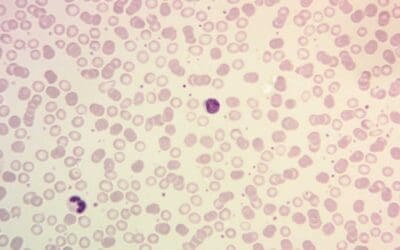
Glanzmann thrombasthenia (GT) is a rare genetic bleeding disorder. Defective platelet aggregation leads to mucocutaneous bleeding. Diagnosis involves specialized lab tests.
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome (BSS) is a rare inherited bleeding disorder characterized by enlarged platelets, low platelet count, and defective platelet function, often presenting in infancy or early childhood.
Understanding Hematoma
A hematoma is a collection of blood outside vessels, often from injury. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and bruising. Diagnosis involves exams and imaging.
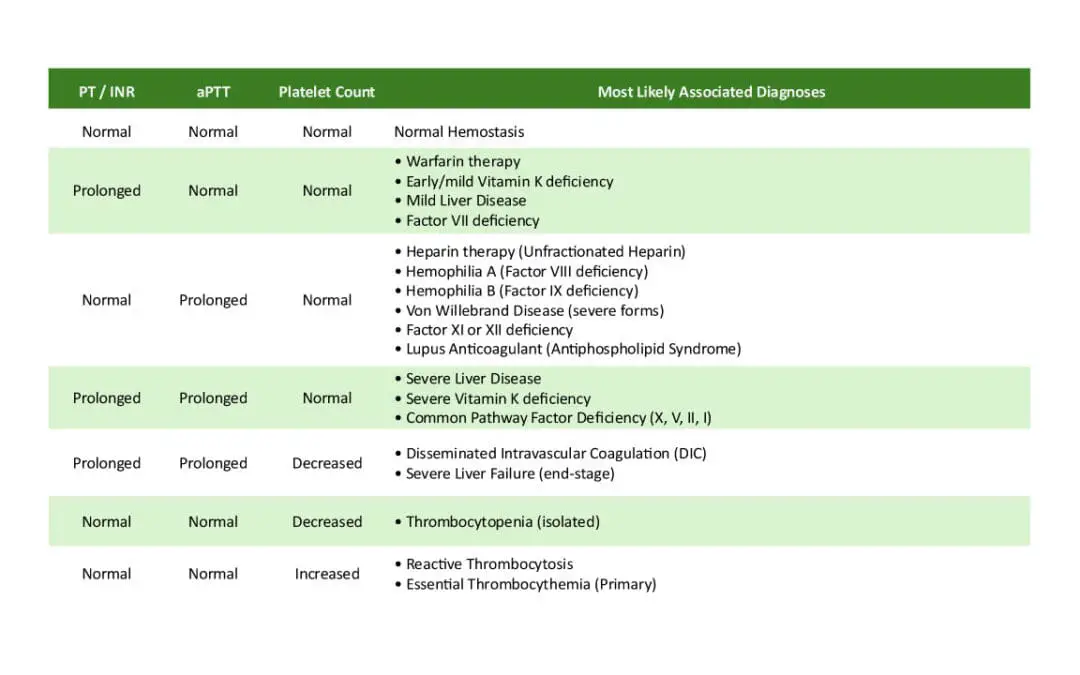
Coagulation Screening Panel Interpretation (Coagulation Panel)
A coagulation screening panel is a vital diagnostic tool. It assesses blood clotting (hemostasis) via PT, aPTT, & platelet count, revealing bleeding or clotting risks.

Glanzmann Thrombasthenia
Glanzmann thrombasthenia (GT) is a rare genetic bleeding disorder. Defective platelet aggregation leads to mucocutaneous bleeding. Diagnosis involves specialized lab tests.
