38.52 nanomoles per liter (nmol/L)
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Folate:
- 140 to 628 ng/mL
- Or 317 to 1422 nmol/L
Why is a Folate Blood Test Important?

A folate blood test is crucial for identifying folate deficiencies, which can lead to serious health issues like neural tube defects in developing fetuses and developmental delays in children. The folate blood test helps determine if you have adequate folate levels, allowing for early intervention with supplementation, personalized treatment plans, and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
If you are considering pregnancy, pregnant, or experiencing symptoms of folate deficiency, a folate blood test is highly recommended.
Recommended Tests

Folate, RBC Blood Test
- Tests for: Folate levels in your red blood cells
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
- Special preparation: Do not take vitamin B9 or folate three to five days before the test. This test may also produce inaccurate results if the patient is taking high doses of biotin supplements (also known as vitamin B7, B8, vitamin H, or coenzyme R). Individuals are advised to stop taking biotin supplements for at least 72 hours prior to the blood draw.
About the test
This folate blood test measures the folate level in your red blood cells. Folate levels measured in red blood cells (RBC-Folate) are more reliable than serum folate levels in diagnosing nutritional deficiencies. This is because serum folate levels can fluctuate significantly based on recent dietary intake and absorption. In contrast, RBC-Folate levels remain relatively stable, making them a more accurate indicator of long-term folate status. Conditions where RBC-Folate levels have particular diagnostic significance include severe alcoholism, malabsorption conditions affecting the small intestine, pregnancy, and various forms of megaloblastic anemia.
Pros
✔ No doctor visit required
✔ Excellent service
Cons
❌ Tests cannot be conducted at lab locations in Arizona, New Jersey, New York, or Rhode Island.
Vitamin B12 and Folate Test

- Tests for: Vitamin B12 and Folate levels in your blood
- How it works: Buy a lab test from Personalabs.com and schedule an appointment at your nearest local lab
- Specimen required: Blood from the veins
- Results in: 2 – 10 business days
- Special preparation: Dietary supplements containing biotin may interfere with this panel, causing results to be either falsely high or falsely low. We recommend pausing biotin-containing supplements 72 hours prior to being tested.
About the test
This test measures the vitamin B12 and folate level in your serum.
Pros
✔ No doctor visit required
✔ Excellent service
✔ HSA/FSA accepted
Cons
❌ Tests cannot be conducted at lab locations in Arizona, New Jersey, New York, or Rhode Island.
Verisana B Vitamins Test (At-home test kit)

- Tests for: Folate and Vitamin B12 level
- How it works: Buy a kit from Amazon.com, collect your blood on a small card and mail it to a Verisana lab with a prepaid envelope
- Specimen required: Finger prick blood sample
- Results in: 7 – 10 business days
About the test
The Verisana Folate and B12 kit is a home test that measures the levels of these two essential vitamins in your blood. Order your kit, collect a sample at your convenience, and return it to the lab. The laboratory uses advanced techniques, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), to analyze the blood sample and determine the levels of folate and vitamin B12. Your results will be available online and emailed to you. The test kit encompasses all necessary components, including sampling instructions, supplies, and a return shipping envelope. No additional fees are incurred – scientific analysis and a comprehensive laboratory report are included.
Pros
✔ Easy-to-use
✔ Can be done at your convenience in the privacy of your own home
✔ CLIA-certified lab
Cons
❌ Needs blood sample to dry for one hour and then shipped within 24 hours
❌ Due to regulatory reasons, this test is currently not available in NY/NJ/RI/MD
❌ Must be at least 18 & over to take the test
Who Can/Should Get Tested?
Individuals who may benefit from a folate blood test include:
- Women planning to become pregnant or who are pregnant: Adequate folate intake is crucial during pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects in the developing fetus.
- Individuals with a family history of neural tube defects: These individuals may have a higher risk of having a child with a neural tube defect and may benefit from testing and supplementation.
- People experiencing symptoms of folate deficiency: These symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and pale skin.
- Individuals with certain medical conditions: Conditions such as alcoholism, malabsorption disorders (like celiac disease), and certain medical treatments can increase the risk of folate deficiency.
- Vegans and vegetarians: While fortified foods can help meet folate needs, some individuals may benefit from testing to ensure adequate intake.
When Should I See a Doctor for Consultation?
You should consult your doctor for:
- Pregnancy Planning: If you are planning to become pregnant, a consultation with your doctor is crucial to discuss preconception health, including folate supplementation.
- Pregnancy: Regular checkups with your doctor throughout your pregnancy are essential to monitor your health and the health of your baby.
- Symptoms of Folate Deficiency: If you are experiencing any symptoms of folate deficiency, such as fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, or pale skin, consult your doctor for evaluation.
- Family History of Neural Tube Defects: If you or your partner have a family history of neural tube defects, consult with your doctor about genetic counseling and potential screening options.
- Concerns about Folate Status: If you have any concerns about your folate intake or status, consult with your doctor for guidance and recommendations.
How is Folate Deficiency Treated?
Folate deficiency is typically treated with:
- Folate Supplements: Your doctor will usually prescribe a daily dose of folic acid supplements to restore your folate levels.
- Dietary Changes: Increasing your intake of folate-rich foods is crucial. Excellent sources include leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), citrus fruits, legumes (beans, lentils), and fortified foods (cereals, bread).
- Addressing Underlying Causes: If an underlying medical condition is contributing to the deficiency (like celiac disease or alcoholism), treating that condition is essential for long-term management.
What Foods are High in Folate?
Foods high in folate include:
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Spinach, kale, romaine lettuce, collard greens, turnip greens, mustard greens, broccoli, asparagus
- Legumes: Beans (kidney, black, pinto), lentils, chickpeas
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges, grapefruit, lemons, limes
- Fortified Foods: Many breakfast cereals, breads, and grains are fortified with folic acid
- Other Good Sources: Avocado, peanuts, sunflower seeds, papaya, bananas, liver
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health.
References
- Anemia: Diagnosis and Treatment (Willis, 2016).
- Management of Anemia: A Comprehensive Guide for Clinicians (Provenzano et al., 2018)
- Goldberg S, Hoffman J. Clinical Hematology Made Ridiculously Simple, 1st Edition: An Incredibly Easy Way to Learn for Medical, Nursing, PA Students, and General Practitioners (MedMaster Medical Books). 2021.
- Zhao G, Ford ES, Li C, Greenlund KJ, Croft JB, Balluz LS. Use of folic acid and vitamin supplementation among adults with depression and anxiety: a cross-sectional, population-based survey. Nutr J. 2011 Sep 30;10:102. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-10-102. PMID: 21962075; PMCID: PMC3200167.
- Khan KM, Jialal I. Folic Acid Deficiency. [Updated 2023 Jun 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
- Viswanathan M, Urrutia RP, Hudson KN, Middleton JC, Kahwati LC. Folic Acid Supplementation to Prevent Neural Tube Defects: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2023 Aug 1;330(5):460-466. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.9864. PMID: 37526714.