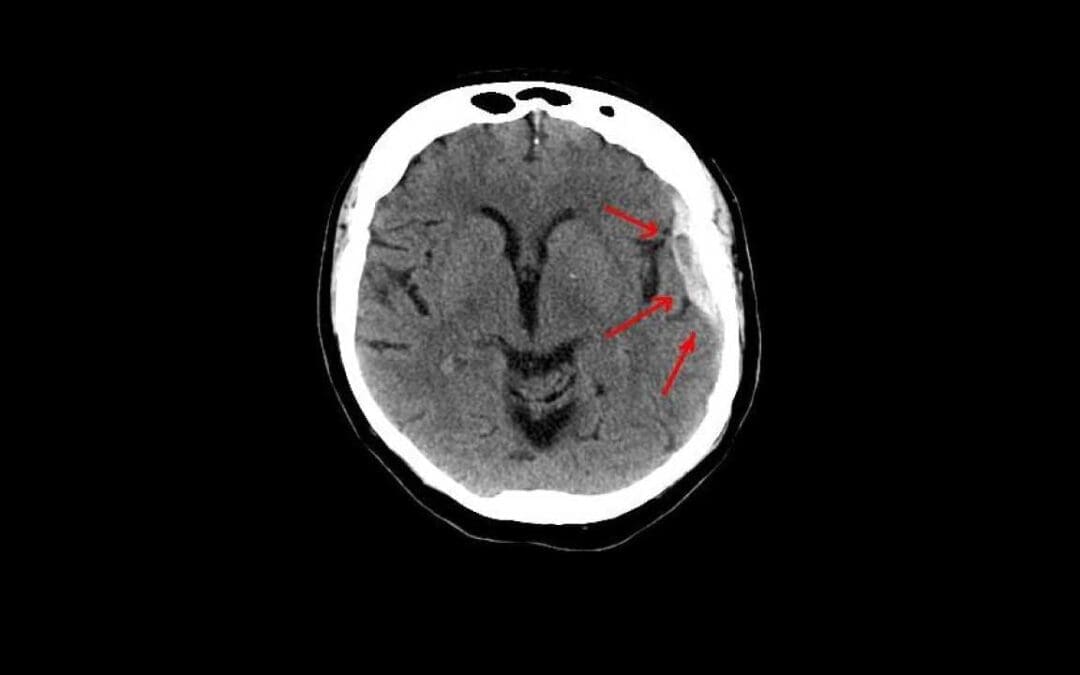
Understanding Hematoma
A hematoma is a collection of blood outside vessels, often from injury. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and bruising. Diagnosis involves exams and imaging.
Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP)
Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP): Palpable rash, joint & belly pain, often in kids. Usually resolves in weeks, but need to monitor kidneys.
Thrombocytosis (High Platelet Count)
Thrombocytosis: High platelet count. Can be reactive (due to other conditions) or essential (bone marrow disorder). Learn causes & significance.
HELLP Syndrome
HELLP syndrome: A serious pregnancy issue with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets. Requires urgent care.
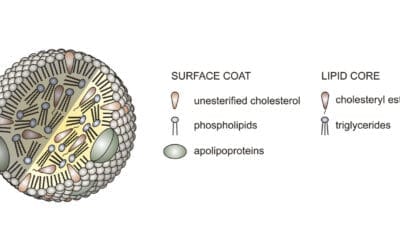
Lipoprotein(a): The Silent Heart Risk You Need to Know
Lp(a): genetic risk for clots & heart disease. Not lowered by diet. Tests measure levels. Manage other risk factors.
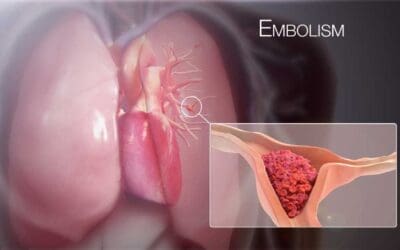
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a life-threatening blockage in lung arteries, often from a leg clot. Urgent diagnosis and treatment are vital.
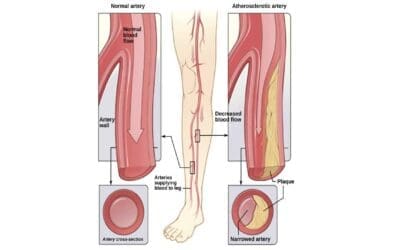
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
PAD: Narrowed leg arteries causing pain, slow healing. Risk factors include smoking & diabetes. Early detection is key to prevent complications.